Question
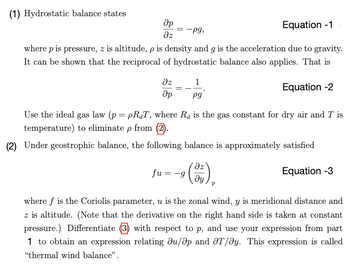
Transcribed Image Text:(1) Hydrostatic balance states
Op
Əz
Equation -1
where p is pressure, z is altitude, p is density and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
It can be shown that the reciprocal of hydrostatic balance also applies. That is
Equation -2
дz
Әр
= -Pg,
=
1
pg
Use the ideal gas law (p = pRT, where R is the gas constant for dry air and Tis
temperature) to eliminate p from (2).
(2) Under geostrophic balance, the following balance is approximately satisfied
Equation -3
fu=-g
¹ (3)
where f is the Coriolis parameter, u is the zonal wind, y is meridional distance and
z is altitude. (Note that the derivative on the right hand side is taken at constant
pressure.) Differentiate (3) with respect to p, and use your expression from part
1 to obtain an expression relating du/ap and T/ay. This expression is called
"thermal wind balance".
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The air quality index in Beijing last year recorded average ozone (O3) levels of 110 ppb (on a mol basis). Does this exceed Canada's acceptable 24 hour National Ambient Air Quality Objective (NAAQO) of 50 micrograms/M3? Assume the average molar mass of air is 29.0 g/mol and its density is 1.225 kg/M3.arrow_forwardAt what height is the atmospheric pressure 29.0% of what it is at sea level? Assume the molar mass of the air molecules to be 29.0 g/mol and that the air temperature is uniformly 287 K. [Answer in kilometres with 3 sig digits, but do not enter units with your answer]arrow_forwardViscosity of fluid plays a significant role in the analyses of many fluid dynamics problems. The viscosity of water can be determined from the following correlation: q10(72,) where e = viscosity (N/s•m²) T- temperature (K) - 2.414 x 10-s 2 - 247.8 (K) s = 14 0 (K) What is the appropriate unit for q, if the above equa- tion is to be homnogeneous in units?arrow_forward
- A modern-day zeppelin holds 9,480 m3 of helium. Compute its maximum payload at sea level. (Assume the helium and air to be at 0°C and 1 atm.)Answer in Narrow_forwardA deep-sea diver should breathe a gas mixture that has the same oxygen partial pressure as at sea level, where dryair contains 20.9% oxygen and has a total pressure of 1.01×105 N/m2. (a) What is the partial pressure of oxygenat sea level? (b) If the diver breathes a gas mixture at a pressure of 2.00×106 N/m2, what percent oxygen shouldit be to have the same oxygen partial pressure as at sea level?arrow_forwardIn a certain region for which o = 0, µ = 2µ,, 10€, and E = J= 60 • sin(10°t – Bz) a, mA/m². Find D and Harrow_forward
- The pressure, volume, and temperature of a mole of an ideal gas are related by the equation PV = 8.31T, where P is measured in kilopascals, V in liters, and T in kelvins. Use differentials to find the approximate change in the pressure if the volume increases from 10 L to 10.6 L and the temperature decreases from 335 K to 330 K. (Note whether the change is positive or negative in your answer. I Round your answer to ti decimal places.arrow_forwardWhat is the RMS speed of Helium atoms when the temperature of the Helium gas is 312.0 K? (Possibly useful 1.66x10-27 kg, Boltzmann's constants: the atomic mass of Helium is 4.00 AMU, the Atomic Mass Unit is: 1 AMU constant is: kg = 1.38×10-23 J/K.) kB Submit Answer Tries 0/12 What would be the RMS speed, if the temperature of the Helium gas was doubled? Submit Answer Tries 0/12 =arrow_forwardVRMS-1 Consider a container of Argon gas at a temperature of 25.0 °C. The mass of an Argon atom is 39.96 AMU, where 1 AMU = 1.66×10-27 kg. (a) What is the average kinetic energy per Argon atom, in Joules (J)? (b) What is the RMS average speed of the Argon atoms, in meters per second (m/s)? (c) What would the temperature of the gas have to be for the RMS average speed to 275 m/s? Give your answer in degrees Celsius (°C).arrow_forward
- The number density of gas atoms at a certain location in the space above our planet is about 0.75 × 1011 m-3, and the pressure is 2.65 × 10-10 Pa in this region. What is the temperature in this region, in degrees Celsius?arrow_forwardA physical chemist measures the temperature inside a vacuum chamber. Here is the result. T=-75.3 degrees celsius Convert to SI units. Round your answer to decimal place.arrow_forwardThe gas constant R has the value 287 J/Kg * K for dry air. Using the ideal gas law (P = PanyRT): a) Find the density of dry air at 72.05 "F with a pressure of 1095 mb. b.) Find the density of molst air at the same pressure and temperature if the relative humidity is 60%. HINT: (for o) stick with Si units (for b) Find e, given T(see lecture slides). Find e given RH. Find pos from: P 0.378e 0.378e Pmoist 1 or Pmoist = Pary RT Parrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios