
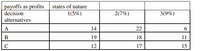
Given the following payoff table with the profits ($m), a firm might expect alternative investments (A, B, C) under different levels of interest rate. (Attached)
(a) Which alternative should the firm choose under the maximax criterion?
(b) Which option should the firm choose under the maximin criterion?
(c) Which option should the firm choose under the LaPlace criterion?
(d) Which option should the firm choose with the Hurwicz criterion with α = 0.2?
(e) Using a minimax regret approach, what alternative should the firm choose?
(f) Economists have assigned probabilities of 0.35, 0.3, and 0.35 to the possible interest levels 1, 2, and 3 respectively. Using expected monetary values, what option should be chosen and what is that optimal expected value?
(g) What is the most that the firm should be willing to pay for additional information? Use Expected Regret
(h) Use the alternative method to verify EVPI
Part 2
Assume now that the pay offs are costs answer the following:
(a) Using an optimistic approach (maximax), which option would you choose?
(b) Using a pessimistic approach (maximin), which option would you choose?
(c) If you are a LaPlace decision maker, which option would you choose?
(d) If you are a Hurwicz decision maker, which option would you choose with α = 0.2?
(e) Using a minimax regret approach, which option would you choose?
(f) Using the same probabilities of 0.35, 0.3, and 0.35 for possible interest levels 1, 2, 3 respectively, which decision alternative will minimise the expected cost? What is the expected annual cost associated with that recommendation?
g) What is the most the firm should be willing to pay to obtain further (perfect) information (EVPI)?
h) Use the alternative method to verify EVPI
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- You are considering three investment alternatives for some spare cash: Old Reliable Corporation stock (A1), Fly-By-Nite Air Cargo Company stock (A2), and a federally insured savings certificate (A3). You expect the economy will either "boom" (N1) or “bust” (N2), and you estimate that a boom is more likely (p1 = 0.6) than a bust (p2 = 0.4). Outcomes for the three alternatives are expected to be (1) $2000 in boom or $500 in bust for ORC; (2) $6000 in boom but $-5000 (loss) in bust for FBN: and (3) $1200 for the certificate in either case. Set up a payoff table (decision matrix) for this problem and show which of it Alternative maximizes expected value.arrow_forwardplease answer d and earrow_forward1. If today stock is trading for $60 a share. You are confident that the stock price will experience a change in the value of over 30% relative to the current price in either upward or downward direction over the course of next year. Today you decide to transact in either one or two stocks maturing in one year. The strike price of both options is $60 a share. The call option premium is $6 and put option premium is $5. Given this information and your belief, you should _______. a. buy 2 calls b. buy 1 call and sell 1 put c. sell 1 call and 1 sell put d. buy 1 call and buy 1 put e. sell 2 puts Please explainarrow_forward
- You are attempting to establish the utility that your boss assigns to a payoff of $1,200. You have established that the utility for a payoff of $0 is zero and the utility for a payoff of $10,000 is one. Your boss has just told you that they would be indifferent between a payoff of $1,200 and a lottery which has a payoff of $10,000 where the probability of losing is 0.9. What is your boss' utility for $1,200? (Round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Utility of $1,200arrow_forwardConsider the following information for the Alachua Retirement Fund, with a total investment of $4 million. [5] Stock Investment Beta A $ 400,000 1.2 B 600,000 -0.4 C 1,000,000 1.5 D 2,000,000 0.8 The market required rate of return is 12 percent, and the risk-free rate is 6 percent. What is its required rate of return? Stock A has the following probability distribution of expected returns: [5] Probability Rate of Return 0.1 -15% 0.2 0 0.4 5 0.2 10 25 What is Stock A’s coefficient of variation? What is Stock T’s coefficient of…arrow_forwardA television station may either extend a current television show for another season or develop a completely new show for that time slot. It will cost $6M to develop the new show. The new show may be very successful, moderately successful, or not successful with associated advertising revenues of $25M, $15M, or $5M, respectively. If the station chooses to extend the current show, it will cost $2M. The extended show may be very successful, moderately successful, or not successful with associated advertising revenues of $15M, $10M, or $5M, respectively. Which of the following are true? A. There are a total of six branches in the entire decision tree. B. There are eight leaves or terminal nodes in the entire decision tree. C. There is one event node in the decision tree. D. None of the abovearrow_forward
- Cachora Dynamics Corp (CDC) has designed a new integrated circuit that will allow it to enter, if it wishes, the microcomputer field. Otherwise, it can sell its rights for $15 million. If it chooses to build computers, the profitability of this project depends on the company's ability to market them during the first year. Two levels of sales are foreseen as two possible outcomes: selling 10,000 computers in case of low demand, but if it is successful it can sell up to 100,000 units (high demand). The cost of installing the production line is $6 million. The difference between the selling price and the variable cost of each computer is $600. a) Develop a formulation for decision analysis and use the non-probabilistic decision rules: Maximin and Minimax. b) Assume that the probability of high demand (p) is 50% and for low demand (1 - p) is 50%, apply the probabilistic criteria: Maximum expected value, Minimum loss of opportunity. c) Determine the VEIP. d) Carry out a sensitivity…arrow_forwardHow would I calculate the expected values for probabilities that aren't a single value such as 1-4% and >4%?arrow_forwardProblem #4 A through Garrow_forward
- 1. Andre and Zac run a salad shop called "Healthy from A to Z". They need to make the salads a day before so they have to decide how many salads to make in advance each day before they know the actual demand. Their choice is between 45, 55 and 65 salads. The following table shows their profit or loss/ payoff table. Amount in Php. Determine the optical decision alternative for the four types of criteria. For Criterion of Realism, consider an index of optimism at α=65%.arrow_forward10. An investor must decide between two alternative investments-stocks and bonds. The return for each investment, given two future economic conditions, is shown in the following payoff table: Economic Conditions Investment Good Bad Stocks $10,000 $-4,000 Bonds 7,000 2,000 What probability for each economic condition would make the investor indifferent to the choice between stocks and bonds?arrow_forwardCheryl Druehl Retailers, Inc., must decide whether to build a small or a large facility at a new location in Fairfax. Demand at the location will either be low or high, with probabilities 0.6 and 0.4, respectively. If Cheryl builds a small facility and demand proves to be high, she then has the option of expanding the facility. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be high, and then the retailer expands the facility, the payoff is $290,000. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be high, but Cheryl then decides not to expand the facility, the payoff is $253,000. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be low, then there is no option to expand and the payoff is $220,000. If a large facility is built and demand proves to be low, Cheryl then has the option of stimulating demand through local advertising. If she does not exercise this option, then the payoff is $35,000. If she does exercise the advertising option, then the response to advertising will…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





