
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![### Price Elasticity of Demand: Homework (Ch 07)
#### Description
This homework focuses on calculating the price elasticity of demand for a given set of data points and interpreting the results to understand the elasticity of demand.
#### Graph Explanation
The graph provided shows a downward-sloping linear demand curve. The axes are labeled as follows:
- **Y-Axis**: PRICE (Dollars per pole per year)
- **X-Axis**: QUANTITY (Thousands of poles)
Points L, M, and N are plotted on the demand curve. The graph's title is "Total Revenue."
#### Instructions
Calculate the price elasticity of demand between points L and M, and points N and O using the midpoint method, then fill in the Price Elasticity of Demand column in the following table. For each price range, identify if demand is elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic. (Hint: Find the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand to determine whether demand is elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic for each price range.)
| Price Range between Points | Absolute Value of Price Elasticity of Demand | Elastic, Inelastic, Unit Elastic | Change in Total Revenue |
|----------------------------|----------------------------------------------|---------------------------------|-------------------------|
| L and M | | | |
| N and O | | | |
#### Guidelines
For each price range, indicate if total revenue increases, decreases, or does not change in the previous table.
##### Note:
To calculate the midpoint price elasticity of demand, use the following formula:
\[ \text{Price Elasticity of Demand} = \frac{\left( \frac{Q_2 - Q_1}{(Q_2 + Q_1)/2} \right)}{\left( \frac{P_2 - P_1}{(P_2 + P_1)/2} \right)} \]
Where:
- \( P_1 \) and \( P_2 \) are the initial and final prices.
- \( Q_1 \) and \( Q_2 \) are the initial and final quantities demanded.
This calculation will assist in determining if the demand is elastic (absolute value > 1), inelastic (absolute value < 1), or unit elastic (absolute value = 1).
#### Actions
Once calculations are done, you can:
- **Grade It Now**
- **Save & Continue**
Please ensure your answers are accurate, as a](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/cc5c0ccd-3977-494d-ba05-e5795e42b68d/be6e3e50-321f-4b37-849c-99d0bb4499b1/xbrn5j8_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:### Price Elasticity of Demand: Homework (Ch 07)
#### Description
This homework focuses on calculating the price elasticity of demand for a given set of data points and interpreting the results to understand the elasticity of demand.
#### Graph Explanation
The graph provided shows a downward-sloping linear demand curve. The axes are labeled as follows:
- **Y-Axis**: PRICE (Dollars per pole per year)
- **X-Axis**: QUANTITY (Thousands of poles)
Points L, M, and N are plotted on the demand curve. The graph's title is "Total Revenue."
#### Instructions
Calculate the price elasticity of demand between points L and M, and points N and O using the midpoint method, then fill in the Price Elasticity of Demand column in the following table. For each price range, identify if demand is elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic. (Hint: Find the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand to determine whether demand is elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic for each price range.)
| Price Range between Points | Absolute Value of Price Elasticity of Demand | Elastic, Inelastic, Unit Elastic | Change in Total Revenue |
|----------------------------|----------------------------------------------|---------------------------------|-------------------------|
| L and M | | | |
| N and O | | | |
#### Guidelines
For each price range, indicate if total revenue increases, decreases, or does not change in the previous table.
##### Note:
To calculate the midpoint price elasticity of demand, use the following formula:
\[ \text{Price Elasticity of Demand} = \frac{\left( \frac{Q_2 - Q_1}{(Q_2 + Q_1)/2} \right)}{\left( \frac{P_2 - P_1}{(P_2 + P_1)/2} \right)} \]
Where:
- \( P_1 \) and \( P_2 \) are the initial and final prices.
- \( Q_1 \) and \( Q_2 \) are the initial and final quantities demanded.
This calculation will assist in determining if the demand is elastic (absolute value > 1), inelastic (absolute value < 1), or unit elastic (absolute value = 1).
#### Actions
Once calculations are done, you can:
- **Grade It Now**
- **Save & Continue**
Please ensure your answers are accurate, as a
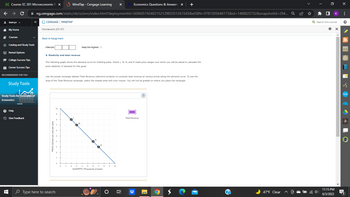
Transcribed Image Text:### Elasticity and Total Revenue
#### 9. Elasticity and total revenue
The following graph shows the demand curve for trekking poles. Points L, M, N, and O mark price ranges over which you will be asked to calculate the price elasticity of demand for this good.
Use the purple rectangle labeled Total Revenue (diamond symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve. To see the area of the Total Revenue rectangle, select the shaded area with your mouse. You will not be graded on where you place the rectangle.
#### Graph Explanation
A demand curve graph is presented, which illustrates the relationship between the price of trekking poles (in dollars per pole per year) and the quantity demanded (in thousands of poles). The graph features the following:
- **X-Axis (Horizontal Axis):** Labeled as "QUANTITY (Thousands of poles)", it ranges from 0 to 10.
- **Y-Axis (Vertical Axis):** Labeled as "PRICE (Dollars per pole per year)", it ranges from 0 to 10.
- Four marked points on the demand curve: **L, M, N, and O**.
Each of these points represents different price and quantity combinations:
- **Point L:** Near the top left of the demand curve, indicating a high price and low quantity.
- **Point M:** Below Point L, indicating a lower price and higher quantity than Point L.
- **Point N:** Below Point M, indicating a lower price and higher quantity than Point M.
- **Point O:** Near the bottom right of the demand curve, indicating the lowest price and highest quantity.
A purple rectangle labeled **Total Revenue** with diamond symbols represents the area under the curve used to calculate the total revenue at various price points along the demand curve.
---
This exercise will help you understand how changes in price influence the quantity demanded and total revenue, aiding your comprehension of price elasticity of demand.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following demand schedule. Price Quantity Demanded $25 $20 $15 $10 $5 20 40 60 80 100 Complete the following table by calculating the price elasticity of demand between specified points and indicating whether the demand is elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic. (Hint: Use the midpoints formula.) Price Elasticity of Demand Interval From P = $25 to P = $15 From P = $25 to P = $20 From P = $20 to P = $10 From P = $20 to P = $15 Elastic, Inelastic, or Unit Elasticarrow_forwardSuppose that in a week the price of spaghetti sauce increases from $5.00 to $5.50 per jar. At the same time, the quantity of spaghetti sauce demanded at a typical grocery store decreases from 10,000 to 8,500 jars per week. What is the price elasticity of demand for spaghetti sauce? Instructions: Round your response to one decimal place. -1.7arrow_forwardElastic, inelastic, and unit-elastic demand The following graph shows the demand for a good. For each region on the graph given in the following table, use the elasticity formula to identify whether the demand for this good is elastic, (approximately) unit elastic, or inelastic.arrow_forward
- 4-6 Suppose that the price of croissants rises from $2 to $3 per unit. Use the mid-point approach to get the elasticity. The quantity of orange juice purchased falls from 10 million bottles to 5 million bottles. What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and orange juice? Are they complements or substitutes? The quantity of jelly purchased increases from 10 million jars to 20 million jars. What is What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and orange juice? Are they complements or substitutes?arrow_forwardINFO: Yesterday, the price of envelopes was $3 a box, and Julie was willing to buy 10 boxes. Today, the price has gone up to $3.75 a box, and Julie is now willing to buy 8 boxes. What is Julie’s elasticity of demand? _____ (Hint: only a number goes here) Is Julie's demand for envelopes elastic or inelastic? Explain your answer in a complete sentence(s) here:arrow_forwardFill out the tables by calculating the price elasticity of demand and of supply (use the mid-point formula). Report elasticities with 2 decimals. Demand and Supply Schedule for Good X: Unit price of x Quantity demanded of x Quantity supplied of x Price elasticity of demand of x (2 decimals) Price elasticity of supply of x (2 decimals) $100 0 5 n/a n/a $95 2 4.5 $90 4 4 $85 6 3.5 $80 8 3 $75 10 2.5 $70 12 2 $65 14 1.5 $60 16 1 $55 18 0.5 Demand and Supply Schedule for Good Y: Unit price of y Quantity demanded of y Quantity supplied of y Price elasticity of demand of y (2 decimals) Price elasticity of supply of y (2 decimals) $100 10 40 n/a n/a $90 11 35 $80 12 30 $70 13 25 $60 14 20 $50 15 15 $40 16 10…arrow_forward
- When income increases by 10 percent (or numerically, 0.1), quantity demanded moves by 168 units. Assuming the income elasticity of demand is 4. What is the original quantity demanded? (assuming further that this is the point elasticity relative to the original point.) Please make sure you give a numerical answer with no units and/or space or period (.) or comma (,) before or after your answer. Enter your answer herearrow_forwardAssistarrow_forwardUse the demand schedule in the table below to answer the following questions. Use the mid-point method when calculating elasticity. Price ($) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Quantity 56 48 42 35 28 21 14 7 0 Instructions: Round intermediate calculations and round your answers to two decimal places. If you are entering a negative number be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of that number. a. The price elasticity of demand for a price change from $2 to $3 is: The slope of the demand curve for a price change from $2 to $3 is: b. The price elasticity of demand for a price change from $3 to $5 is: | The slope of the demand curve for a price change from $3 to $5 is: [ c. The price elasticity of demand for a price change from $6 to $7 is: [ The slope of the demand curve for a price change from $6 to $7 is:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education