
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
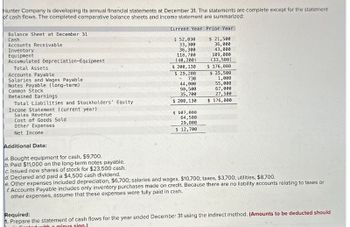
Transcribed Image Text:Hunter Company is developing its annual financial statements at December 31. The statements are complete except for the statement
of cash flows. The completed comparative balance sheets and income statement are summarized:
Current Year Prior Year
Balance Sheet at December 31
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Equipment
Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment
Total Assets
Accounts Payable
Salaries and Wages Payable
Notes Payable (long-term)
Common Stock.
Retained Earnings
Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
Income Statement (current year)
Sales Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold
Other Expenses
Net Income
Additional Data:
a. Bought equipment for cash, $9,700.
b. Paid $11,000 on the long-term notes payable.
c. Issued new shares of stock for $23,500 cash.
d. Declared and paid a $4,500 cash dividend.
$ 52,030
33,300
$ 21,500
36,000
36,300
118,700
(40,200)
$ 200,130
$ 29,200
-730
43,000
109,000
(33,500)
$ 176,000
$ 25,500
1,000
44,000
55,000
90,500
67,000
35,700
27,500
$176,000
$ 200,130
$ 107,000
64,500
29,800
$ 12,700
e. Other expenses included depreciation, $6,700; salaries and wages, $10,700; taxes, $3,700; utilities, $8,700.
f. Accounts Payable includes only inventory purchases made on credit. Because there are no liability accounts relating to taxes or
other expenses, assume that these expenses were fully paid in cash.
Required:
1. Prepare the statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31 using the indirect method. (Amounts to be deducted should
with a minus sign.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education