
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Given the population mean hypothesis H0: μ = 150 and H1: μ ≠ 150
identify the the type of test distribution.
(A) Right-tail test (B) Two-tail test
(C) Left-tail test (D) None of these
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given,
The population mean hypothesis is,
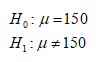
The objective is identify the the type of test distribution.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose we want to test that the average age of a The following table shows the Excel output for this test. Pstudent is not 27 years old. t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means Score Dummy Mean 25.89474 Variance 5.43275 Observations Pearson Correlation Hypothesized Mean Difference 19 19 #DIV/O! 27 df 18 t Stat P(T<=t) one-tail t Critical one-tail P(T<=t) two-tail t Critical two-tail -2.06696 0.02671 1.7341 0.05343 2.1009 Select the p-value for this test. 2.1009 O 0.05343 0.02671arrow_forwardTest the research hypothesis that there is a difference in weights between the two groups at the 0.05 significance level? Assume the equality of variance, adequate sample size, and normal distribution for both the groups to test the hypothesis. X1 = 200 X2 = 198 n1 = 17 n2 = 17 s1 = 2.45 s2 = 2.35 Please show all the necessary steps of hypothesis testing to answer this question.arrow_forwardUsing the two histograms and the bootstrap dotplot based on whether there is a difference between age and marital status (married/not married). What does this data tell us in terms of whether there is a difference between age and marital status or not? Does our interval include or exclude 0? What should we do with the null hypothesis?arrow_forward
- A random sample of n1 = 49 measurements from a population with population standard deviation ?1 = 3 had a sample mean of x1 = 10. An independent random sample of n2 = 64 measurements from a second population with population standard deviation ?2 = 4 had a sample mean of x2 = 12. Test the claim that the population means are different. Use level of significance 0.01. (a) Check Requirements: What distribution does the sample test statistic follow? Explain. The Student's t. We assume that both population distributions are approximately normal with known standard deviations.The standard normal. We assume that both population distributions are approximately normal with known standard deviations. The Student's t. We assume that both population distributions are approximately normal with unknown standard deviations.The standard normal. We assume that both population distributions are approximately normal with unknown standard deviations. (b) State the hypotheses. H0: ?1 = ?2;…arrow_forward13-arrow_forwardEarrow_forward
- III MAT 2100 Final Exam STUDY GUIDE Question 37 of 40 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of 1 Time Remaining: 20:45 Takaila Español <= 26 = 27 = 28 = 29 = 30 = 31 32 = 33 = 34 = 35 36 37 Suppose there is a claim that a certain population has a mean, μ, that is different than 7. You want to test this claim. To do so, you collect a large random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test at the 0.10 level of significance. To start this test, you write the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H₁, as follows. Ho: μ=7 H₁ = 7 Suppose you also know the following information. The value of the test statistic based on the sample is 1.799 (rounded to 3 decimal places). The p-value is 0.072 (rounded to 3 decimal places). (a) Complete the steps below for this hypothesis test. Continue Standard Normal Distribution Step 1: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. O One-tailed ○ Two-tailed Step 2: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 04 0.3+ Step 4: Enter the…arrow_forward3/12arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman