
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337115773
Author: Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Need help with this general accounting question please answer
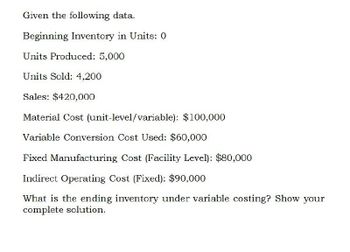
Transcribed Image Text:Given the following data.
Beginning Inventory in Units: 0
Units Produced: 5,000
Units Sold: 4,200
Sales: $420,000
Material Cost (unit-level/variable): $100,000
Variable Conversion Cost Used: $60,000
Fixed Manufacturing Cost (Facility Level): $80,000
Indirect Operating Cost (Fixed): $90,000
What is the ending inventory under variable costing? Show your
complete solution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- K Suppose that a company offers quantity discounts. If up to 1,000 units are purchased, the unit price is $12; if more than 1,000 and up to 5,000 units are purchased, the unit price is $8.00; and if more than 5,000 units are purchased, the unit price is $7.50. Develop an Excel template using the VLOOKUP function to find the unit price associated with any order quantity and compute the total cost of the order. Complete the formulas in the spreadsheet below. Select the correct VLOOKUP function in cell C8 to find the unit price for the order quantity. (Type integers or decimals rounded to two decimal places as needed.) 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 6 A B C Purchase Quantity 1 to 1000 1001 to 5000 5001 or more Quantity Ordered Unit Price Total Cost 2400 D Unit Price $ $ $arrow_forwardFor the following product and associated specification given answer accountingarrow_forwardHan Products manufactures 30,000 units of part S-6 each year for use on its production line. At this level of activity, the cost per unit for part S-6 is: Direct materials $ 5.10 Direct labor 7.00 Variable manufacturing overhead 2.40 Fixed manufacturing 18.00 overhead 32.50 Total cost per part An outside supplier has offered to sell 30,000 units of part S-6 each year to Han Products for $46.50 per part. If Han Products accepts this offer, the facilities now being used to manufacture part S-6 could be rented to another company at an annual rental of $767,000. However, Han Products has determined that two-thirds of the fixed manufacturing overhead being applied to part S-6 would continue even if part S-6 were purchased from the outside supplier.arrow_forward
- The carrying value of ending inventory under variable costing would be: present as is if higher or present it in comma if it is less ex: (200) Under absorption costing, the cost of goods sold would be:arrow_forwardInventory Valuation under Variable Costing Refer to the data for Pelham Company on the previous page. Required: 1. How many units are in ending inventory? 2. Using variable costing, calculate the per-unit product cost. 3. What is the value of ending inventory under variable costing? Use the following information for Brief Exercises 3-30 and 3-31: During the most recent year, Pelham Company had the following data associated with the product it makes:arrow_forwardInventory Valuation under Variable Costing Refer to the data for Judson Company above. Required: 1. How many units are in ending inventory? 2. Using variable costing, calculate the per-unit product cost. 3. What is the value of ending inventory under variable costing? Use the following information for Brief Exercises 3-21 and 3-22: During the most recent year, Judson Company had the following data associated with the product it makes:arrow_forward
- Use a cost-volume graph to determine the type of cost behavior exhibited in Groups A, B, and C. In the graph, volume should range from 0 to 38, 400 units (in 4,000 unit increments), and cost should range from $0 to $49,000 (in $5,000 increments). Volume Group A Group B Group C (applicable to each group) Costs Costs Costs 3,200 $3,640 $1,400 $ 3,360 19,200 17,640 8,400 3,360 25,600 23,240 11,200 3, 360 32,000 28,840 14,000 3,3601. Identify the cost behavior (fixed, mixed, or variable) in the three groups. Group Cost behavior A B C 2. What is the expected total cost for Group B if volume is 0? $Answer 3. What is the expected total cost for Group C if volume is 0?arrow_forwardDo not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardStar manufacturing has the following solve this accounting questionsarrow_forward
- Compute the following: Operating income under variable (direct) costing method Operating income under absorption costing method Operating income under throughput costing methodarrow_forwardNeed Answer Please Provide help with correct answerarrow_forwardEvaluate the quantity at which revenue equals to costs (break-even point). <use Goal seek> Assumptions: Fixed cost: 5000 Material costs per item: 2.25 Labor costs per item: 6.5 Shipping costs per 100 items: 200 Price per item: 12.99arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning