
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
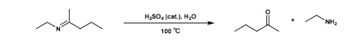
Transcribed Image Text:H2SO4 (cat.), H₂O
100 °C
NH₂
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The heat of neutralization, Hneut, can be defined as the amount of heat released (or absorbed), q, per mole of acid (or base) neutralized. Hneut for nitric acid is -52 kJ/mol HNO3. At 27.3C, 50.00 mL of 0.743M HNO3 is neutralized by 1.00 M Sr(OH)2 in a coffee-cup calorimeter. (a) How many mL of Sr(OH)2 were used in the neutralization? (b) What is the final temperature of the resulting solution? (Use the assumptions in Question 11.)arrow_forwardHow much heat is produced when loo mL of 0.250 M HCl (density, 1.00 g/mL) and 200 mL of 0.150 M NaOH (density, 1.00 g/mL) are mixed? HCl(aq)+NaO(aq)NaCl(aq)+H2O(l)H298=58kJ If both solutions are at the same temperature and the heat capacity of the products is 4.19 J/g C, how much will the temperature increase? What assumption did you make in your calculation?arrow_forwardDefine the joule in terms of SI base units.arrow_forward
- What will be the final temperature of a mixture made from equal masses of the following: water at 25.0C, ethanol at 35.5C, and iron at 95C?arrow_forwardA 21.3-mL sample of 0.977 M NaOH is mixed with 29.5 mL of 0.918 M HCl in a coffee-cup calorimeter (see Section 6.6 of your text for a description of a coffee-cup calorimeter). The enthalpy of the reaction, written with the lowest whole-number coefficients, is 55.8 kJ. Both solutions are at 19.6C prior to mixing and reacting. What is the final temperature of the reaction mixture? When solving this problem, assume that no heat is lost from the calorimeter to the surroundings, the density of all solutions is 1.00 g/mL, the specific heat of all solutions is the same as that of water, and volumes are additive.arrow_forwardThe enthalpy of combustion of diamond is -395.4 kJ/mol. C s, dia O2 g CO2 g Determine the fH of C s, dia.arrow_forward
- Starting with equation 2.27 andthe original definitionof enthalpy, derive the fact that Cp-=Cv-+Rarrow_forwardIn the 1880s, Frederick Trouton noted that the enthalpy of vaporization of 1 mol pure liquid is approximately 88 times the boiling point, Tb, of the liquid on the Kelvin scale. This relationship is called Troutons rule and is represented by the thermochemical equation liquid gas H = 88 Tb, joules Combined with an empirical formula from chemical analysis, Troutons rule can be used to find the molecular formula of a compound, as illustrated here. A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen is 85.6% C and 14.4% H. Its enthalpy of vaporization is 389 J/g, and it boils at a temperature of 322 K. (a) What is the empirical formula of this compound? (b) Use Troutons rule to calculate the approximate enthalpy or vaporization or one mole of the compound. Combine the enthalpy of vaporization per mole with that same quantity per gram to obtain an approximate molar mass of the compound. (c) Use the results of parts (a) and (b) to find the molecular formula of this compound. Remember that the molecular mass must be exactly a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula mass, so considerable rounding may be needed.arrow_forwardDetermine whether the statements given below are true or false. Consider enthalpy (H). (a) It is a state property. (b) qreaction(atconstantP)=H=HproductsHreactants (c) The magnitude of H is independent of the amount of reactant. (d) In an exothermic process, the enthalpy of the system remains unchanged.arrow_forward
- When one mol of KOH is neutralized by sulfuric acid, q=56 kJ. (This is called the heat of neutralization.) At 23.7C, 25.0 mL of 0.475 M H2SO4 is neutralized by 0.613 M KOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter. Assume that the specific heat of all solutions is 4.18J/gC, that the density of all solutions is 1.00 g/mL, and that volumes are additive. (a) How many mL of KOH is required to neutralize H2SO4? (b) What is the final temperature of the solution?arrow_forwardOn complete combustion at constant pressure, a 1.00-L sample of a gaseous mixture at 0C and 1.00 atm (STP) evolves 75.65 kJ of heat. If the gas is a mixture of ethane (C2H6) and propane (C3H8), what is the mole fraction of ethane in the mixture?arrow_forwardA 29.1-mL sample of 1.05 M KOH is mixed with 20.9 mL of 1.07 M HBr in a coffee-cup calorimeter (see Section 6.6 of your text for a description of a coffee-cup calorimeter). The enthalpy of the reaction, written with the lowest whole-number coefficients, is 55.8 kJ. Both solutions are at 21.8C prior to mixing and reacting. What is the final temperature of the reaction mixture? When solving this problem, assume that no heat is lost from the calorimeter to the surroundings, the density of all solutions is 1.00 g/mL, and volumes are additive.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning