
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please help label the following:
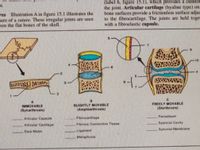
Transcribed Image Text:(label 6, figure 15.1), which provides a cushion
the joint. Articular cartilage (hyaline type) on
bone surfaces provide a frictionless surface adjac
to the fibrocartilage. The joints are held toger
with a fibroelastic capsule.
S.
res Illustration A in figure 15.1 illustrates the
ture of a suture. These irregular joints are seen
een the flat bones of the skull.
10
B.
SLIGHTLY MOVABLE
(Amphiarthrosis)
FREELY MOVABLE
(Diarthrosis)
IMMOVABLE
(Synarthrosis)
Periosteum
Articular Capsule
Fibrocartilage
Articular Cartilage
Fibrous Connective Tissue
Synovial Cavity
Dura Mater
Ligament
Synovial Membrane
Metaphysis
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The point where the meeting of the two or more bones take place is known as joint.
The joints are divided into fibrous, cartilaginous and synovial joints based on the structural classification of joints. This classification is based upon the material which forms the joint and if the joint contains or does not contain a cavity.
The structure classification of joint-
1.Fibrous joints- the bones in this joint are held together by the fibrous connective tissue. These are almost immovable joints as in between the bones there is absence of cavity or space.
- Cartilaginous joint -in this joint, the bones of the joint are held together by the cartilage.
- Synovial joints-there is presence of space in between the bones forming this joint. This space is known as synovial cavity and is filled with synovial fluid. There is presence of articular cartilage(type of hyaline cartilage)covering the ends of the bones forming the joint. An articular capsule surrounds this entire joint formed of connective tissue. There can also be the presence of cartilage in the articular capsule holding the bones of joint together.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Know about the inheritance of sex-linked disorders:arrow_forwardGive the Blood Type of the Following Genotypes (Review Rh genetics in the ABO Lab Document and Bombay Phenotype) Genotype Phenotype (Blood type) a) IAIB CcDDeeHh ___ (+ or -) b) IAi CcddEehh ___ c) ii ccddeehh ___ d) IBIB Ccddeehh ___arrow_forwardDescribe the major complications of eye infections and STDs.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,
Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc., Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780135168059
Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,

Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780078024283
Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa Bidle
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780321927040
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON