
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
A hot-film probe is mounted on a cone-and-rod system in a sea level
airstream of 45 m/s, as in Fig. Estimate the maximum
cone vertex angle allowable if the flow-induced bending
moment at the root of the rod is not to exceed 30 N .cm.
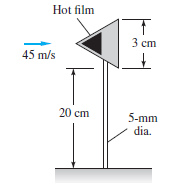
Transcribed Image Text:Hot film
3 cm
45 m/s
20 cm
5-mm
dia.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The gutter and smooth drainpipe in Fig. remove rainwaterfrom the roof of a building. The smooth drainpipe is7 cm in diameter. (a) When the gutter is full, estimate therate of draining. (b) The gutter is designed for a suddenrainstorm of up to 5 inches per hour. For this condition, whatis the maximum roof area that can be drained successfully?arrow_forwardEngine oil at 100°C flows on the top surface of a 1-m-long flat plate maintained at 20°C. The oil’s freestream speed (u infinity) is 0.1 m/s. Find the engine oil properties from the table A.5 A. Evaluate the Reynolds number, local convection coefficient, heat flux and shear stress at the end of the plate (x = L). Is the air flow laminar or turbulent over the plate?B. Evaluate the average convection coefficient, average heat flux, average shear stress and drag force over the plate.arrow_forward(1) Experiments show that in a slightly Viscorur flund at on a молод high speeds the drag force fo exerted on body depends on several parametes. An engineer assumes that the drag force fo is a functon of the budy width normal to the upstream Velocity, I upstream Velouty, ✓, the upstream flud veElucay P viscosity, M, speed of sound, I and the airfoils surface roughnars. " use the Buckingham ♬ Theorem to determine the functional dependence of to on non-dimensional flow similarity parameters (2:) Lot the transition to turbulence occur when I = 1.01m, V= 1·01m/s and M₁P = 1:01·10⁰5 m² s. Calculate the transchen Reynolds number, Retrains.arrow_forward
- In this era of expensive fossil fuels, many alternativeshave been pursued. One idea from SkySails, Inc., shownin Fig. is the assisted propulsion of a ship by a largetethered kite. The tow force of the kite assists the ship’spropeller and is said to reduce annual fuel consumptionby 10–35 percent. For a typical example, let the ship be120 m long, with a wetted area of 2800 m2. The kite areais 330 m2 and has a force coefficient of 0.8. The kite cablemakes an angle of 258 with the horizontal. Let Vwind =30 mi/h. Neglect ship wave drag. Estimate the ship speed(a) due to the kite only and (b) if the propeller delivers1250 hp to the water. [Hint: The kite sees the relativevelocity of the wind.]arrow_forwardAn isothermal long cylinder with square (side of 0.4 m and diagonal of 0.5657 m) cross-section is placed in a flow with a velocity of 1 m/s as shown. The properties of the fluid are: kinematic viscosity is 1.38 x 10-5 m²/s, thermal conductivity is 0.024 W/m.°C, and Prandtl number is 0.73. What is the average Nusselt number for the flow? 1253 a Figure 1: Flow configuration for Problem 6. The dimensions are: a=0.4 m, b=0.5657 marrow_forwardThe present pumping rate of crude oil through the AlaskaPipeline, with an ID of 48 in, is 550,000 barrels per day(1 barrel = 42 U.S. gallons). (a) Is this a turbulent flow?(b) What would be the maximum rate if the flow wereconstrained to be laminar? Assume that Alaskan oil fitsFig. A.1 at 60°C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY