
Hi guys can you check the given problem below and provide me with a solution and also the steps showing how you arrive at the answers. Thank you.
Using fuzzy logic to predict college GPA
A college admissions director wants to use High School GPA and ACT score to predict the final GPA when a student graduates from her institution. She divides GPAs into 5 fuzzy sets:
- Poor – student is at risk for being admitted because of risky HS GPA
- Marginal – student is marginally qualified due to his HS GPA
- Average – student has average HS GPA
- Good – student has a good HS GPA
- Very Good – student has a very good HS GPA
She will use the same fuzzy sets for College GPAs and HS GPAs shown below.
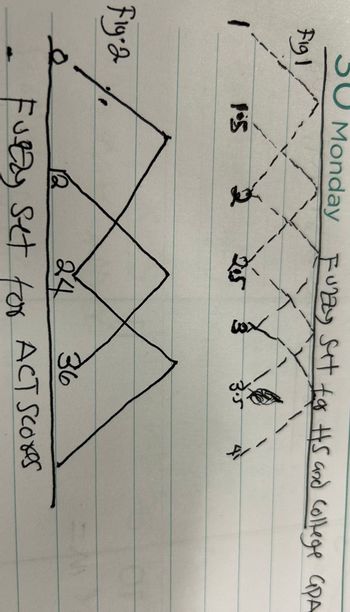
Fuzzy Sets for HS and College GPA Diagram here is showing in the image below
From left, the fuzzy sets are:
Poor. Poor intersects x axis when x = 1, and x=2. The apex is at (1.5,1)
Marginal: Marginal intersects the x axis at x = 1.5 and x = 2.5. The apex is at (2,1.0)
Fair: Fair intersects the x axis at 2, and 3.. The apex is at (2.5,1)
Good: Good intersects the x axis at 2.5 and 3.5. The apex is at (3,1)
Very Good: Very good intersects the x axis at 3 and 4. The apex is at (3.5,1)
Fuzzy Sets for ACT Scores Diagram here showing in the image below
The admissions director divides ACT scores into 3 groups:
Marginal – marginal intersects the x (ACT) axis at 0 and 24
Average – average intersects the x axis at 12 and 36
High – high intersects the x axis at 24 and 48. Note that ACT scores range from 0-36. Individual scores are determined each year.
Admissions director predicts college GPAs. The admissions director’s calculus is a bit rusty, so she decides to use 4 techniques for each student:
- a) Weighted average – for this method, she determines that the representative members in each of the GPA fuzzy sets will be the one with maximum membership.
- for poor, the max is 1.5; for marginal the max is 2;, for fair, the max is 2.5; for good, the max is 3; and for very good the max is 3.5
b)First of maximum
c)Middle of maximum
d)Largest of maximum
Developing the Fuzzy Rules and Working Problems
1) Fuzzy rules set 1 and Problem 1
- If HS GPA is marginal and ACT is average, then college GPA is average.
- If HS GPA is fair and ACT is High then college GPA is High
Use the method of weighted averages and determine the college GPA for a student with HS GPA = 2.1 and ACT = 26.
2) Fuzzy Rules Set 2 Problem 2
- If HS GPA is good and ACT is Average, then College GPA is Good
- If HS GPA is very good and ACT is High, then College GPA
Use the methods of First of Max, Middle of Max, and Largest of Max to find the college GPA for a student whose HS GPA is 3.4and whose ACT score is 32.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

- The following is true about sensitivity: Group of answer choices a) The output of the model is said to be inversely sensitive if the output of the model changes a small amount for a large change in an input variable b) Sensitivity is not an important concept in modeling c) It can help the modeler tell, on a relative basis, what are the important variables d) A variable is considered NOT very sensitive if a small change in the variable results `in a large change in the output of the model.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardExhibit what we mean by coding norms.arrow_forward
- Solve using theoretical fuzzy logic rules, not codearrow_forwardTrain an ID3 decision tree for a dataset shown in the following table. The table contains 2 categorical attributes (refund and marital status) and 1 continuous attribute (taxable income). Once you got the model then use it to classify the input X1 (No, Single, 95K) and X2 (Yes, Divorced, 120K)arrow_forwardSelect the answer below that best describes a dependent variable: It is the variable that we are using to predict the independent variable (response/explanatory, the z variable) It is the variable that we are trying to predict (outcome/response, the y variable) It is the variable that we are using to predict the dependent variable (predictor/explanatory, the x variable) It is the variable that is the quantitative variable (numeric whole/numeric decimal, the w variable)arrow_forward
- A team averaging 106 points is likely to do very well during the regular season. The coach of your team has hypothesized that your team scored at an average of less than 106 points in the years 2013-2015. Test this claim at a 1% level of significance. For this test, assume that the population standard deviation for relative skill level is unknown. Use the information in the picture to write a block of code. Here is some information that will help you write this code block. Reach out to your instructor if you need help. The dataframe for your team is called your_team_df. The variable 'pts' represents the points scored by your team. Calculate and print the mean points scored by your team during the years you picked. Identify the mean score under the null hypothesis. You only have to identify this value and do not have to print it. (Hint: this is given in the problem statement) Assuming that the population standard deviation is unknown, use Python methods to carry out the hypothesis…arrow_forwardTrain an ID3 decision tree for a dataset shown in the following table. The table contains 2 categorical attributes (refund and marital status) and 1 continuous attribute (taxable income). Once you got the model then use it to classify the input X1 (No, Single, 95K) and X2 (Yes, Divorced, 120K)arrow_forwardThe following dataset is a historic record of 14 houses that were sold in a small town in BC. The dataset is used to predict whether a new house in the same town will be sold in 10 days if listed with a specific price based on certain attributes. We are considering only four attributes (price, number of bedrooms, size, and distance to bus stop) just to simplify the calculations in this assignment but more attributes should be considered in real applications. Build a decision tree to predict whether a new house listing in the same town will be sold in 10 days based on the given attributes. Use ID3 algorithm. To answer this question, you need to complete the following steps: Calculate the entropy of the whole dataset After identifying the first attribute, repeat the same steps to identify the next attribute to split on in every leaf of the tree based on information gain analysis. Repeat this step until you complete the tree. Draw the final treearrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





