
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
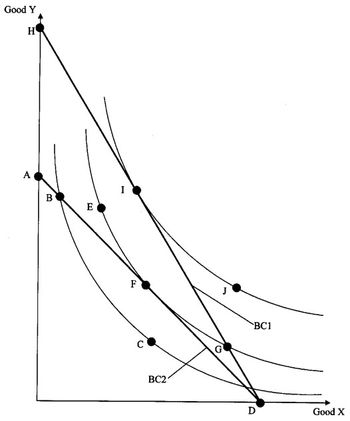
If BC2 is the relevant budget constraint, then this consumer is indifferent between bundles
Transcribed Image Text:Good Y
H
A
B
E
F
с
BC2
G
BC1
D
Good X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Answers are A and B, D and E, E and F, F and H, or H and I
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Answers are A and B, D and E, E and F, F and H, or H and I
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- = x 2 y. This Consider a consumer with the utility function U (x, y) = Vxy 글3글2-iy and MU, Vx = x? They have 1 function gives MU Va a budget of $60, and pr 1 and Py 2. Find optimal consumption of x and y.arrow_forwardEXERCISE 5 Loise spends £20 on tea (T) and coffee (C). Her preferences for these goods can be described by the following utility function: ( , ). Suppose that one cup of tea costs £1.60 while one cup of Loise’s favourite coffee costs £4.00. Find Loise’s optimal consumption bundle. Provide both algebraic and graphical solution. Explain your reasoning. Discuss how Loise’s optimal consumption choice would change when her disposable budget changes. If the price of tea increases to £2.00 per cup, how should the price of coffee change so that Loise can be as well off as before this change in prices? Discuss the implications of the price change from c) on Loise’s optimal choice. In your discussion, include the analysis of the substitution and income effects as well as Loise’s demand for tea and/or coffee.arrow_forwardAnthony seeks to maximize the following utility function u(x, y) = x'/3y2/3 subject to the budget constraint Pæa + PyY = I 1 where pr, Py, x, y, I > 0. a) Find Anthony's utility-maximizing bundle (x*, y*) as a function of pæ, Py, and I. b) Show that y* is decreasing in py and increasing in I (hint: use partial derivatives). c) What share of Anthony's income is spent on x? What share is spent on y? In other words, calculate Pa and Pu. Are these shares a function of prices? Pyy* Note: The above utility function is Cobb-Douglas, and all Cobb-Douglas functions have these share formulas for any values for the exponents. d) What is the impact of a change in pr on Anthony's utility?arrow_forward
- In the graph below, you initially maximize utility at point A relative to the B1 budget constraint. Your income changes, which puts you on a new budget constraint (B2). x2 14 13 12 10 w 10 11 12 13 14 15 If good 1 is normal and good 2 is inferior, then point 1st attempt Y Y W Z is the new optimal bundle of consumption.arrow_forwardSuppose you are given the following information for a particular individualconsuming two goods, a and b: Pa = $5, Pb = $6, MUa = 100, MUb = 200, and income (m) = $200.a) Sketch the budget set. What is the slope of the Budget Line? What are maximal possibleconsumptions of a and b?b) What is the MRSab for the two goods?c) Is this person maximizing her utility? How can you tell?d) Should she consume more of good a or of b? Explain.e) Why can’t you tell what her optimal bundle is? Explain.arrow_forwardAssume that you have a budget of Taka 4000 that can spend on two goods like: coke and burger. Suppose coke costs Taka 100 per unit and burger costs 400 per unit. Suppose also that your utility function is given by the equation U(B, C) = 20BC. Write your budget equation. What combination of coke and burger should you buy to maximize utility?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education