
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
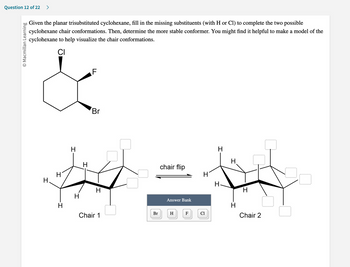
Transcribed Image Text:**Cyclohexane Chair Conformations: Understanding Stability and Substituents**
To enhance your knowledge of cyclohexane chair conformations, let’s explore a given planar trisubstituted cyclohexane and work through completing the two possible chair conformations. Following this, we will determine the more stable conformer. It is recommended to utilize a model of cyclohexane for a better grasp of the chair conformations.
### Exercise Overview:
The given molecule is a trisubstituted cyclohexane with Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), and Fluorine (F) substituents.
#### Objective:
1. Complete the missing substituents (with H or Cl).
2. Determine the more stable conformer.
### Molecular Structure:
**Planar Cyclohexane Structure:**
- The cyclohexane ring is depicted with three substituents:
- Cl (Chlorine)
- F (Fluorine)
- Br (Bromine)
**Chair Conformations:**
Visualize two chair conformations labeled Chair 1 and Chair 2.
**Chair 1 and Chair 2:**
- **Chair 1 Diagram:**
The first chair conformation shows the cyclohexane ring in a 3D chair form with several hydrogen (H) atoms marked. There are also several positions where substituents are missing.
- **Chair 2 Diagram:**
A mirrored chair form of Chair 1 is depicted, indicating a 'chair flip.' Similar to Chair 1, this structure has several hydrogen atoms with a few positions requiring substitutions.
**Answer Bank:**
An answer bank containing four substituents is provided:
- Br (Bromine)
- H (Hydrogen)
- F (Fluorine)
- Cl (Chlorine)
### Completing the Chair Conformations:
1. **Identify Substituents’ Axial and Equatorial Positions:**
- On the cyclohexane chair forms, substituents can occupy either axial (vertical) or equatorial (horizontal) positions.
- Determine where each substituent (Cl, Br, F) and hydrogen atoms (H) should be placed in both Chair 1 and Chair 2 conformations.
2. **Chair Flip Concept:**
- The chair flip involves an inversion of axial and equatorial positions.
- Substituents on axial positions in Chair 1 will
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given cyclohexane in a chair conformation, construct the more stable conformation of 1-methyl-1-(2-methylpropyl)cyclohexane. by filling in the missing atoms or groups. Use the numbering provided on the ring. H. Answer Bank H. 2-methylpropyl Н 5 H 1 H- methyl H. 3 14 H H. COarrow_forwardHelp pleasearrow_forwardplzz answer this in detail, draw all possible chair conformation and mark the most stable one , please do with clean handwrittingarrow_forward
- draw most stable and least stable conformations for eacharrow_forwardStarting from the structure below (sighting down the indicated bond). rotate the back carbon to provide an eclipsed conformer of the structure. Ph H H HI!!! ++||||4 CH₂CH3 I I I I I I H Draw Newman Projection I I Iarrow_forwardDo not give handwriting solution.arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwarda) Draw two chair conformations and label the most stable conformation. For consistency between assignments, use the diagrams given. You may redraw but keep the orientation the same; otherwise, it becomes difficult for students to mark! I have added the Br to carbon 1 for the first chair conformation as a start. b) What is the dihedral angle between the chlorine atom and the methyl group in the most stable chair conformation. total for for correct drawing correct drawing for Br correct angle Br dihedral 1 angle = CI" 4 CH3 H *** : for identifying most stablearrow_forwardIn kcal/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY