
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The figure shows a distance vs. time graph of an object with three distinct regions I, II, and III.
The object’s velocity is positive in region(s)
(picture)
is the answer:
I
no region
III
II
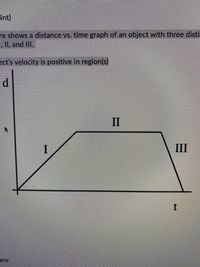
Transcribed Image Text:int)
re shows a distance vs. time graph of an object with three disti
I, II, and IlI.
ect's velocity is positive in region(s)
d.
II
III
t
ons
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you set up equations with variables for the two cases described? An example of a situation that I might be able to use an equation with a single unknown would be, suppose I live in a town 100 miles away from my office. How long will it take me to reach my office if I am driving at 75 mph. Time will be unknown, and I am assuming I am driving at a constant speed, so I will apply the following linear equation, Speed = Time Distance → Time = Speed Distance = 1.33hours = 1 hour 20 minutes. Now I'm in the same position as before, but now there are traffic jams, or maybe roadwork, so the speed is not constant, (it varies with time) so in this case speed(time) = time distance → time = speed(time) Distance will therefore fail in this case. In the first case, in the linear case, we can assume that the speed will be constant and independent of other variables, time, which makes the linear method useful in this situation. On the other hand, in our second example, speed is a function of…arrow_forwardShown is a motion diagram of a car traveling down a street. The camera took one frame every second. A distance scale is provided.a. Use the scale to determine the x-value of the car at each dot. Place your data in a table, similar to Table 2.1, showing each position and the instant of time at which it occurred.b. Make a graph of x versus t, using the data in your table. Because you have data only at certain instants of time, your graph should consist of dots that are not connected together.arrow_forwardTime left 0:42:41 15 velocity (m/sec) vs time (sec) 13 16.5 55 65 13 The diagram above shows the velocitylm/s) versus time(s) graph of a man driving a car along a straight line from home to his work. During which time intervals was he traveling in a positive direction? 13 16.5 s O b. 3-5.5s O c. none of the listed choices O d. 6.5-8s O e. 9-13s Of. 8-9sarrow_forward
- The position vs. time graph of a moving particle for a time interval of 23 seconds is shown below. Each square unit in the horizontal axis corresponds to one second, and each square unit in the vertical axis corresponds to one meter. 1) What is the instantaneous velocity of the particle at t = 11 s? m/s 2) What is the average velocity of the particle from t = 17 s to t = 18 s? m/sarrow_forwardwill someone please help me with this physics questions? Part A: draw a detailed motion diagram to this question: An object covers a distance of 8 m in the first second of travel, another 8 m during the next second, and 8 m again during the third second the objects acceleration is ? 1. 5m/s 2. 1.2 m/s 3. 9.8 m/s 4. 11.0 m/s 5. 11.760 m/s Part B A steel ball is dropped from a diving platform from rest. Given that g=9.8 m/s^2, what is the velocity of the ball 1.2 seconds after it's release? (Ignore air resistance) 1. 0 m/s 2. 1.2 m/s 3. 9.8 m/s 4. 11.0 m/s 5. 11.76 m/s Part C: (Notice this is different from part B) A steel ball is dropped from diving platform from rest. Given that g=9.8 m/s^2, how far does it fall in the first 1.2 seconds of its flight ignoring air resistance. 1. 5.880 m 2. 7.056 m 3. 11.760 m 4. 14.112 marrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle as a function of time is given by the graph below: velocity vs time 20 15 10 8 9 10 -5 -10 -15 -20 time (s) Part A The displacement of the particle would best be approximated as -5 m O -20 m O 20 m 95 m (s/w) Aapojanarrow_forwardTwo vehicles start out traveling side by side along a straight road. Their position functions, shown in the following graph, are given by s = f(t) and s = g(t) , where s is measured in meters and t is measured in seconds. 10+ 7- 4 s=ft) s= g(t) Which vehicle has traveled farther at t = 2 seconds? Vehicle f Vehicle g What is the approximate velocity of the f vehicle at t = 3 seconds? meters per second What is the approximate velocity of the g vehicle at t = 3 seconds? meters per second Which vehicle is traveling faster at t = 4 seconds? Vehicle f O Vehicle garrow_forwardHow do I solve 55?arrow_forward
- I can't figure this one out!arrow_forwardThe velocity-versus-time graph for an object moving along an x-axis is shown below. The initial position of the object is xo = -10.0 m. V (m/s) 4- t (s) 4 0. a) Draw a motion diagram of the object. Be sure to label your velocity and acceleration vectors. 0. b) What are the position, velocity, and acceleration of the object at t = 3 s? You must show all %3D of your work to get full credit. c) Sketch the object's position-versus-time graph and acceleration-versus-time graph. 2.arrow_forwardq1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON