
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please do not give solution in image format thanku
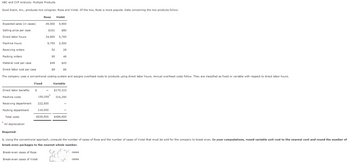
Transcribed Image Text:ABC and CVP Analysis: Multiple Products
Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow:
Expected sales (in cases)
Selling price per case
Direct labor hours
Machine hours
Receiving orders
Packing orders
Material cost per case
$49
Direct labor cost per case
$8
The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours.
Direct labor benefits
Machine costs
Receiving department
Packing department
*
Total costs
All depreciation
Fixed
$
Rose Violet
190,000*
222,500
116,000
$528,500
Break-even cases of Rose
49,500 9,900
$101
$80
34,850 5,700
9,750 2,500
Break-even cases of Violet
52
95
28
46
$43
$6
Variable
$170,310
316,290
Required:
1. Using the conventional approach, compute the number of cases of Rose and the number of cases of Violet that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round variable unit cost to the nearest cent and round the number of
break-even packages to the nearest whole number.
G F
$486,600
cases
cases

Transcribed Image Text:2. Using an activity-based approach, compute the number of cases of each product that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round all computed amounts to the nearest cent and round the number of break-even packages
to the nearest whole number.
Break-even cases of Rose
Break-even cases of Violet
X cases
X cases
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Introduction to CVP Analysis
VIEW Step 2: Statement showing calculation of overhead cost per unit under conventional approach
VIEW Step 3: Calculation of break-even point under conventional approach
VIEW Step 4: Statement showing calculation of overhead cost per unit under activity-based approach
VIEW Step 5: Calculation of break-even point under activity-based approach
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please see imagesarrow_forwardCan you please enter the information clearly without so many spaces? The information is hard to read.arrow_forwardSelect the letter of the item below that best matches the definitions that follow. a. Data Files CD ________ b. Lists ________ c. Forms ________ d. Registers ________ e. Reports and graphs ________ f. Restoring a backup ________ g. Icon bar ________ h. Home page ________ i. Backing up a file ________ 1. One click access to QuickBooks Accountant Centers and Home page. 2. The process of rebuilding a backup file to a full QuickBooks Accountant file ready for additional input. 3. Electronic representations of paper documents used to record business activities such as customer invoices, vendor bills, and checks. 4. A big-picture approach of how your essential business tasks fit together organized by logical groups such as customers, vendors, and employees. 5. Groups of names such as customers, vendors, employees, items, and accounts. 6. Contains backups of all the practice files needed for chapter work and completion of assignments. 7. The process of creating a copy of a…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education