
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Given the x vs t graph for an object as shown, which of the choices best describes the velocity versus time for this object?
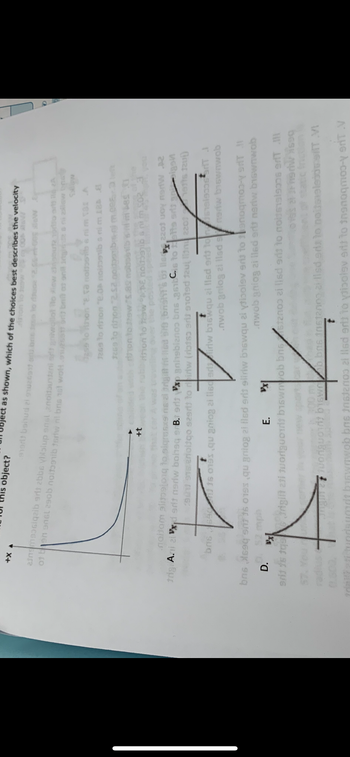
Transcribed Image Text:+X
object?
as shown, which of the choices best describes the velocity
ition to tow
91orit bahud 21 91026911 an
u2 19ro ar izA
aingmoodiqaib grit abbs vbislupanst znoitandani ogniwollo To Kiew 230
of ben snGL 290b noitegnib tortw ni bris 1st wolt.9125311 orit brit as snil ingentes ni alew
+t
Sallow
8
se to rinon eta noteba ni m 18 A
1269 to non "e.O moiserib s nim 18A
Jess to rition "2.52 notoribisni me
berib
mhon to 129
non to 19w
tit
2201 uoy nemW 2
noitam slitejong to sigranxs rs al trigint in lica SH0 (onsht
trig. Ani zid erit norw boisq sr B. srls xp anhsblanco bns 361bCs to fette sits an
und severoitgo sz9rl) to ririw (ratsa eri stoted 12u lim 2201 hefts 1zu1)
485 0
02 3
bris seni is 019s ,qu aniog ai liscerla irlw bis qu zi lisd eri tosalecos T J
.nwob gniog zi llad s neriw brownwob
VX|
A K
bns Aseg snit is 019s ,qu griog ei fled grit sliriw biswqu i ytibolev gris to sanoqmos-y HT 11
.nwob gniog zi lled ortt neriw biswnwob
D.
E.
snit is jqs
tuonguoidi biswreb brs instanco
t
rigilt zti tuorlguoit biswmvob bno stanoo zi lled srit to noid6199006 9T III
Lovas 21 JF herwiseq
da to noitaveledde ellT VI
wowok bas jostenos zi llad er to yaisolev ent to inanogmos-y rT.V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A graph of position versus time for a certain particle moving along the x-axis is shown in the figure below. Find the instantaneous velocity at the instant t = 1s 2 m/s 3 m/s 4 m/s 5 m/sarrow_forwardYou qualitatively analyzed the motion of a van earlier. Now, using the example of the ball thrown into the air, you can do a more detailed analysis of the van's motion. The table shown here includes the time and position data, with one worked example for finding acceleration. Time Position Velocity Ad Acceleration t(s) (m/s) Ar (m/s") 0.0 0.0 6.0 2.0 12 +3.0 12 4.0 36 Sample Calculation Notice that the velocity that will be plotted at t = 1.0 s is the average velocity between t = 0.0 s and t 2.0 s. The velocity that will be plotted at t 3.0 s is the average velocity between t = 2.0 s and 4.0 s. The acceleration that will be plotted at t= 2.0 s is the average acceleration between t = 1.0 s and t = 3.0s. 6.0 48 8.0 96 10.0 142 12.0 190 14.0 226 16.0 250 Adgd-d 12 m-0.0 m 2.0 s-0.0 s V = 18.0 262 Alo2 t2-lo 12 m 2.0 s %3D Analyze and Conclude 1. How well do the average and instantaneous velocities that you calculated agree with = 6.0 m each other? 36 m-12 m V= Afz4 %3D %3D 2 Separate the…arrow_forwardIf we apply the above equations to the case of an object that does not change its direction of travel as it moves with constant acceleration, we find that the object: Undergoes a displacement Ax = x- x, . Note that displacement is a positive quantity if x > x, and a negative quantity if x < x,. Has average velocity v = (x - x )/t = (v + vo)/2. Note that velocity has the same sign as displacement. Travels distance d = |Ax| = |x – x,| . Note that distance is always a positive quantity. Has average speed d/t . Note that speed is always a positive quantity. Has constant acceleration a = (v – vo)/t . Acceleration may be positive or negative, depending on how velocity changes. - Xo For the case of an object that does change its direction of travel as it moves with constant acceleration, which of the quantities listed above are different? Questionarrow_forward
