
Concept explainers
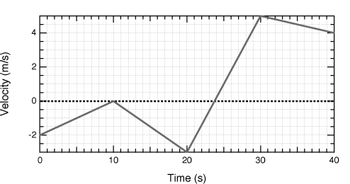
A particle moves along the x-axis. The velocity of this particle as a function of time is shown in the figure. Assume the particle is located at x = 0 m at time t = 0 s. What is the acceleration of the particle at time t = 26.0 s? What is the position of the particle along the x-axis at time t = 26.0 s? What is the net displacement of the particle between time t = 8.0 s and t = 34.0 s?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

I believe that part C is wrong and isn't the answer that my instructor has provided me with. Is there any other method to solve this problem?
I believe that part C is wrong and isn't the answer that my instructor has provided me with. Is there any other method to solve this problem?
- Hello. I am working on a problem with motion. The questions asks me to calculate the maximum height (h1), total time (t2), and speed of a ball right before it hits the ground. The question states that A person is throwing a ball upward into the air with an initial speed Vo = 10m/s. Assume that the instant when the ball is released, the person's hand is at a height ho = 1.5m. The speed of the ball at its peak height is zero, and the question needs to be solved in ascending part and descending part. I don't understand how to solve for the maximum height. What is the correct formula to use and why? For other questions like this, I will be able to solve them if I know the formulas for the ascending of the ball and the descent of the ball as well as the explanation. Thank you. For the sake of the question, the ball is being thrown straight up.arrow_forwardAn object travels 146 m due east when it turns around and returns to its starting position. The entire trip takes 69.0 seconds. a) What is the magnitude of the displacement of the object? 73.0 m 146 m 292 m 0 m b) What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the object? 2.12 m/s 0 m/s 1.06 m/s 4.23 m/sarrow_forwardYour roommate drops a tennis ball from a third-story balcony. It hits the sidewalk and bounces as high as the second story. Draw a motion diagram, using the particle model, showing the ball’s velocity vectors from the time it is released until it reaches the maximum height on its bounce.arrow_forward
- A cart is given an initial velocity of 8.1 m/s and experiences a contestant acceleration of 3.4m/s2. What is the magnitude of the cart's displacement during the first 15s of its motion?arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle is given by v(t) =t² – 2t. The position of the particle at the time t = 0 is S(0) = 0. 1. Find a formula for the position S(t) at time t. 2. Find the displacement of the object on [0,3]. 3. Find the total distance traveled by the particle on [0,3].arrow_forwardOn the x-axis, a particle is accelerated from 6m and from 4m/s to 8m/s for a total time of 3 seconds, t = 3 seconds a. Find its final position, its displacement at t= 3 seconds b. Determine its final velocity and the distance traveled at t = 8 seconds.arrow_forward
- A scooter begins at rest at t0=0 seconds. The scooters starts moving, and eventually covers a distance d= 651m, in a time tf= 104 seconds. In a coordinate system with north being the positive x-direction, the scooter's motion is in the northern direction. What wa the scooter's average speed, during this time period, in meters per second? What was the scooters displacement in the northern direction during this person, in meters? What was the scooter's average velocity in the northern direction, in this period in meters per second? If the scooter's final velocity at tf was 12 m/s, what was the scooter's average acceleration in the northern direction, during this period in m/s%^2?arrow_forwardThe bacterium Escherichia coli (or E. coli) is a single-celled organism that lives in the gut of healthy humans and animals. When grown in a uniform medium rich in salts and amino acids, these bacteria swim along zig-zag paths at a constant speed of 20 μm/s. The figure shows the trajectory of an E. coli as it moves from point A to point E. Each segment of the motion can be identified by two letters, such as segment BC. (Figure 1) Figure y (μm) 40 30 20 10- 0 -10- -20 -30 A -40 C E D B 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 1 of 1 x (μm) For the segment AB in the bacterium's trajectory, calculate the x and y components of its displacement. Express your answers in micrometers to two significant figures separated by a comma. ΨΕ ΑΣΦ XAB, YAB Submit = Part B Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; One attempt remaining ? um For the segment BC in the bacterium's trajectory, calculate the x and y components of its displacement. Express your answers in micrometers to two significant…arrow_forwarda) What is the distance it travelled during 2 seconds?b) In what direction did it ravel (angle with the positive x-axis)? c) What is the acceleration vector of this particle?arrow_forward
- A model rocket is launched straight upward with an initial speed of 40.0 m/s. It accelerates with a constant upward acceleration of 1.50 m/s2 until its engines stop at an altitude of 180 m. what is the max height reached by rocket? how long after liftoff does the rocket reach its max-height? how long is the rocket in the air?arrow_forwardA car accelerates in the +x direction from rest with a constant acceleration of a1 = 1.55 m/s2 for t1 = 20 s. At that point the driver notices a tree limb that has fallen on the road and brakes hard for t2 = 5 s until it comes to a stop. How far, in meters, from the original location of the limb will the car be when it stops?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





