
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
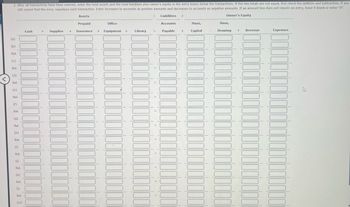
Transcribed Image Text:2. After all transactions have been entered, enter the total assets and the total liabilities plus owner's equity in the entry boxes below the transactions. If the two totals are not equal, first check the addition and subtraction. If you
still cannot find the error, reanalyze each transaction. Enter increases to accounts as positive amounts and decreases to accounts as negative amounts. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank or enter "0".
Assets
= Liabilities +
Owner's Equity
Prepaid
Office
Accounts
Haas,
Haas,
Cash
Supplies
+
+
Insurance
+ Equipment
+
Library
=
Payable +
Capital
Drawing
Revenue
Expenses
(a)
(b)
Bal.
(c)
Bal.
(d)
Bal.
(e)
Bal.
(f)
Bal.
(g)
Bal.
(h)
Bal.
(i)
Bal.
(s)
Bal.
(k)
Bal.
(1)
Bal.
(m)
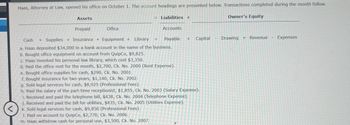
Transcribed Image Text:Haas, Attorney at Law, opened his office on October 1. The account headings are presented below. Transactions completed during the month follow.
Assets
Liabilities +
Owner's Equity
Prepaid
Office
Accounts
Cash
+ Supplies + Insurance + Equipment + Library
Payable + Capital
Drawing Revenue Expenses
a. Haas deposited $34,000 in a bank account in the name of the business.
b. Bought office equipment on account from QuipCo, $9,825.
c. Haas invested his personal law library, which cost $3,350.
d. Paid the office rent for the month, $2,700, Ck. No. 2000 (Rent Expense).
e. Bought office supplies for cash, $290, Ck. No. 2001.
f. Bought insurance for two years, $1,140, Ck. No. 2002.
g. Sold legal services for cash, $8,925 (Professional Fees).
h. Paid the salary of the part-time receptionist, $1,855, Ck. No. 2003 (Salary Expense).
i. Received and paid the telephone bill, $438, Ck. No. 2004 (Telephone Expense).
j. Received and paid the bill for utilities, $435, Ck. No. 2005 (Utilities Expense).
k. Sold legal services for cash, $9,850 (Professional Fees).
1. Paid on account to QuipCo, $2,770, Ck. No. 2006.
m. Haas withdrew cash for personal use, $3,500, Ck. No. 2007.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The normal balance of an account is the side of the account (either the debit side or the credit side in the ledger) where we expect to find a positive dollar amount. The normal balance of an asset account is a _________________ balance. Group of answer choices break-even debit negative creditarrow_forwardWhen an account becomes uncollectible and must be written off as a?arrow_forwardPosting errors are identified in the following table. In column (1), enter the amount of the difference between the two trial balance columns (debit and credit) due to the error. In column (2), identify the trial balance column (debit or credit) with the larger amount if they are not equal. In column (3), identify the account(s) affected by the error. In column (4), indicate the amount by which the account(s) in column (3) is under- or overstated. Item (a) is completed as an example. Note: Select "None" if there is no effect. (1) Difference between Description of Posting Error Debit and Credit Columns Larger Total (2) Column with the (3) Identify Account(s) Incorrectly Stated (4) Amount of account over- or understatement a. $1,720 debit to Rent Expense is posted as a $1,270 debit. $ 450 Credit Rent Expense Rent Expense is understated by $450 b. $3,440 credit to Cash is posted twice as two credits to Cash. c. $1,570 debit to Prepaid Insurance is posted as a debit to Insurance Expense.…arrow_forward
- Which of the following is incorrect? Group of answer choices A. In a double-entry accounting system every transaction will affect at least two accounts. B. Across all accounts, the total amount of debits must always equal the total amount of credits. C. A debit can be recorded on either side of the t-account depending on the type of account. D. The difference between the total debit and credit amounts for an account is called the account balance.arrow_forward(b) To record estimated liability. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.) Period 1 Account Titles and Explanation Period 2 Account Titles and Explanation Save for Later Debit Debit Credit Credit Attempts: 0 of 1 used Submit Answerarrow_forwardanswer in text form please (without image), Note: .Every entry should have narration pleasearrow_forward
- farrow_forwardHi I asked this question previously and the individual did not explain things clearly. For instance he provided the I'm guessing standard method of finding a missing amount on a certain type of T-Account but then would turn around and solve it using a different method. I am posting the response that were not clear below. If you could tell me what the actual method is and if there exceptions and if so what those are.Answer #1 I needed the BEGINNING balance of a debit account. As you can see the response below the individual provided a formula that included the BB which is UNKOWN because that is WHAT I NEED. At the bottom they change around the equation to come to the answer. So what is the proper way???Part-1. Begining balance of cash account is missing. The cash account is having a debit balance always. The formula for Cash account is as under:Ending balance of Cash Account = Begining Balance of cash account + All debits - All creditsHere,Ending Balance of cash = 9800All debits…arrow_forwardIdentify the type of account (Asset, Liability, Equity, Revenue, Expense), normal balance (Debit, Credit), financial statement (Balance Sheet, Income Statement), and whether the account is closed at the end of the period (Yes, No) by selecting the letter that best describes those attributes. If an account is a contra or adjunct account, the answer will show the account type in parentheses. Answer items may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Retained Earnings 1. Equity, Credit, Balance Sheet, No 2. Freight-Out Liability, Credit, Balance Sheet, No V Loss on Impairment of Intangible Assets 3. Expense, Debit, Income Statement, Yes 4. Gain on Acquisition of Business (Equity), Debit, Balance Sheet, No 5. Amortization of Copyrights Asset, Debit, Income Statement, Yes Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 6. Expense or Loss, Credit, Income Statement, Yes Land 7. Revenue or Gain, Credit, Income Statement, Yes Federal Income Tax Withheld 8. (Revenue or Gain), Debit, Income Statement, Yes…arrow_forward
- If a $335.00 debit item in the general journal is posted as a credit: By how much will the trial balance be out of balance? Explain how you might detect such an error.arrow_forwardIndicate whether a debit or credit decreases the normal balance of each of the following accounts. Decrease Normal Balance a. Prepaid Rent b. Cash c. Office Supplies d. Notes Receivable e. Accounts Receivable f. Interest Payablearrow_forwardplease step by step solution. please introductio of this solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education