
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
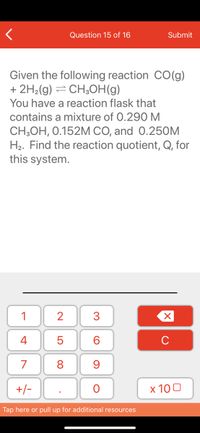
Transcribed Image Text:Question 15 of 16
Submit
Given the following reaction CO(g)
+ 2H2(g) = CH3OH(g)
You have a reaction flask that
contains a mixture of 0.290 M
CH;OH, 0.152M CO, and 0.25OM
H2. Find the reaction quotient, Q, for
this system.
1
3
4
6.
7
8
+/-
x 10 0
Tap here or pull up for additional resources
N LO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2 NO(g) + Cl_(4)(g) ⇔ 2 NOcl (g)Into a 50L vessel 0,600 mol NO, 0,200 mol Cl2 and 0,500 mol NOCL are added. At equilibrium there is 0,600 mol NOCl. At 1100K what is the equilibrium constant?arrow_forwardGiven the following reaction CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇒ CH₂OH(g) You have a reaction flask that contains a mixture of 0.170 M CH₂OH, 0.152 M CO, and 0.250 M H₂. Find the reaction quotient, Q, for this system. + 1 4 7 +/- 3 5 6 8 9 0 2 X C ×100arrow_forwardConsider an initial pressure of I2(g) of 0.100 atm in a 500 mL flask at 1000 K. With an equilibrium constant for dissociation of KP = 3.76 x 10 -3 calculate the total pressure of the system at equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Given the following reaction CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g) You have a reaction flask that contains a mixture of 0.240 M CH₃OH, 0.152M CO, and 0.250M H₂. Find the reaction quotient, Q, for this system.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 3H2(g)+N2(g)⇌2NH3(g) at 225 ∘C the equilibrium contant is 1.7×10 ^2. If the equilibrium mixture contains 0.19 M H2 and 0.015 M N2, what is the molar concentration of NH3? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardAt 100 °C, Keg = 1.5E8 for the reaction: CO(g) + Cl2(g) - COCI2(g) Using appropriate approximation, calculate the partial pressure of CO at 100 °C at equilibrium in a chamber that initially contains COCI2 at a pressure of 0.302 bar.arrow_forward
- The initial concentrations or pressures of reactants and products are given for each of the following systems. Calculate the reaction quotient and determine the direction in which each system will proceed to reach equilibrium. (The system is considered in equilibrium if Kc and Qc are within 5% of each other.) (a) 2 NH3(g) equalibrium arrow N2(g) + 3 H2(g), [NH3]i = 0.400 M, [N2]i = 0.155 M, [H2]i = 0.110 M, Kc = 16 What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? (b) 2 NH3(g) equalibrium arrow N2(g) + 3 H2(g), Pi(NH3) = 2.10 atm, Pi(N2) = 10.70 atm, Pi(H2) = 10.70 atm, Kp = 8.3 ✕ 104 What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? (c) 2 SO3(g) equalibrium arrow 2 SO2(g) + O2(g), [SO3]i = 1.90 M, [SO2]i = 1.90 M, [O2]i = 1.90 M, Kc = 0.23 What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? (d) 2 SO3(g) equalibrium arrow 2 SO2(g) + O2(g), Pi(SO3) = 0.100 atm, Pi(SO2) =…arrow_forwardPart B Consider the reaction between bromine and chlorine gases to form bromochloride: Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g) = 2BRC1(g), K. 1.11 x 10-4 at 150 K A reaction vessel contains 0.20M Br2, 0.35 M Cl2, and 3.0 x 10-3 M BrCl. Calculate the reaction quotient, Q, and determine in which direction the reaction proceeds to reach equilibrium. > View Available Hint(s) O 4.3 x 10 2, the reaction system proceeds to the left O 1.3 x 10 4, the reaction system proceeds to the left O 1.1 x 104, the reaction system is at equilibrium O 1.3 x 104, the reaction system proceeds to the right Submit Part C Complete previous part(s) Next > Provide Feedback MacBook Airarrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 1.29x10-2 at 600 K. coCI,(g) ? CO(g) + Cl2(g) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.373 moles of COCI2(g) are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 600 K. [COCI2] = [CO] M [Cl2] M ΣΣΣarrow_forward
- Consider the hypothetical reaction A(g) 2B(g). A flask is charged with 0.74 atm of pure A. after which it is allowed to reach equilibrium at 0 °C. At equilibrium the partial pressure of A is 0.37 atm Part A What is the total pressure in the flask at equilibrium? Express your answer using two significant figures. VS ΑΣΦ 4 P₁ = Submit Part B What is the value of Kp? Express your answer using two significant figures. K₂= Submit Part C Request Answer |VL ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer What could we do to maximize the yield of B? → Request Answer [w] ? O Doing the reaction in a larger flask maximizes the yield of B. O Doing the reaction in a smaller flask maximizes the yield of B. atmarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature , the given reaction has an equilibrium constant of K_{p} = 363; PCl 3 (g)+Cl 2 (g) rightleftharpoons PCl 5 (g); PC*l_{5} is placed in a sealed container at an initial pressure of 0.0640 bar. What is the total pressure at equilibrium ? Use the quadratic formula in solving steps.arrow_forwardPar B Consider the reaction between bromine and chlorine gases to form bromochloride: Br2(g) + Cl₂ (g) = 2BrCl(g), Kc = 1.11 x 10-4 at 150 K A reaction vessel contains 0.20 M Br2, 0.35 M Cl₂, and 3.0 x 10-3 M BrCl. Calculate the reaction quotient, Q, and determine in which direction the reaction proceeds to reach equilibrium. View Available Hint(s) O 4.3 x 10-2, the reaction system proceeds to the left O 1.1 x 104, the reaction system is at equilibrium O 1.3 x 10-4, the reaction system proceeds to the left O 1.3 x 104, the reaction system proceeds to the right Submit Review I Constants | Periodic Table P Pearsonarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY