Question
Demonstrate (with a formula) in the refraction time of the "n" layer refraction wave is faster than the direct wave, but at some distance it is slower than the "n + 1" layer refraction (hint: take a model/example)
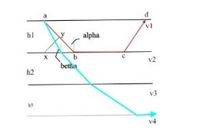
Transcribed Image Text:hl
alpha
v2
betha
h2
v3
14
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given figure as,
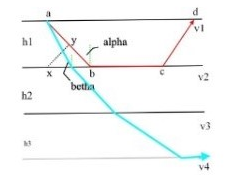
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Let Ap be the difference between the phase shift a Helium-Neon laser beam expe- riences on traversing a given length of vacuum and on traversing the same length of plasma. What is Ad when the laser beam passes through 10 cm of plasma having a density of n = 102? m?? How could this be used as a density diagnostic? The wavelength of the He-Ne laser radiation is 632.8 nmarrow_forwardPhysics 20: SUMMER Assignment 13 7. Use the following information and diagram to answer parts a and b. A reflecting surface is inclined 30° above the horizontal. A wave is traveling horizontally and reflects off the surface, as shown below. The solid grey line is the barrier and the black arrow is the wave. (1) (1) a) What is the angle of incidence? 30° 1 b) What is the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray? 4arrow_forward?Which is describe Gaussian profile TEM00 mode Cavity longitudinal Longitudinal mode. Transverse Modes When Radii of curvature of the mirrors R1= L/2 and R2=-L then Cavity is stable and g1g2=3 O Cavity is unstable g1g2=-1 O Cavity is unstable g1g2=0 O Cavity is unstable g1g2=-2 -When the TEM32 the m=-3, n=-2 O m=3, n=2 O m=2, n=3 O m=3, n=3arrow_forward
- TV uses satellites that hover above one point over our planet as the rest rotates. The satellites give out 10 GHz EM waves that a dish (with a diameter of 40cm) on a house's roof absorbs. The dishes are like circular apertures to collect signals. These dishes have to distinguish signals from two adjacent satellites to get good signal. Draw and label a diagram, show all work, and explain throughly using physics equations: What is the maximum amount of satellites that can be used for TV ? Earth radius = 6.38 x 106 m Earth mass = 6 x 1024 kgarrow_forwardFind the largest wavelength (in nm) of light falling on double slits separated by 7.5o µm for which there is a second-order maximum. nm Is this in the visible part of the spectrum? Yes Noarrow_forwardBelow, the most intense peaks of x-ray diffraction patterns obtained from two samples the same material. What could have caused the differences in the XRD peaks give below? Explain? A В 20 (Degrees) Intensity (arbitrary units)arrow_forward
- Q3: If at -Vụ, and y is a wave function in one dimension. Prove 2m дх2 that (p) = S dxy* (-iharrow_forwardNote :- Answer all questions Q1/Determine the expected diffraction angle for the second -order reflection from the (200) set of planes for Simple Cubic crystal when monochromatic radiation of wavelength ( 0.122 nm) and radius (0.144 nm) are used ?arrow_forwardQ4: For the geometry below, assume the carrier frequency is 900 MHz Tx Rx 50 m| 50 m 500 m 500 m a. Determine the height of the obstacle required to induce 23 dB diffraction loss. Given, b. Discuss two factors impact the amount of diffraction loss?arrow_forward
- Q1) A 10 GHz uniform plane wave is propagating along the +z - direction, in a material such that & = 81, µr = 1 and σ = 2 mho/m. a) (20 pts.) Find the values of y, a and B. b) (10 pts.) Find the intrinsic impedance. c) (20 pts.) Write the phasor form of electric and magnetic fields, if the amplitude of the electric field intensity is 0.5 V/m.arrow_forwardWhat relationship does the slit width have with the diffraction envelope in a single slit experiment? Is there a correlation between the slit width and the maxima (distance between side orders)-- Is there any theory behind it? Explain.arrow_forwardTo observe interference in a thin film, why must we consider a film that is not very thick (with a thickness of only a few wavelengths)? What happens if we exceed that thickness? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios