
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781305087408
Author: Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
hello I need help please
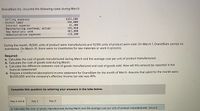
Transcribed Image Text:GrandSlam Inc. incurred the following costs during March:
Selling expenses
Direct labor
Interest expense
Manufacturing overhead, actual
Raw materials used
Administrative expenses
$161,600
284,000
42,300
155,850
463,000
116,300
During the month, 19,500 units of product were manufactured, and 10,100 units of product were sold. On March 1, GrandSlam carried no
inventories. On March 31, there were no inventories for raw materials or work in process.
Required:
a. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during March and the average cost per unit of product manufactured.
b. Calculate the cost of goods sold during March.
c. Calculate the difference between cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold. How will this amount be reported in the
financial statements?
d. Prepare a traditional (absorption) income statement for GrandSlam for the month of March. Assume that sales for the month were
$1,035,000 and the company's effective income tax rate was 40%.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A and B
Req C
Req D
a. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during March and the average cost per unit of product manufactured. (Round
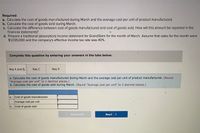
Transcribed Image Text:Required:
a. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during March and the average cost per unit of product manufactured.
b. Calculate the cost of goods sold during March.
c. Calculate the difference between cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold. How will this amount be reported in the
financial statements?
d. Prepare a traditional (absorption) income statement for GrandSlam for the month of March. Assume that sales for the month were
$1,035,000 and the company's effective income tax rate was 40%.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A and B
Req C
Req D
a. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during March and the average cost per unit of product manufactured. (Round
"Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places.)
b. Calculate the cost of goods sold during March. (Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places.)
a.
Cost of goods manufactured
Average cost per unit
b.Cost of goods sold
KReq A and B
Req C >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- During the month, a company with no departmentalization incurred costs of 45,000 for materials, 36,000 for labor, and 22,500 for factory overhead. There were no units in process at the beginning or at the end of the month, and 20,000 units were completed. Determine the unit cost for the month for materials, labor, factory overhead, and the total unit cost. (Round unit costs to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardEllerson Company provided the following information for the last calendar year: During the year, direct materials purchases amounted to 278,000, direct labor cost was 189,000, and overhead cost was 523,000. During the year, 100,000 units were completed. Refer to Exercise 2.21. Last calendar year, Ellerson recognized revenue of 1,312,000 and had selling and administrative expenses of 204,600. Required: 1. What is the cost of goods sold for last year? 2. Prepare an income statement for Ellerson for last year.arrow_forwardOReilly Manufacturing Co.s cost of goods sold for the month ended July 31 was 345,000. The ending work in process inventory was 90% of the beginning work in process inventory. Factory overhead was 50% of the direct labor cost. No indirect materials were used during the period. Other information pertaining to OReillys inventories and production for July is as follows: Required: 1. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month of July. (Hint: Set up a statement of cost of goods manufactured, putting the given information in the appropriate spaces and solving for the unknown information. Start by using cost of goods sold to solve for the cost of goods manufactured.) 2. Prepare a schedule to compute the prime cost incurred during July. 3. Prepare a schedule to compute the conversion cost charged to Work in Process during July.arrow_forward
- Queen Bees Honey, Inc., estimated its annual overhead to be $110,000 and based its predetermined overhead rate on 27,500 direct labor hours. At the end of the year, actual overhead was $106,000 and the total direct labor hours were 29,000. What is the entry to dispose of the over applied or under applied overhead?arrow_forwardEllerson Company provided the following information for the last calendar year: During the year, direct materials purchases amounted to 278,000, direct labor cost was 189,000, and overhead cost was 523,000. During the year, 100,000 units were completed. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost of direct materials used in production. 2. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured. Calculate the unit manufacturing cost. 3. Of the unit manufacturing cost calculated in Requirement 2, 2.70 is direct materials and 5.30 is overhead. What is the prime cost per unit? Conversion cost per unit?arrow_forwardDuring the year, a company purchased raw materials of $77,321, and incurred direct labor costs of $125,900. Overhead is applied at the rate of 75% of the direct labor cost. These are the inventory balances: Compute the cost of materials used in production, the cost of goods manufactured, and the cost of goods sold.arrow_forward
- helloarrow_forwardHello, Grandslam Inc incurred the following costs during March. Selling Expenses $156,100 Direct Labor 308,000 Interest Expense 41,800 Manufacturing Overhead, actual 45,930 Raw materials used 466,000 Admin Expenses 116,400 During the month, 18,100 units were manufactured and 10,600 units of products were sold. On March 1, Grandslam Inc. carried no inventories. On March 31, there were no inventories for raw materials or work in progress. Question 7d: Prepare a traditional (absorption) income statement for Grandslam Inc. for the month of June. Assume that sales for the month were $1,038,000 and the company's effective income tax rate was 30%. (Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places. Sales $1,038,000 Cost of Goods sold ? Gross Profit ? ? Operating Income ? ? Income Before taxes ? Income Tax Expense ? Net Income ? Thanks.arrow_forwardGrandSlam Incorporated incurred the following costs during March: Selling expenses Direct labor $ 158,200 291,000 Interest expense 42,900 117,960 462,000 121,300 Manufacturing overhead, actual Raw materials used Administrative expenses During the month, 19,100 units of product were manufactured and 10,700 units of product were sold. On March 1, GrandSlam carried no inventories. On March 31, there were no inventories for raw materials or work in process. Required: a. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during March and the average cost per unit of product manufactured. b. Calculate the cost of goods sold during March. c. Calculate the difference between cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold. How will this amount be reported in the financial statements? d. Prepare a traditional (absorption) income statement for GrandSlam for the month of March. Assume that sales for the month was $1,035,000 and the company's effective income tax rate was 30%. Complete this question by…arrow_forward
- help pleasearrow_forwardhello help pleasearrow_forwardHello, Buck and Company incurred the following costs during August: Raw materials purchased $41,400 Direct labor ($13.6 per hour) 60,384 Manufacturing overhead (actual) 90,420 Selling expenses 31,890 Administrative expenses 14,070 Interest expense 6,112 Manufacturing overhead is applied on the basis of $20 per direct labor hour. Assume that overapplied or underapplied overhead is transferred to the cost of goods sold only at the end of the year. During the month, 4120 units of product were manufactured and 4,400 units of product were sold. On August 1 and August 31, Buck and Company carried the following inventory balances. August 1 August 31 Raw materials $19,000 $17,800 Work in progress 53,000 56,000 Finished goods 40,100 27,267 Question a-1: Prepare a statement of costs of goods manufactured for the month of August. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign). Buck and Company Statement of Goods manufactured for the month of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,