
Exploring Economics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781544336329
Author: Robert L. Sexton
Publisher: SAGE Publications, Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
5
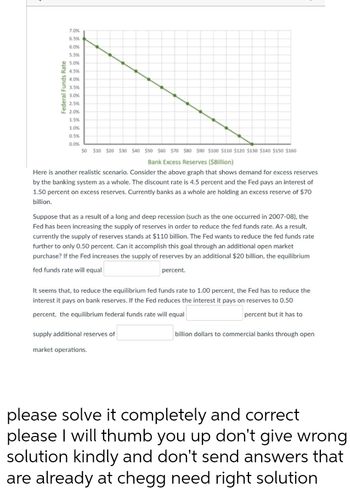
Transcribed Image Text:Federal Funds Rate
7.0%
6.5%
6.0%
5.5%
5.0%
4.5%
4.0%
3.5%
3.0%
2.5%
2.0%
1.5%
1.0%
0.5%
0.0%
50 510 520 530 540 550 560 570 580 590 $100 $110 $120 $130 $140 $150 $160
Bank Excess Reserves ($Billion)
Here is another realistic scenario. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves
by the banking system as a whole. The discount rate is 4.5 percent and the Fed pays an interest of
1.50 percent on excess reserves. Currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70
billion.
Suppose that as a result of a long and deep recession (such as the one occurred in 2007-08), the
Fed has been increasing the supply of reserves in order to reduce the fed funds rate. As a result,
currently the supply of reserves stands at $110 billion. The Fed wants to reduce the fed funds rate
further to only 0.50 percent. Can it accomplish this goal through an additional open market
purchase? If the Fed increases the supply of reserves by an additional $20 billion, the equilibrium
fed funds rate will equal
percent.
It seems that, to reduce the equilibrium fed funds rate to 1.00 percent, the Fed has to reduce the
interest it pays on bank reserves. If the Fed reduces the interest it pays on reserves to 0.50
percent, the equilibrium federal funds rate will equal
percent but it has to
billion dollars to commercial banks through open
supply additional reserves of
market operations.
please solve it completely and correct
please I will thumb you up don't give wrong
solution kindly and don't send answers that
are already at chegg need right solution
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the asset-liability time mismatch that all banks face?arrow_forwardExplain the difference between how you would characterize bank deposits and loans as assets and liabilities on your own personal balance sheet and how a bank would characterize deposits and loans as assets and liabilities on its balance sheet.arrow_forwardWhy are banks more willing to lend to well-established firms?arrow_forward
- Explain why the money listed under assets on a bank balance sheet may not actually be in the bank?arrow_forwardSuppose the Fed conducts an open market sale by selling $10 million in Treasury bonds to Acme Bank. Sketch out the balance sheet changes that will occur as Acme restores its required reserves (10% of deposits) by reducing its loans. The initial balance sheet for Acme Bank contains the following information: Assets - reserves 30, bonds 50, and loans 250; Liabilities - deposits 300 and equity 30.arrow_forwardHow do banks create money?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781285165912
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...
Economics
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning