
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
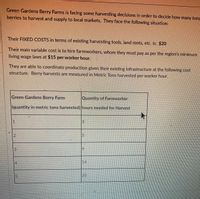
Transcribed Image Text:Green Gardens Berry Farms is facing some harvesting decisions in order to decide how many tons
berries to harvest and supply to local markets. They face the following situation:
Their FIXED COSTS in terms of existing harvesting tools, land rents, etc. is: $20
Their main variable cost is to hire farmworkers, whom they must pay as per the region's minimum
living wage laws at $15 per worker hour.
They are able to coordinate production given their existing infrastructure at the following cost
structure. Berry harvests are measured in Metric Tons harvested per worker hour.
Green Gardens Berry Farm
Quantity of Farmworker
(quantity in metric tons harvested)|hours needed for Harvest
13
2.
114
20

Transcribed Image Text:How many metric tons of berries would Green Berries Farm produce in order to Maximize Profits?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using Techniques Units of Variable Inputs Produce K 1 unit of output A 8 B 4 12 2 units of output A 14 12 B 20 3 units of output A 16 12 B 12 22 1) Assume that the relevant time period is the short run. Assuming the price of labor (L) is RM5 per unit and the price of capital (K) is RM10 per unit, the average variable cost of producing two units of output is, -(1M) Working calculation: 20 Assume the price of labor (4) is RM5 per unit, the price of capital (K) is RM10 per unit, and that firms attempt to minimize costs. The marginal cost of producing the third unit of output is - (1M) Working calculation:arrow_forwardIn this Assignment, you will define and calculate the remaining six major cost elements of a business, when given the Total Costs and the Quantity Produced, as well as to use the computed costs to determine a minimum cost output level for that business. In addition, you will compute both the break-even price and the shut-down price for a hypothetical business in a perfectly competitive market, and determine if that business would incur an economic profit at various market prices, and should the firm continue to produce at each of those price levels. Questions Table 2.a. shows an LED light bulb manufacturer’s total cost of producing LED light bulbs. Table 2.a. Cases of LED light bulbs produced in an hour Total Cost 0 $4,500 10 $4,900 20 $5,100 30 $5,300 40 $5,400 50 $5,700 60 $6,700 70 $7,900 80 $9,700 90 $11,800 1. What is this manufacturer’s fixed cost? Explain why. 2. Assuming that you only know…arrow_forwardIn this Assignment, you will define and calculate the remaining six major cost elements of a business, when given the Total Costs and the Quantity Produced, as well as to use the computed costs to determine a minimum cost output level for that business. In addition, you will compute both the break-even price and the shut-down price for a hypothetical business in a perfectly competitive market, and determine if that business would incur an economic profit at various market prices, and should the firm continue to produce at each of those price levels. Questions Table 2.a. shows an LED light bulb manufacturer’s total cost of producing LED light bulbs. Table 2.a. Cases of LED light bulbs produced in an hour Total Cost 0 $4,500 10 $4,900 20 $5,100 30 $5,300 40 $5,400 50 $5,700 60 $6,700 70 $7,900 80 $9,700 90 $11,800 1. What is this manufacturer’s fixed cost? Explain why. 2. Assuming that you only know…arrow_forward
- Three production processes - A, B, and C - have the following cost structure: the selling price is 5.26 per unit Process Fixed Cost per Year Variable Cost per Unit A 119164 2.54 B 80631 4.52 C 70617 5.27 1. What is the cost of process A for a volume of 7104 units? (round to the nearest cent).arrow_forwardAt an output of 3,000 units per year, a firm's total variable costs are $1,000 and its average fixed costs are $2. Its total costs per year are:arrow_forwardA firm faces the following costs: total cost of capital = $8,000; price paid for labor = $20 per labor unit; and price paid for raw materials = $6 per raw-material unit. Initially, the firm can produce 2,000 units of output by combining its fixed capital with 250 units of labor and 400 units of raw materials. After the firm improves its production process, it can produce 5,000 units of output by combining its fixed capital with 150 units of labor and 300 units of raw materials. How will the firm's total costs change as a result of the improved production process? Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. Total cost changes from $ ___ using the original process to $ ___ using the improved process. plz answer correct asap dont answer by pen pepararrow_forward
- c) The product function of a company is given by 1 v2 , where v is the number of units of fv) = the input factor. The company buys the input factor at a fixed price per unit given at 5 q =. Assume further that the company has fixed costs which in their entirety are sunk costs, and which is given by F= 100 . Show that the company's cost function is CO 20= y? +100 . d) Take as a starting point the information given in task (c), and assume that the company can sell finished goods in the market at a fixed price given by = 800 Formulate the company's profit function, and calculate which production volume maximizes corporate profits.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardParadise Pottery had the following costs in May when production is 800 ceramic pots: materials, $8,700; labor (variable), $2,900; depreciation, $1,100; rent, $900; and other fixed costs, $1,500. If production changes to 900 units, how much will the total variable costs and total fixed costs be, respectively?arrow_forward
- Tomas Ocampo has just been appointed chairperson of the Accountancy Department of ADEB College. In reviewing the department’s cost records, Tomas has found the following total cost associated with MAS Part 2 subject over the last several terms: Semester/Term Number of Subjects Offered Total Cost AY2004, First Semester 4 P10,000 AY2004, Second Semester 6 14,000 AY2004, Summer 2 7,000 AY2005, First Semester 5 13,000 AY2005, Second Semester 3 9,500 Tomas knows that there are some variable costs, such as amounts paid to student assistants, associated with the course. He would like to have variable and fixed cost components separated for planning purposes. Using the least-squares method, what is the variable cost per section of MAS?arrow_forward26) Which of the following is a fixed cost for a chocolate factory over the course of a month? A) Depreciation of machines due simply to their age B) Overtime pay C) The cost of cocoa D) The cost of electricity (paid quarterly) for running the mixing machinesarrow_forwardPlease select all that are true regarding Minimum Efficient Scale (MES): Quantities (x-axis) less than MES exhibit decreasing returns to scale due to diminishing marginal returns Average costs do not include fixed cost since they don't change MES is the quantity demanded where total costs for a firm are at a minimum MES is the quantity produced where average costs for a firm are at a minimum Long run average costs include fixed cost steps as quantities (scale) increase Quantities (x-axis) greater than MES exhibit decreasing returns to scale due to diminishing marginal returns Short run average cost curves are for a given level of fixed cost, individually If the quantity demanded is greater than MES, then the lowest cost solution is for one firm to supply the marketarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education