Question
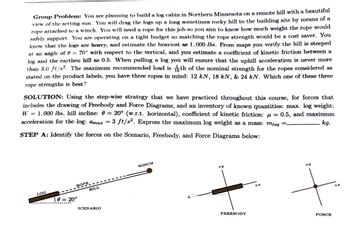
Transcribed Image Text:**Group Problem:** You are planning to build a log cabin in Northern Minnesota on a remote hill with a beautiful view of the setting sun. You will drag the logs up a long sometimes rocky hill to the building site by means of a rope attached to a winch. You will need a rope for this job so you aim to know how much weight the rope would safely support. You are operating on a tight budget so matching the rope strength would be a cost saver. You know that the logs are heavy, and estimate the heaviest as 1,000 lbs. From maps you verify the hill is steeped at an angle of θ = 70° with respect to the vertical, and you estimate a coefficient of kinetic friction between a log and the earthen hill as 0.5. When pulling a log you will ensure that the uphill acceleration is never more than 3.0 ft/s². The maximum recommended load is \(\frac{1}{10}\)th of the nominal strength for the ropes considered as stated on the product labels, you have three ropes in mind: 12 kN, 18 kN, & 24 kN. Which one of these three rope strengths is best?
**SOLUTION:** Using the step-wise strategy that we have practiced throughout this course, for forces that includes the drawing of Freebody and Force Diagrams, and an inventory of known quantities: max. log weight: W = 1,000 lbs, hill incline: θ = 20° (w.r.t. horizontal), coefficient of kinetic friction: μ = 0.5, and maximum acceleration for the log: a_max = 3 ft/s². Express the maximum log weight as a mass: m_log = ______ kg.
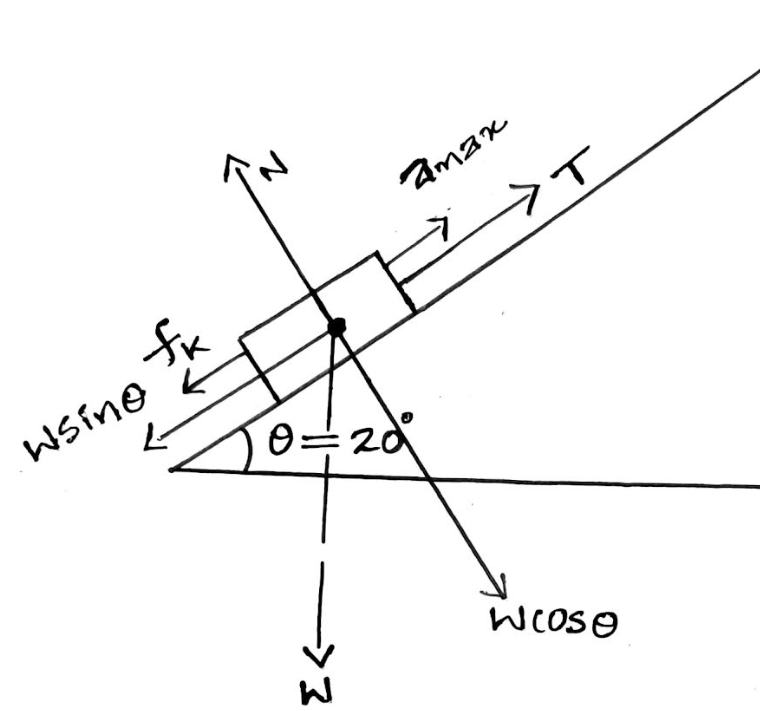
**STEP A:** Identify the forces on the Scenario, Freebody, and Force Diagrams below:
- **Scenario Diagram:** Displays a log on a hill inclined at 20° with a rope attached to a winch.
- **Freebody Diagram:** Shows a log with two vectors: one pointing up along the incline and another perpendicular to the incline.
- **Force Diagram:** Depicts a point with vectors indicating forces in both +x and +y directions.
These diagrams illustrate the forces acting on the log as it is pulled up the hill.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Part A What is the minimum work needed to push a 900-kg car 860 m up along a 9.5° incline? Ignore friction. Express your answer with the appropriate units. WP = µÅ Value Units ?arrow_forwardIn the figure the pulley has negligible mass, and both it and the inclined plane are frictionless. Block A has a mass of 1.3 kg, block B has a mass of 2.2 kg, and angle 0 is 32°. If the blocks are released from rest with the connecting cord taut, what is their total kinetic energy when block B has fallen 28 cm? Number Units Barrow_forwardA3arrow_forward
- 1. A roofer is dragging a 15.0 kg bundle of shingles up a roof at a constant speed. The roof is sloped at an angle of 30o with respect to the horizontal. a) Draw a free-body diagram of the forces involved b) What is the force component perpendicular to the roof of the weight of the bundles of shingles? show work. C ) What is the magnitude of the force of friction on the bundle of shringles as it is pulled up the roof if the coefficient of kinetic friction of the shingle bundle on the roof is 0.520? Show your work. d)Calculate the force parallel to the roof with which the roofers must pull on the rope to move the shringles at a constant speed up the roof.Answer to 3 significant digits. e) Suppose an astronaut was building a similar structure on Mars.What would be the force component perpindicular to the roof of the weight of a 15.0 kg bundle of materials on the surface of Mars? The mass of Mars is 6.42x1023kg and the radius of mars is 3.30x106 m. Answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA box slides down a plank of length d that makes an angle of θ with the horizontal as shown. μk is the kinetic coefficient of friction and μs is the static coefficient of friction. 1.Enter an expression for the minimum angle θ (in degrees) the box will begin to slide. 2.Enter an expression for the nonconservative work done by kinetic friction as the block slides down the plank. Assume the box starts from rest and θ is large enough that it will move down the plank. 3.For a plank of any length, at what angle θ (in degrees) will the final speed of the box at the bottom of the plank be 0.85 times the final speed of the box when there is no friction present? Assume μk = 0.39.arrow_forward1. A 7.50-kg box initially at rest slides down a 15.0 m long incline that makes an angle of 22.0° with the horizontal (see figure). At the bottom of the incline, the speed of the box is 3.00 m/s. a) Draw a free body diagram, detailing all of the forces acting on the box. b) Using the work done by non-conservative forces relationship, find the algebraic expression for the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the incline. c) Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction.arrow_forward
- A horizontal carousel is rotating around its axis with constant angular velocity w. On the carousel there is a straight track passing through its middle. A cart of mass m is traveling along the track with constant velocity v relative to the carousel. Note that there is friction between the cart and the carousel. FR XRarrow_forwardProblem 9: A roller coaster, shown in the figure, is pulled up to point A where it and its screaming occupants are released from rest. Assuming no friction, calculate the speed at points B, C, D. A m 22 m B C 32 m 16 marrow_forwardYou are using a modified block and tackle pulley system to lift a concrete block. You need to lift the concrete block (mass = 200 kg) a distance of 5 meters upward. The system is designed to reduce the force load of 4. How much rope must you pull down on the other side of the pulley to lift the block the proper distance? Hint: There is a very simple way to solve this if you remember that work in = work out.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios