
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
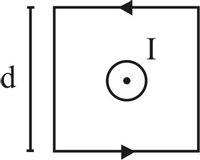
Here we have a wire with current I=3.6 A pointing out of the page. Let's draw an Amperian path around that wire as shown in the picture belwo, with side length d=0.4 m and direction indicated by the arrows. What is the magnitude of the quantity ∮B⃗ ⋅dℓ⃗ for that Amperian path, in T*m?
Transcribed Image Text:d.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wire with resistivity ρ (resistance per unit length) is bended in a way to form a shape like bb-8 in the movie Star Wars. (See the figure on the right.) We can approximate it as two circles of radius R and 2R lying in the same plane. Note the wire has an insulating shell, and it crosses over itself at joint of the two circles. The wire is then placed in a magnetic field that is spatially uniform, but increases its magnitude over time with B = bt, where b is a constant of appropriate dimension. (a) What is the total resistance of the wire? Express your answer in terms of ρ and R. (b) What is the emf induced in the upper circle? In which direction? Express your answer in terms of R and b. (c) What is the emf induced in the lower circle? In which direction? Express your answer with R and b. (d) Find the net induced current flowing in the wire. Also specify the direction of the induced current. (It is better to indicate the direction by drawing arrows on the figure…arrow_forwardthe answer is -35 m/s2arrow_forwardSolve with no calculus.arrow_forward
- Consider two current-carrying wires, separated by a distance d = 4.9 cm, as shown in the figure. The left wire is directed out of the page with current I1, and the right wire is directed into the page with current I2. The point P is a distance d from both wires, so the wires and the point form an equilateral triangle. If the current from the first wire is 7.5 A and the current from the second is 15 A, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field, in tesla, at point P?arrow_forwardparallel current bearing wires shown in the figure below; each wire carries a 3.00 Ampere current, and the wires are 0.150 meters apart. In the leftmost configuration (panel a), the currents are in the same direction. In the rightmost configuration (panel b), the currents are in the opposite direction. On the figure sketch the forces on the wires for both sets of wires, showing the direction of the force for each wire. . I (a) (b) Current configurations for #3 b. What is the magnitude of the force per unit length for panels (a) and (b)? c. What is the magnitude of the force per unit length among the wires if the distance between them is doubled?arrow_forwardWhen a steady current, I, is flowing through a conductor (e.g. the carbon paper here) with a non-negligible resistance, R, it will be possible to maintain a potential difference, ∆V = IR, between parts of the conductor along the direction of the current. Explain why in this situation there should be an electric field in the direction of the current but not in the direction perpendicular to the current.arrow_forward
- The figure below shows the same long straight wire with current i to the right and wire loops thatwe have seen previously. In this problem, we will focus just on loop (a), the larger square loop onthe left. At the time depicted in the figure, the upper edge is at some distance y from the long wire,the loop has edge length L, and has resistance R. Note that the flux calculation is essentially thesame as presented in example 27.2 in the text.arrow_forwardConsider two current-carrying wires, separated by a distance d = 4.5 cm, as shown in the figure. The left wire is directed out of the page with current I1, and the right wire is directed into the page with current I2. The point P is a distance d from both wires, so the wires and the point form an equilateral triangle. Part (a) If both wires are carrying a current of 4.5 A, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field, in tesla, at point P? Part (b) If the current from the first wire is 4.5 A and the current from the second is 14 A, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field, in tesla, at point P?arrow_forwardThe figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I, = 1.14 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I2 = 3.04 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following. (a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point а. magnitude -Select- direction (b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point b. magnitude HT direction ---Select--arrow_forward
- Three long, straight wires are seen end-on in the figure below. The distance between the wires is r= 0.254 m. Wires A and B carry current IA = IB = 1.78 A, and wire C carries current Ic = 3.30 A. %3D Assume (for example) the only forces exerted on wire A are due to wires B and C. Find the force per unit length exerted on the following. (Express your answers in vector form.) A IA IB Ic C B (a) wire A N/m %3D (b) wire B fB N/marrow_forwardThe figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I1 = 1.12 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I2 = 3.04 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following.arrow_forwardDerive an expression for the current in a system like shown, under the following conditions. The resistance between the rails is R , the rails and the moving rod are identical in cross section A and have the same resistivity ρ .The distance between the rails is l, and the rod moves at constant speed v perpendicular to the uniform field B . At time zero, the moving rod is next to the resistance R .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON