
Concept explainers
How temperature affects density? Please explain
Density always holds inverse relation with volume and the volume holds direct connection with temperature. The higher density reflects how dense any object is or how close the particles exist in any object.
The formula or the density is shown below.
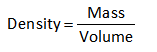
It is clear from the above expression that the density carries direct relation with volume. An increment in substance’s volume will cause the decrement in its density and vice-versa.
When any substance gets heated up its weight (mass) will be same (constant) but the volume basically gets changed. On rising its temperature the space held by substance’s particles will increase and thus the expansion in that its volume will occur. At this state that substance will contain larger volume and thus its density will become less.
For example- hot air carries less density whereas cold air carries high density because the hot air’s volume is higher due to its high temperature, the particles exist at far distance so that hot air contains low density. And cold air’s volume is lesser due to its low temperature, the particles exist at close distance thus the cold air contains high density.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Elliot Page is using his winter break to study up on science for their role as Vanya in Umbrella academy. He was given test data from a ballon suit. At morning time the temperature is 22 C and the suit is expanded to a volume of 333 L. If the balloons have expanded to 444 L by lunch, what must the temperature be ?arrow_forwardA sample of gas was determined to have a mass of 20.41g and a density of 0.810g/mL. What is the volume (in units of milliliters, mL) of the gas?arrow_forward1. Which of the following is stated by the kinetic molecular theory? A. At the same temperature, the object with the most mass heats quicker. B. Particles are always in motion. C. Particles ONLY move in liquids and gases. D. Particles will NOT move if energy is NOT applied. 2. If you place a balloon in a freezer, what happens to the size of the balloon? A. Decreases B. Doubles C. Increases D. No change 3. What is the FUNDAMENTAL basis of the physical properties of substances? A. Chemical bond C. Kinetic molecular theory D. Physical state B. Intermolecular forcesarrow_forward
- tab Using heat of fusion or vaporization to find the heat needed to melt or bo... caps lock Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 119. g of solid methanol (CH3OH) and bring it to a temperature of -84.5 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. Explanation. Esc Type here to search de ! Check 1 F1 Q A S NO 2 F2 W S J F3 # 3 X □ E 0x D 14 St $ 4 5 R F5 01 8 % 5 LL F 99% DELL F6 T A 10 6 G 2 F7 Y & 7 4 B H FB © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center 57°F Cloudy ^ 40 O FO 4 ( 8 9 ? prt sc F10 5 home K O 1 end 0/5 POS L Danasia V Accessibility 10:30 AM 11/13/2023 neart + = ? ESTA alo □ dabebs backarrow_forwardab Y Part A Calculate the density of krypton gas at a pressure of 747 mmHg and a temperature of 44 °C. Express the density to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. esc p= Value Submit Provide Feedback μА Request Answer Mother to Son &....pdf ! 1 F1 Q @ 2 C Units F2 W #3 ? 80 F3 E S4 $ a F4 R % 5 0 KO F5 MacBook Air T F6 6 & 7 Yarrow_forwardThis is not graded! It is strictly for practice. Do questions 1-5.arrow_forward
- Space probes to Mars have shown that its atmosphere consists mostly of carbon dioxide. The average temperature on the surface of Mars is –55°C with a pressure of 0.00629 atm. Compare the density of CO2 on Mars’s surface with that on the Earth’s surface at 23°C and one atmosphere. Density on Mars/Density on Earth= ____________/1arrow_forwardA volume of 23.5L of oxygen is 120 degrees Celsius at 6.63atm. It is changed to 2.89atm and a volume of 3.38L. What is the new temperature ?arrow_forwardConvert 1 PSI (pound square inch) to PSF (pound square feet) :arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





