
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
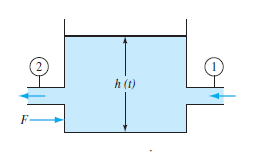
Water at 20 ° C fl ows steadily through the tank in Fig.
P3.101. Known conditions are D 1 = 8 cm, V 1 = 6 m/s, and
D 2 = 4 cm. A rightward force F = 70 N is required to keep
the tank fi xed. ( a ) What is the velocity leaving section 2?
( b ) If the tank cross section is 1.2 m 2 , how fast is the water
surface h ( t ) rising or falling?
Transcribed Image Text:h (t)
F-
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given,
V1 = 6 m/s
D1= 8 cm
D 2 = 4 cm
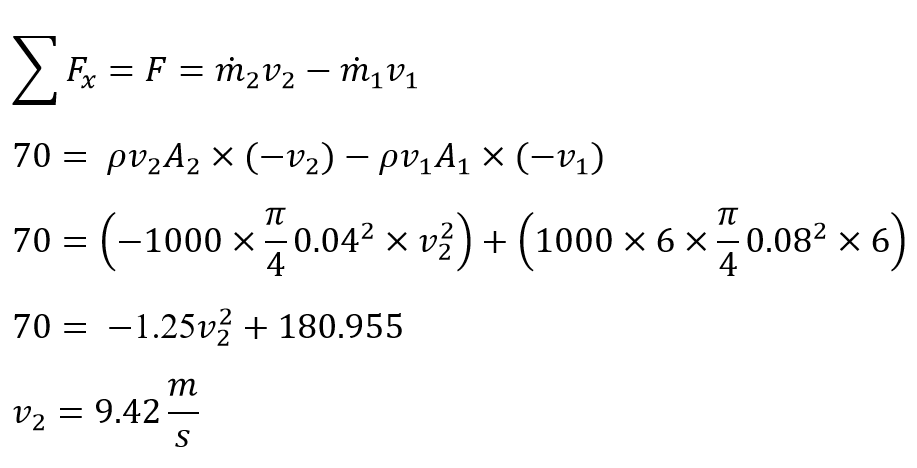
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PDI The pump in Fig. P3.191 creates a 20°C water jet oriente to travel a maximum horizontal distance. System friction head losses are 6.5 m. The jet may be approximated by the trajectory of frictionless particles. What power must be delivered by the pump? Jet De = 5 cm 25 m D= 10 cm %3D 15 m 2 m Pump P3.191arrow_forwardFor the pipe-fl ow-reducing section of Fig. P3.54, D 1=8 cm, D 2 = 5 cm, and p 2 = 1 atm. All fl uids are at 20 ° C. IfV 1 = 5 m/s and the manometer reading is h =58 cm, estimatethe total force resisted by the fl ange bolts.arrow_forwardGasoline enters section 1 in Fig. P3.18 at 0.5 m 3 /s. It leavessection 2 at an average velocity of 12 m/s. What is the averagevelocity at section 3? Is it in or out?arrow_forward
- A necked-down section in a pipe flow, called a venturi, develops a low throat pressure that can aspirate fluid upward from a reservoir, as in Fig. P3.124. Using Bernoulli's equation with no losses, derive an expression for the velocity V, that is just sufficient to bring reservoir fluid into the throat. D, V2» P2=Pa Water V Pa Water Р3.124arrow_forwardIn Fig. P3.131 both fl uids are at 20 ° C. If V 1 = 1.7 ft/s andlosses are neglected, what should the manometer readingh ft be?arrow_forwardThe rocket in Fig. P3.68 has a supersonic exhaust, and theexit pressure p e is not necessarily equal to p a . Show that theforce F required to hold this rocket on the test stand isF = ρe AeV2e+ Ae( pe - pa) . Is this force F what we termthe thrust of the rocket?arrow_forward
- Consider Fig. P3.36 as a general problem for analysis of amixing ejector pump. If all conditions ( p , ρ , V ) are knownat sections 1 and 2 and if the wall friction is negligible,derive formulas for estimating ( a ) V 3 and ( b ) p 3 .arrow_forwardThe 35 °C water fl ow of Fig. P3.135 discharges to sea-levelstandard atmosphere. Neglecting losses, for what nozzlediameter D will cavitation begin to occur? To avoidcavitation, should you increase or decrease D from thiscritical value?arrow_forwardP3.21 For the two-port tank in Fig. E3.5, let the dimensions remain the same, but assume V₂ = 3 ft/s and that V₁ is unknown. If the water surface is rising at a rate of 1 in/s, (a) determine the average velocity at section 1. (b) Is the flow at section 1 in or out?arrow_forward
- answer very quicklarrow_forwardWater from a storm drain fl ows over an outfall onto aporous bed that absorbs the water at a uniform verticalvelocity of 8 mm/s, as shown in Fig. P3.19. The system is5 m deep into the paper. Find the length L of the bed thatwill completely absorb the storm water.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY