
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
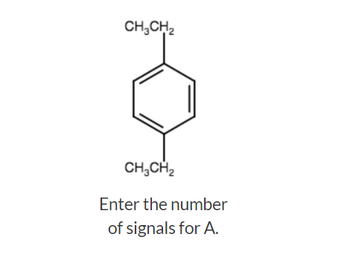
Transcribed Image Text:CH₂CH₂
CH₂CH₂
Enter the number
of signals for A.

Transcribed Image Text:How many signals would you expect to find in the proton-decoupled 13℃ spectra of the following isomeric compounds?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Following is the mass spectrum of bromocyclopentane. The molecular ion m/z 148 is of such low intensity that it does not appear in this spectrum. Assign structural formulas for the cations of m/z 69 and 41.arrow_forwardFor the following compound how many different signals would you see in the carbon NMR? (Assume that you can see them all.) 4 O 5 O 3 09 CO |arrow_forward4. How many signals would you observe in the ¹H-NMR spectra of the following molecules? NH OHarrow_forward
- Pls explain tooarrow_forwardHow many peaks would the 1H NMR spectrum of the following molecule have?arrow_forwardWhich one of the following pieces of information cannot be obtained from an infra-red spectrum? * the presence of C=0 bonds the framework of compound the presence of O-H bonds the identity of a compound through comparison with other spectraarrow_forward
- 8. Sketch the off-resonance-decoupled 1³C spectra of the following compound. H H C C-H H The splitting pattern of off-resonance decoupled spectrum indicates the number of protons attached to the carbon. 13C nuclei are split only by the protons attached directly to them. The N + 1 rule applies: a carbon with N number of protons gives a signal with N + 1 peaks (e.g. carbon atom with one proton appears as a doublet; carbon with two attached protons gives a triplet etc.) • Carbon atoms with more hydrogens absorb more strongly.arrow_forwardI need help calculating the NMR chemical shifts for this compound.arrow_forwardIn a proton NMR spectrum, indicate the number of peaks and their multiplicity for the following compounds: CH3 - CH2 - CO - CH3 para-chloromethylbenzenearrow_forward
- HO 4. (a) How many different signals would you expect in the 1HNMR of this product? (b) How many different signals would you expect in the 13 CNMR of this product?arrow_forwardThe following molecule will give two signals in the proton (¹H) NMR. H₂C What is the ratio of the signal intensities for the two peaks? 2:2 O 3:1 3:2 CH₂ O 2:1arrow_forwardHow many different signals would we expect in the 1C NMR spectrum of the following compound? (Give a number) HO HO, OHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning