
How can we determine the direction of the strains?
In this question, it is assumed that state of stress is not given for a material.
We can not measure state of stress in material under loading. We can measure strain. Even on top of that, we can only measure strain on surface of a material. there are many methods to measure strain. simplest is to draw a line on the surface and measure the length of the line after deformation. However, this method only gives average value of strain in deformation.
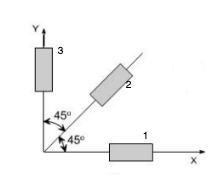
More accurate and widely used method is by electrical strain gauges. A single strain gauge can measure strain only one direction, not in the perpendicular of a strain gauge or shear of plane. So, more than one strain gauge is required to completely measure the state of strain. To get two-dimensional state of strain we need three values, two linear strains in perpendicular direction and shear strain. We need to obtain measurements from three strain gages. These three gages must be arranged at different orientations on the surface to form a strain Rossett. A typical example of strain rosette is shown in fig.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- A 20 foot long x 4 feet wide x ½ inch thick sheet of an aluminum alloy is cold rolled to a thickness of ¼ inch. During the rolling operation the with of the sheet increases by 10%. The strength coefficient (K) and the strain hardening coefficient (n ) for the aluminum alloy are 25,500 psi and 0.3, respectively Calculate the true strain at the end of the rolling process.arrow_forwardHow does the increase in strain rate affect the Youngs modulus, UTS and ductility of material? (At the same Temperature).arrow_forwardSince Creep is the time dependant deformation of a material, does temperature or stress play an important role?arrow_forward
- Equation 6.16: εT = ln(li / l0)arrow_forwardA 20 foot long x 4 feet wide x ½ inch thick sheet of an aluminum alloy is cold rolled to a thickness of ¼ inch. During the rolling operation the with of the sheet increases by 10%. The strength coefficient (K) and the strain hardening coefficient (n ) for the aluminum alloy are 25,500 psi and 0.3, respectively. Calculate the length of the sheet after the rolling operation in feet.arrow_forwardWhy are the deformations that take place within a body are almostinfinitesimal?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





