
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
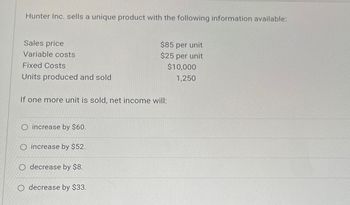
Transcribed Image Text:Hunter Inc. sells a unique product with the following information available:
Sales price
Variable costs
Fixed Costs
Units produced and sold
$85 per unit
$25 per unit
If one more unit is sold, net income will:
$10,000
1,250
O increase by $60.
O increase by $52.
O decrease by $8.
O decrease by $33.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Zeus, Incorporated produces a product that has a variable cost of $6 per unit. The company's fixed costs are $40,000. The product sells for $11 a unit and the company desires to earn a $25,000 profit. What is the volume of sales in units required to achieve the target profit? Note: Do not round Intermediate calculations. Multiple Choice 8,500 units 13,000 units 8,000 units 7,625 unitsarrow_forwardZeta Company sells a single product with a selling price of $300 per unit. Per unit variable costs are $82.00 and total fixed costs are $127,500. The number of units Zeta needs to sell to achieve its target profit of $50,000 is closest to: 610 814 a. b. C. d. 1,555 2,165arrow_forwardYour Company sells 3 products, A, B and C that use the same company, facility and resources. Details are below: A Average monthly units sold 10,000 2,000 8,000 Sales price per unit 2,000 1,000 5,000 Variable cost per unit 1,500 500 3,000 Total break even units are 1,000. 1. Calculate: i. Quantity and value of units of each A, B and C at breakeven Fixed cost based on the data given above ii. 2. Without making further calculations, explain that if fixed cost increases by 10% what impact would this have on the break-even point?arrow_forward
- Tackett Company sells a single product for $75 cach. the variable costs are $45 cach. Total fixed costs are $225,600. How many units must the company sell to achieve operating income of $90,000? O A. 7013 O B. 10520 O C. 6230 O D.4208arrow_forwardhelp mearrow_forwardREQUIRED Calculate the number of orders that should be placed based on the quantity that will keep the cost of placing the orders and the holding costs at a minimum. INFORMATION The following information was supplied by KL Suppliers for the only product that it sells: Monthly demand Unit cost Fixed cost per order Carrying cost per unit EOQ 300 units R20 R25 10% of the unit cost 300 unitsarrow_forward
- The Atlantic Company sells a product with a break-even point of 4,369 sales units. The variable cost is $65 per unit, and fixed costs are $144,177. Determine the unit sales price. Round answer to nearest whole number.$fill in the blank 1 Determine the break-even point in sales units if the company desires a target profit of $39,204. Round answer to the nearest whole number.fill in the blank 2 unitsarrow_forwardPau, Inc., which has fixed costs of $51401, sells two products whose sales price, variable cost per unit, and percentage of sales units are presented in the table below. Sales Price Variable Cost Sales Mix Product A Product B $ $ $23 $8 40 % 16 7 60% How many units of Product B must Pau sell to break even Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest whole number. 0 out of 1 pointsarrow_forwardStella Company sells only two products, Product A and Product B. Product A $50.00 $36.00 Selling price Variable cost per unit Total fixed costs Product B $50.00 $21.00 A. 54,018 units of Product A and 27,009 units of Product B B. 57,000 units of Product A and 28,500 units of Product B C. 28,500 units of Product A and 57,000 units of product B D. 27,009 units of Product A and 54,018 units of Product B Total $1,539,500 Stella sells two units of Product A for each unit it sells of Product B. Stella faces a tax rate of 20%. Stella desires a net after-tax income of $68,000. The breakeven point in units would be (Round any intermediary calculation up to the next whole unit.)arrow_forward
- Helparrow_forwardPau, Inc., which has fixed costs of $88,333, sells two products whose sales price, variable cost per unit, and percentage of sales units are presented in the table below. Product A Product B $ 22 $ 9 40 % Sales Price $ $ 17 Variable Cost Sales Mix 60% How many units of Product B must Pau sell to break even Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education