- Your roommate drops a tennis ball from a third-story balcony. It hits the sidewalk and bounces as high as the second story. Draw a motion diagram, using the particle model, showing the ball’s velocity vectors from the time it is released until it reaches the maximum height on its bounce.arrow_forwardThe following graph depicts the velocity of someone playing tag over a short period of time. Use this velocity graph to answer the following questions. The person's maximum magnitude for velocity is 4.5 m/s in both the positive and negative directions. A is at time point 3 seconds, B is at time point 4.5 seconds, C is at time point 5.5 seconds, D is at time point 7 seconds, E is at 8 seconds, F is at 9 seconds and G is at 10 seconds. What is the acceleration in meters/second2 (m/s2) at the 2 second mark of playing tag? What is the acceleration in meters/second2 (m/s2) at the 5 second mark? What is the velocity in meters/second (m/s) at the 5 second mark? What is the acceleration in meters/second2 (m/s2) at the 6.5 second mark? What is the acceleration in meters/second2 (m/s2) at the 8.5 second mark? What is the velocity in meters/second (m/s) at the 9.5 second mark?arrow_forwardIf a particle increases in speed at a constant rate as it moves in the positive direction along an x axis, which of the following describes a plot of its velocity versus time? O plot has constant positive slope plot has constant negative slope O plot has zero slopearrow_forward
- The graph depicts an particle's velocity (in the x-direction) vs. time. At which points is the object's acceleration negative? (Check all that apply.) Group of answer choices C B D A Earrow_forwardThe graph below plots the position versus time for a particular body moving along the x-axis. What is the average velocity over the following time intervals (in m/s)? (Indicate the direction with the signs of your answers.) A coordinate plane has a horizontal axis labeled t (s) and a vertical axis labeled x (m). There are five connected line segments. The first goes from (0, 0) to (2.00, 14.0); the second from (2.00, 14.0) to (4.00, 6.00); the third from (4.00, 6.00) to (5.00, 6.00); the fourth from (5.00, 6.00) to (7.00, −8.00); and the fifth from (7.00, −8.00) to (8.00, 0).arrow_forwardA position function is given by F(t)= (10m+20t)i-5t²j. What is the velocity of the object it describes at t=2.0s? Using the same position function as the previous problem, what is the acceleration function? Using the same position function again, make an accurate plot of the object's trajectory over the first two seconds of flight. What's the lowest speed of the object in the prior problem in that time interval? Iarrow_forward
- The diagram represents the acceleration versus time graph of an object. Which statement is true about the motion of the object? (m-s-2) a t (s) The object is moving with constant non-zero acceleration. The object is moving a constant velocity. The object is at rest. None of the choices provided.arrow_forwardQ1: A dolphin in an aquatic show jumps straight up out of the water at a velocity of 13.0 m/s. (a) List the knowns in this problem. (b) How high does his body rise above the water? To solve this part, first note that the final velocity is now a known and identify its value. Then identify the unknown, and discuss how you chose the appropriate equation to solve for it. After choosing the equation, show your steps in solving for the unknown, checking units, and discuss whether the answer is reasonable. (c) How long is the dolphin in the air? Neglect any effects due to his size or orientation.arrow_forwardThe height above the ground of a drone is given by h = 3.50 t³, where h is in meters and t is in seconds. Calculate at t = 2.50 s (a) the height of the drone above the ground and (b) the velocity of the drone. At this time (t = 2.50 s) the drone releases a package (c) how long does it take the package to reach the ground? Include a complete diagram of the situation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON