
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The diameter of a pipe carrying water changes
gradually from 6 inches at a lower point to 18 inches
at a higher point by 15 ft. What will be the difference
in pressure, in psi, between these points if 6.2 cfs is
flowing considering no loss in energy.
please use the photo for ung format solutions and i request that the solution is encoded so that i can understand it. Please input figures. Thank you
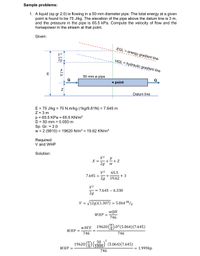
Transcribed Image Text:Sample problems:
1. A liquid (sp gr 2.0) is flowing in a 50 mm diameter pipe. The total energy at a given
point is found to be 75 J/kg. The elevation of the pipe above the datum line is 3 m,
and the pressure in the pipe is 65.5 kPa. Compute the velocity of flow and the
horsepower in the stream at that point.
Given:
EGL = energy gradient line
V2
2g
HGL hydraulic gradient line
E
50 mm ø pipe
Q
• point
Datum line
E = 75 J/kg = 75 N.m/kg (1kg/9.81N) = 7.645 m
Z = 3 m
p = 65.5 KPa = 65.5 KN/m²
D = 50 mm = 0.050 m
Sp. Gr. = 2.0
w = 2 (9810) = 19620 N/m3 = 19.62 KN/m³
%3D
Required:
V and WHP
Solution:
V2
+
E =
2g
+ Z
V2
65.5
+
19.62
7.645 =
+3
2g
V2
= 7.645 – 6.338
2g
V = V(2g)(1.307) = 5.064m/s
wQH
WHP =
746
WAVE
19620 (4) D?(5.064)(7.645)
WHP =
746
746
2
50
19620 (4) To00) (5.064)(7.645)
1000.
WHP =
1.999hp
%D
746
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning