
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Graph on graph paper
- If you have a question or any information related to this experience, write it down
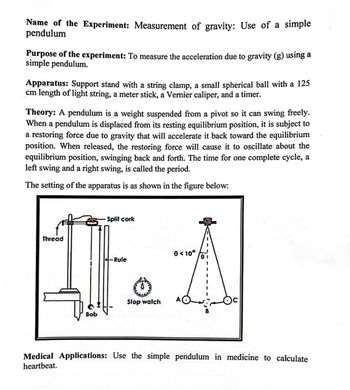
Transcribed Image Text:Name of the Experiment: Measurement of gravity: Use of a simple
pendulum
Purpose of the experiment: To measure the acceleration due to gravity (g) using a
simple pendulum.
Apparatus: Support stand with a string clamp, a small spherical ball with a 125
cm length of light string, a meter stick, a Vernier caliper, and a timer.
Theory: A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so it can swing freely.
When a pendulum is displaced from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to
a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium
position. When released, the restoring force will cause it to oscillate about the
equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a
left swing and a right swing, is called the period.
The setting of the apparatus is as shown in the figure below:
-Split cork
0 <10°
-Rule
IF.A
Stop watch
Thread
Bob
Medical Applications: Use the simple pendulum in medicine to calculate
heartbeat.
![T
30cm
Method:
1. Measure the length of the pendulum to the middle of the pendulum bob.
Record the length of the pendulum (L) in the table below.
2. With the help of a lab partner, set the pendulum in motion until it completes 10
oscillations, taking care to record this time. Then the period T for one oscillation is
just the number recorded divided by 10.
3. You will make a total of eight measurements for g using two different masses at
four different values for the length L. Note: - 3.14,4 m²= 39.44
Readings:
1- The period, T of a simple pendulum (measured in seconds) is given by the
formula:
T=2π √√L/g.......(1)
time for 10 oscillations
10 oscillations
T=
..(2)
Using equation (1) to solve for g, L is the length of the pendulum (measured in
meters) and g is the acceleration due to gravity (measured in meters/sec²). Now
with a bit of algebraic rearranging, we may solve Eq. (1)for the acceleration due to
gravity g. (You should derive this result on your own).
47² L
T²
47²
slope
1- Put your readings in the following table:
Readings:
L (cm) Time for 10 Time for 10 Period T (sec) T¹ (sec¹)
oscillation
oscillation/10
g=
g=
T' (sec)²
.......
2- Plot a graph of T2 on y- axis versus L on x- axis then find the slope.
6-23
T. I Год.
10 cm 6-28 6.19
20cm 8.19 8.6 8.4
30cm 10.8 10-6 10.7
40cm 12.5 123 124
(3)
..(4)
To
L (cm)
T
0.623 0.389
0.840 0.659
1.37 1.144
·1-24 1.537
0
16
1.5
1.1.
1-2-
1-2-
11-
]
14
0-9 -
6.F.
0.7-
0.6.
24
"24
10
Slope - ATAL
15x152
0.7
24 3. Yo
slap==—=—
g=
اد
-Lx/²
==_017
47²
slope 4.66
16x10²
+2
0
4X1-8
² = 8.42](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/94458cf2-014b-466a-bada-fa68de68f3b9/0213b7de-70be-4fcc-8b9d-c3b3b3b62bb8/zpgddv_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:T
30cm
Method:
1. Measure the length of the pendulum to the middle of the pendulum bob.
Record the length of the pendulum (L) in the table below.
2. With the help of a lab partner, set the pendulum in motion until it completes 10
oscillations, taking care to record this time. Then the period T for one oscillation is
just the number recorded divided by 10.
3. You will make a total of eight measurements for g using two different masses at
four different values for the length L. Note: - 3.14,4 m²= 39.44
Readings:
1- The period, T of a simple pendulum (measured in seconds) is given by the
formula:
T=2π √√L/g.......(1)
time for 10 oscillations
10 oscillations
T=
..(2)
Using equation (1) to solve for g, L is the length of the pendulum (measured in
meters) and g is the acceleration due to gravity (measured in meters/sec²). Now
with a bit of algebraic rearranging, we may solve Eq. (1)for the acceleration due to
gravity g. (You should derive this result on your own).
47² L
T²
47²
slope
1- Put your readings in the following table:
Readings:
L (cm) Time for 10 Time for 10 Period T (sec) T¹ (sec¹)
oscillation
oscillation/10
g=
g=
T' (sec)²
.......
2- Plot a graph of T2 on y- axis versus L on x- axis then find the slope.
6-23
T. I Год.
10 cm 6-28 6.19
20cm 8.19 8.6 8.4
30cm 10.8 10-6 10.7
40cm 12.5 123 124
(3)
..(4)
To
L (cm)
T
0.623 0.389
0.840 0.659
1.37 1.144
·1-24 1.537
0
16
1.5
1.1.
1-2-
1-2-
11-
]
14
0-9 -
6.F.
0.7-
0.6.
24
"24
10
Slope - ATAL
15x152
0.7
24 3. Yo
slap==—=—
g=
اد
-Lx/²
==_017
47²
slope 4.66
16x10²
+2
0
4X1-8
² = 8.42
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How does density differ from mass? Mass decreases as density increases. Density is the mass of an object. Density is a per-volume metric of mass. Mass is a per-volume metric of density.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements accurately defines density? Density is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Density is the amount of matter in an object. Density is the mass of an object per unit volume. Density is the volume of an object divided by its weight.arrow_forward2. Classify the following statements as either True or False : c) Races of different students in a class is quantitative data. True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON