
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Hi! I need help to find the molar concentration of solute, and ksp values please. Thank you.
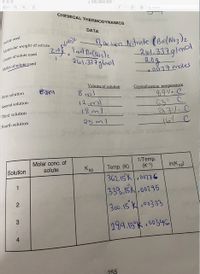
Transcribed Image Text:a IMG 0654.HEIC
Q Search
CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
DATA
Solute used
Imel BacNoz)z
261.337glmol
Barlum Mitrate (BalNo3)z
261.337g|mol
2.0g
0077moles
Grams of solute used
Moles of solute used
Volume of solution
Crystallization temperature
First solution
8 ml
११५. ९.
651. c
a7/.C
H67 c
Second solution
12.ml
18 ml
25 ml
Third solution 5
Fourth solution
Molar conc. of
solute
1/Temp.
(K-1)
Solution
Ksp
362.15K.00276
338.15k.00295
Temp. (K)
In(K sp)
1
300.15 K,00333
SHA Mn
289.15 K 00346
255
2.
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 13 Which of the following compounds is soluble? O SrCO, O CaCO3 O CuCO, O K,CO3 P Type here to search w F8 F9 F4 F5 F6 F7 F1 F2 F3 # $4 % 3 4arrow_forwardHow would you prepare 580 mL of 8.3 M NaCl solution? Dissolve _______________g of NaCl in a minimum amount of water, then dilute the resulting solution to a final volume of ______________mL.arrow_forwardHow do I calculate the mass of Na2CO3 needed for the .25 ml of solution? Use the following image to helparrow_forward
- Part C A sucrose solution is prepared to a final concentration of 0.140 M. Convert this value into terms of g/L, molality, and mass %. (Use the following values: molecular weight MW sucrose = 342.296 g/mol; density Psol'n = 1.02 g/mL ; and mass of water, mwat=972.1 g). Note that the mass of solute is included in the density of the solution. Express the concentrations in grams per liter, molality, and mass percent to three significant figures separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s) | Doto r o for Part redo for eart C restor Part C keyboard shortcuts for Part C help for Part C sucrose concentrations = 47.9,1.4410-4,4.93 Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining for Part for Part Gravimetric analysis Gravimetric analysis is a technique by which information is obtained based on massed values. One application of gravimetric analysis can allow the solubility of a solid to be determined. This is achieved by adding a known mass of solid to solution, then…arrow_forwardCalcium carbonate decomposes according to the following reaction. ????3(?)⟺???(?)+??2(?)CaCO3(s)⟺Cao(s)+CO2(g) The tabulated data below was determined at 25 °C. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) CO2(g) Δ?∘?ΔHf∘ Δ?∘?ΔHf∘, kJ/mol -1206.9 -635.1 -393.5 ?∘S∘ ?∘S∘, kJ/(mol K) 0.0929 0.0382 0.2137 Δ?∘?ΔGf∘ Δ?∘?ΔGf∘, kJ/mol -1128.8 -603.5 -394.4 What is ΔG° at 25 °C for this reaction? Is the reaction spontaneous at 25 °C? What is ΔG° at 1000 °C for this reaction? Is the reaction spontaneous at 1000 °C? Calculate KP for this reaction at 25 °C and 1000 °C.arrow_forward1a. How many moles of M9SO, are contained in 50. mL of a 3.0 M solution? 1b. How many grams of CaClą are dissolved in 80.0 mL of a 0.75 M solution? 1c. What is the molarity of 300 ml of a solution that contains 0.60 mol of dissolved ammonia?arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution...arrow_forwardQ9 chapter 15 preparing solutions Solve Asap pleasearrow_forward3)Use Table 7.2 from textbook to answer this question. TABLE 7.2 Examples of Solute Solubilities in Water (0°C) Solute Solubility Name Formula (g solute/100g H,O) Ammonium chloride NH,CI 29.7 Ammonium nitrate NH,NO, 118.3 Ammonium orthophosphate NH,H,PO, 22.7 Ammonium sulfate (NH,) SO, 70.6 Calcium carbonate CaCO, 0.0012 Calcium chloride CaCl, 53.3 Calcium sulfate CaSO, 0.23 101 Potassium carbonate K,CO, 29.2 Potassium chloride KCI 6.9 Sodium bicarbonate NaHCO, Sodium bromide NaBr 11 7.1 Sodium carbonate Na,CO, Sodium chloride NaCI 35.7 Nal 144.6 Sodium iodide Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) C,H,O, 33 Ethyl alcohol C,H,OH Ethylene glycol (antifreeze) C,H,(OH)2 Glycerin C,H;(OH), 179.2 Sucrose (table sugar) "Soluble in all proportions. OCn Leng A Rig Rered 48.6 g of ammonium sulfate is added to a flask containing 100.0g of water at 0.0 C. The mixture is then stirred to dissolve as much of the (NH4)2SO4 as possible. Is the mixture unsaturated or saturated? Explain with a sentence or two.arrow_forward
- E D Sodium hydroxide is extremely soluble in water. At a certain temperature, a saturated solution contains 573 g NaOH(s) per liter of solution. Calculate the molarity of this saturated NaOH(aq) solution. concentration: 80 $ 4 R gog F4 F V % LO 5 FS T G A 6 B MacBook Air F6 Y H & 7 N 44 F7 U * 00 8 M Question Source: McQuarrie, Rock, And Gallogly 4e-General Chemistry | Publisher: University Science Books Pi Pll FB T MOSISO K ( 9 DD FO H O presented by Macmillan Learning ) 0 command F10 P || B 180 F11 option + 11 4) F12 M } delete ret 8arrow_forwardA scientist needs to make a 250 mL of a solution of ethanol in water that has a molaritv of 0.12 Unfortunately, the only scales are available. [Water: M = 18.02 g/mol, d=0.997 g/mL] [Ethanol: M = 46.07 g/mol, d = 0.789 g/mL]) a. Calculate the mass of each substance needed to make this solution. b. Calculated the volume percent of each substance?arrow_forwardcalculate the mass of QCl2 that can be dissolved in 873.3 mL of solution. The molar mass QCl2 is 355.21 g/mol ksp=4.4 * 10-7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY