
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
ANSUR II 2012 ANSUR I 1988
Here is the numbers:
67.5 78.5
90.9 80.4
95.4 90.2
103.7 78.6
79.1 72.1
77.3 85.5
112.4 87.9
94.9 102.2
84.7 86.7
68.4 66.3
85.8 67.2
105.4 88.0
85.1
92.0
104.2
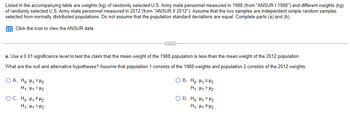
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Resource: Statistical Hypothesis Testing**
**Objective:**
We aim to test the claim that the mean weight of U.S. Army male personnel in 1988 is less than the mean weight in 2012. The data are based on independent random samples from two separate years: 1988 and 2012.
**Procedure:**
- Significance Level: 0.01
- Population 1: 1988 weights
- Population 2: 2012 weights
**Hypotheses:**
1. **Null Hypothesis (H₀)**:
- Statement: The mean weight in 1988 (μ₁) is equal to the mean weight in 2012 (μ₂).
- Notation: H₀: μ₁ = μ₂
2. **Alternative Hypothesis (H₁)**:
- Statement: The mean weight in 1988 (μ₁) is less than the mean weight in 2012 (μ₂).
- Notation: H₁: μ₁ < μ₂
**Options for Hypotheses Selection:**
- **Option A:**
- H₀: μ₁ = μ₂
- H₁: μ₁ < μ₂
- **Option B:**
- H₀: μ₁ < μ₂
- H₁: μ₁ ≥ μ₂
- **Option C:**
- H₀: μ₁ ≠ μ₂
- H₁: μ₁ = μ₂
- **Option D:**
- H₀: μ₁ = μ₂
- H₁: μ₁ ≠ μ₂
**Conclusion:**
For testing the claim that the 1988 mean weight is less than the 2012 mean weight using a significance level of 0.01, choose **Option A**.
**Note:**
Click the icon to view the detailed ANSUR data.
This analysis assumes normal distribution for both populations and does not assume equal population standard deviations.

Transcribed Image Text:The test statistic: □ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is: □ (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test:
A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean weight of the 1958 population is less than the mean weight of the 2012 population.
B. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean weight of the 1958 population is less than the mean weight of the 2012 population.
C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean weight of the 1958 population is less than the mean weight of the 2012 population.
D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean weight of the 1958 population is less than the mean weight of the 2012 population.
b. Construct a confidence interval appropriate for this hypothesis test in part (a):
□ < μ1 - μ2 < □ (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- urgent pleqasearrow_forwardThere were 53 competitors in a downhill skiing event. Their times (in seconds) are shown below. Complete parts a through d below. 98.06 98.14 98.17 98.32 98.37 98.47 98.82 98.85 99.16 99.24 99.27 99.29 99.42 99.43 99.68 99.93 100.13 100.15 100.55 100.71 100.71 100.73 100.77 100.95 100.98 101.85 101.97 102.03 102.65 102.65 103.02 103.08 103.21 103.35 103.66 104.22 104.31 104.68 104.85 105.05 105.09 105.11 105.29 105.68 105.82 105.98 108.08 111.15 112.15 113.94 115.28 115.38 115.55 a) The mean time was 103.08 seconds, with a standard deviation of 4.67 seconds. If the Normal model is appropriate, what percent of times will be less than 98.41 seconds? % (Round to the nearest integer as needed.)arrow_forwardThe 285 observations: 5.00 11.00 16.00 23.00 36.00 58.00 29.00 20.00 10.00 8.00 3.00 0.00 0.00 2.00 11.00 27.00 47.00 63.00 60.00 39.00 28.00 26.00 22.00 11.00 21.00 40.00 78.00122.00103.00 73.00 47.00 35.00 11.00 5.00 16.00 34.00 70.00 81.00111.00101.00 73.00 40.00 20.00 16.00 5.00 11.00 22.00 40.00 60.00 80.90 83.40 47.70 47.80 30.70 12.20 9.60 10.20 32.40 47.60 54.00 62.90 85.90 61.20 45.10 36.40 20.90 11.40 37.80 69.80106.10100.80 81.60 66.50 34.80 30.60 7.00 19.80 92.50154.40125.90 84.80 68.10 38.50 22.80 10.20 24.10 82.90132.00130.90118.10 89.90 66.60 60.00 46.90 41.00 21.30 16.00 6.40 4.10 6.80 14.50 34.00 45.00 43.10 47.50 42.20 28.10 10.10 8.10 2.50 0.00 1.40 5.00 12.20 13.90 35.40 45.80 41.10 30.10 23.90 15.60 6.60 4.00 1.80 8.50 16.60 36.30 49.60 64.20 67.00 70.90 47.80 27.50 8.50 13.20 56.90121.50138.30103.20 85.70 64.60 36.70 24.20 10.70 15.00 40.10 61.50 98.50124.70 96.30 66.60 64.50 54.10 39.00 20.60 6.70 4.30 22.70 54.80 93.80 95.80 77.20 59.10…arrow_forward
- Plz complet answerarrow_forward(b) Determine and interpret the interquartile range. The interquartile range is ______ crimes per 100,000 population.arrow_forwardFahrenheit is the measurement of temperature commonly used in the US. On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32 F and boils at 212 F (at sea level). What is the data type and measurement scale of a dataset that records Fahrenheit temperature? a. Numerical and ratio b. Numerical and interva c. Categorical and ratio d. Categorical and ordinalarrow_forward
- Consider the diagram below. 5.66 5.66 Which of the following represent the values of x, y, and z to the nearest hundredth? x = 9.78 y = 7,95arrow_forwardThe number of countries shown in this bar chart where the rate of rapes is below 10 for every 100,000 is Rape at the national level, number of police-recorded 70 offences (rate/100,000)- United nations (2012) 60 50 40 30 20 10 66.5 34.1 33.0 29.8 29.6 27.6 Jamaica Bolivia Sweden 26.6 24.9 22.3 Belgium USA 18.7 Costa Rica 1.7 1.6 1.5 Finland Source: United nations office on drugs and crime "CTS2013 SexualViolence.xls" 1.4 Hong Kong Slovakia Norway 1.0 0.9 8. 0.9 0.7 Japan UAE Greece 18 Canada Serbia 10 Indonesia New Zealand Brazilarrow_forwardFourteen different second-year medical students at a hospital measured the blood pressure of the same person. The systolic readings (mm Hg) are listed below. Use the given data to construct a boxplot and identify the 5-number summary. 135 120 131 125 O A. 138 O C. The 5-number summary is ☐☐☐☐, and all in mm Hg. (Use ascending order. Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Which boxplot below represents the data? 120 120 130 129 Blood 140 sure (mm Hg) 130 140 Blood Pressure (mm Hg) 150 150 Q Q 125 Q 130 ... OB. O D. 150 120 120 143 126 140 130 Blood Pressure (mm Hg) 130 140 Blood Pressure (mm Hg) 140 150 150 126 150 D₂₁arrow_forward
- Answer all the questions please badly need:<arrow_forwardCan I please get some help. Never seen a problem like this. Thank youarrow_forwardData was collected for 300 fish from the North Atlantic. The length of the fish (in mm) is summarized in the GFDT below. Lengths (mm) Frequency 80 - 83 1 84 - 87 16 88 - 91 71 92 - 95 108 96 - 99 83 100 - 103 18 104 - 107 3 What is the upper class limit for the fifth class?upper class limitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman