
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
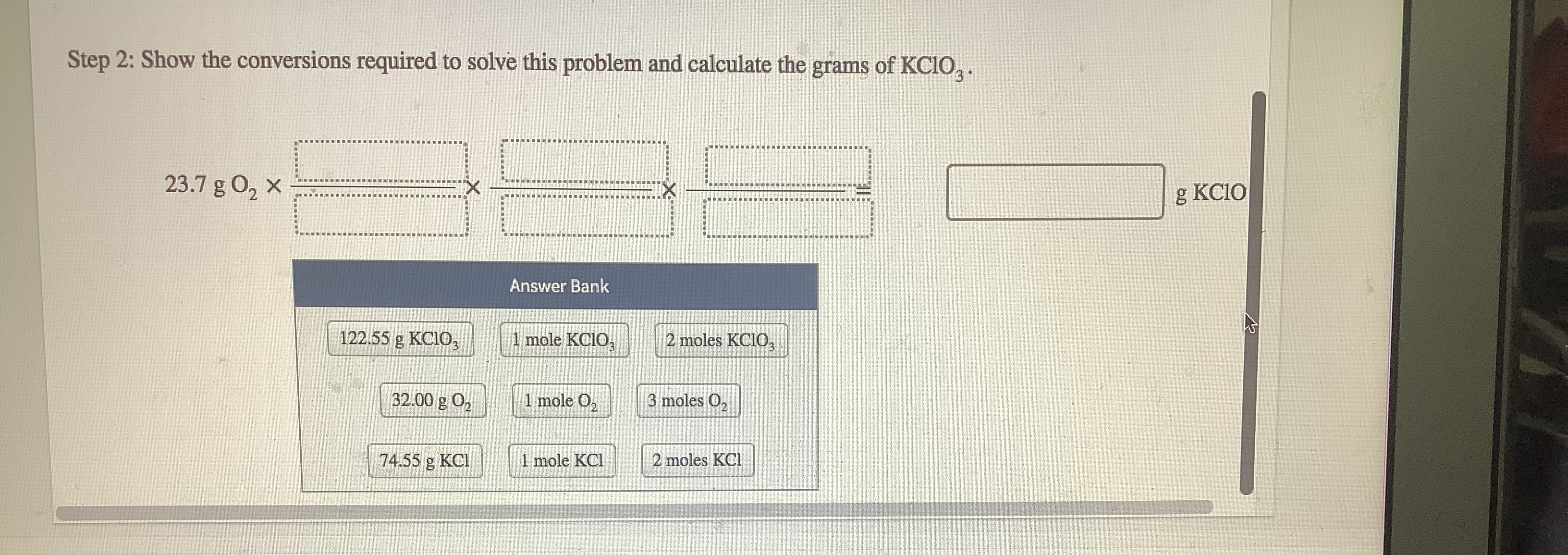
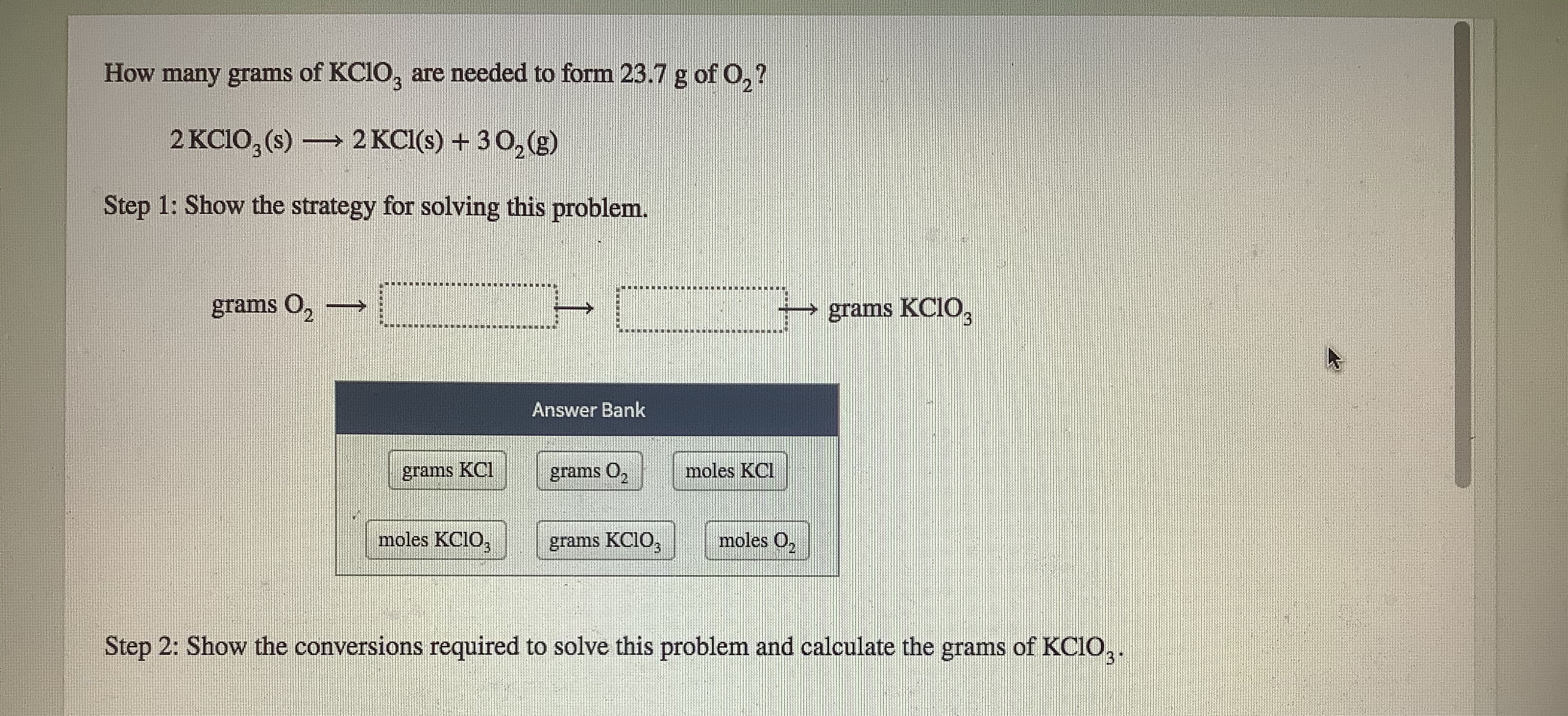
Transcribed Image Text:How many grams of KC1O, are needod to form 23.7 g of 0,7
2 KCIO, (s) → 2 KCI() + 30 (3)
Step 1: Show the strategy for solving this problem.
grums 0,
grams KCIO,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.8 mol of H,0, 0.30 mol of CO and 0.10 mol of H,. This reaction becomes possible: CH,(2) + H,O(g) → CO(g) + 3H,(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of H,O. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. CH, H,O H, CO initial change equilibrium Explagation Check O Type here to search 2022 McGraw Hl LLC A Rights Reserved Terms of Use Pvacy Center Accessibaty US ZenBook Q R Alt Dla Xarrow_forwardA student sets up and solves the following equation to solve a problem in solution stoichiometry. Fill in the missing part of the student's equation. 6.6 :-) ( mol L -3 10 L 1 mL (135.35) = 0.89 mL x10 ロ・ロ X μ Oloarrow_forwardCalculate the theoretical yield in grams All3 from the complete reaction of 18.3 grams Al according to the following balanced chemical equation: 2 Al(s) + 3 12(s) → 2 All;(s) -> STARTING AMOUNT ANSWER RESET ADD FACTOR * ( ) 18.3 407.7 3 1.47 277 26.98 0.678 1 138 mol All3 g All3 g/mol All; g/mol Al g Al mol Al WIDA A AR 2.arrow_forward
- Please answer number 2. The data is only that. Nothing more nothing lessarrow_forward??(??)3+?2??4⟶?Al(OH)3+H2SO4⟶? How many grams of Al(OH)3 are required to completely convert 81.972 g of H2SO4 into Al2(SO4)3? Hint: Balance and complete the reaction above as a double-displacement reaction. You Answeredarrow_forward(D) 131% 11. If the reaction produces 400.0 mL of 1.5 M MgCl2, how many moles of HCl reacted? (A) 0.30 moles (B) 0.60 moles (C) 1.20 moles (D) 2.40 moles Unit 8 Exam - Reactions 12. What is the end result of reacting the following molecules according to the equation below? N2 + 3 H2 > 2 NH3 21 Illuminate EducationTM Inc. DELL F1 F2 F3 F4 E5 F6 F7 F8 F9 Co %23 & 2 7 8. W T Y Earrow_forward
- STARTING AMOUNT O esc X 2 W #m 3 How many moles of aluminum are required to completely react with 107 mL of 6.00 M H₂SO4 according to the balanced chemical reaction: 0.428 ADD FACTOR e * ( ) mL H₂SO4 0.0374 4 2 Al(s) + 3 H₂SO4(aq) → Al₂(SO4)3(aq) + 3 H₂(g) 98.08 M H₂SO4 % 5 Question 9 of 34 1 2 3 g H₂SO4 6 107 6.022 x 1023 gAl MOO D y & ANSWER 7 h 428 1000 mol H₂SO4 g Al₂(SO4)3 8 6.00 RESET 0.001 5 0.963 LH₂SO4 CD Mar 2 5:28 Submit +arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.60 mol of H,S, 0.10 mol of CS, and 1.5 mol of H,. This reaction becomes possible: CH (g) + 2H,S (g) =CS,(g)+4H, (g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of CH4. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. CHA H,S cs, H2 initial change equilibriumarrow_forwardGiven the following equation: , Ag were produced, how many atoms of Cu reacted? Cu + __ AGNO, →. Cu(NOs)2 + Ag If 89.5 grams of Answer: Molten iron and carbon monoxide are produced in a blast furnace by the reaction of iron(III) oxide and coke (pure carbon). If 25.0 grams of pure Fe2O3 are used, how many molecules of carbon monoxide can be produced? Fe:Os +. Fe + _CO Answer: Given the following equation: NaClO3 - NaCl + , O2 How many grams of NaCl are produced when 80.0 Liters of O2 are produced at STP? Answer:arrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.3 mol of H,S, 1.2 mol of CS, and 0.70 mol of H,. This reaction becomes possible: CH,(s) + 2H,S (g) – cs,(e)+ 4H,(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of CH. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. CH H,S Cs, H2 initial change equilibrium Olo X Oarrow_forwardSuppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.10 mol of CH, 0.50 mol of H,O and 1.8 mol of H,. This reaction becomes possible: CH, (g) +H,0(g) = CO(g)+3H,(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of CO. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. dla CH, H,O CO H, initial change equilibriumarrow_forwardI need help with this conversion factors with labels on itarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY