
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Strain energy for those 2 structures please help
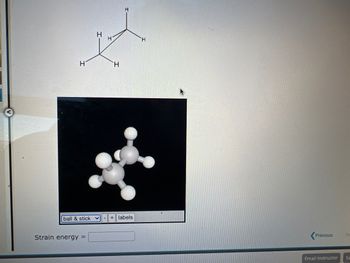
Transcribed Image Text:H
H
ball & stick ♥
Strain energy =
H
H
H
labels
Previous
Email Instructor
No
Sa
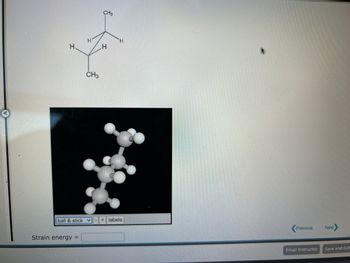
Transcribed Image Text:H.
H
Strain energy =
CH3
ball & stick v
CH3
H
+ labels
Previous
Email Instructor
Next
Save and Exit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Rate the bonds strongest to weakest H2CO, NH3, CH4, LiF and CF4arrow_forwardLearning Goal: When two bonded atoms attract electrons with equal strength, the result is a nonpolar covalent bond. A polar covalent bond is one in which the electrons are unequally shared between the atoms. An ionic bond results when the sharing is so unequal that fully charged ions form. Electronegativity difference can be used to predict bond type. If electronegativities differ by more than 2 units, the bond is substantially ionic; if they differ by less than 2 units, the bond is polar covalent; and if the values are equal, the bond is nonpolar covalent. If you are not given electronegativity values, you can still predict the bond type using the periodic table. Metals have low electronegativity compared to nonmetals. So in general, we can predict that any metal- nonmetal combination will be ionic and any nonmetal-nonmetal combination will be covalent. If electronegativity values aren't given, you should assume that a covalent bond is polar unless it is between two atoms of the same…arrow_forwardWhat type of strain energy is present in a molecule of cyclopropane? A. Torsional strain B. Angle strain C. Steric strain D. Only A and B E. A, B, and Carrow_forward
- Why do molecules of Florine attract each other? (get close together and stick)arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hend raitingarrow_forwardExamine the three-dimensional structures of each of the following molecules in the simulation, which can be found in the Real Molecules mode. Then, identify which molecules are polar and which are nonpolar. Assume that every bond in each molecule is polar covalent. It may be easier to visualize if you uncheck the box labeled Show Lone Pairs. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. ► View Available Hint(s) Polar H₂O SF6 SFA NH3 XeF4 CO₂ Nonpolar PC15 CIF 3 Resetarrow_forward
- What is the LUMO of the Li₂ molecule? please explain with answer...don't quite understand book explanation Thanksarrow_forwardMore energy is required to break a bond with an order of3/2than is required to break a bond of order 2 . True False. Please type answer no write by hend.arrow_forwardH T H H H H H What type of strain is present in the circled portion of this molecule? I H H A) Torsional B) Angle C) Stericarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardthe box next to each molecule on the right that has the shape molecules model (check all that apply) O NO, O HOCI O H,0 O None of the above Note for advanced students: the length of bonds and size of atoms in the m geometry and 3D shape of the molecule. I Don't Know Submitarrow_forwardDetermine the number of electron groups around the central atom for each of the following CH2 Cl2 molecules, Express your answer as an integer. ? electron groups Submit Request Answer Part B SBr2 Express your answer as an integer. ? electron groups Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY