
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Given the figure shown below, what is the mass of block B on the smooth incline if the system is in static
equilibrium? A spring, with a spring constant of 300 N/m and resting length of 1.5 m, runs from block B
up to A.
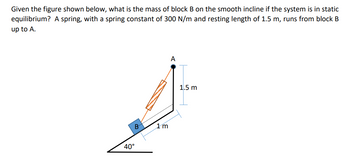
Transcribed Image Text:Given the figure shown below, what is the mass of block B on the smooth incline if the system is in static
equilibrium? A spring, with a spring constant of 300 N/m and resting length of 1.5 m, runs from block B
up to A.
B
40°
1m
A
1.5 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An ornament of mass 41.4 g is attached to a vertical ideal spring with a force constant (spring constant) of 13.6 N/m. The ornament is then lowered very slowly until the spring stops stretching. How much does the spring stretch?arrow_forwardThe operation of the fuel pump for an automobile depends on the reciprocating action of the rocker arm ABC, which is pinned at B and is spring loaded at A and D. The smooth cam C is in the position shown. The vertical force acting on the rocker arm at A is F₁60 N, and at C it is Fo 155 N (Eigure 1) Figure 50 mm Figure 10 mm 50 mm The operation of the fuel pump for an automobile depends on the reciprocating action of the rocker arm ABC, which is pinned at B and is spring loaded at A and D. The smooth cam C is in the position shown. The vertical force acting on the rocker arm at A is F =60 N. and at C it is Fe=155 N. (Figure 1) 20 mm- 10 mm 1 of 1 mm. 1 of 1 Part A Z Determine the and y components of the reaction force on the rocker arm ABC at the pin for equilib Express your answers using three significant figures separated by a comma. 195] ΑΣΦ | 11 | voc | B₁, B,= Submit Part B Part B Fo Submit Request Answer Determine the magnitude of the force along the spring DF for equilibrium.…arrow_forwardIn each figure below, a system consisting of two blocks that are tied together is attached to a spring. The systems are all at rest, and all of the springs are stretched by the same amount. The blocks on the horizontal surface are all identical, but the masses of the blocks on the inclined surfaces and the spring constants of the springs vary as shown in the figures. There may be friction between the blocks and the surfaces. A B C 4 kg k = 120 N/m 7kg k = 150 N/m 5 kg k = 120 N/m D E F k = 150 N/m 5 kg k = 180 N/m k = 150 N/m 4 kg 5 kg Rank these cases on the basis of the spring potential energy. _2. Greatest 1 3 4 5 Least OR, The spring potential energy is the same for all these systems, but it is not zero. OR, The spring potential energy is zero for all these systems. OR, We cannot determine the ranking for the spring potential energy. Please explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- A spring oriented vertically is attached to a hard horizontal surface as in the figure below. The spring has a force constant of 1.32 kN/m. How much is the spring compressed when a object of mass m = 2.15 kg is placed on top of the spring and the system is at rest?arrow_forwardull T-Mobile LTE 5:27 PM O 21% O Done 11 of 11 A spring 1.50 m long with force constant 460 N/m is hung from the ceiling of an elevator, and a block of mass 14.0 kg is attached to the bottom of the spring. (a) By how much is the spring stretched when the block is slowly lowered to its equilibrium point? (Enter the magnitude only.) (b) If the elevator subsequently accelerates upward at 1.68 m/s², what is the position of the block, taking the equilibrium position found in part (a) as y = 0 and upwards as the positive y-direction. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m (c) If the elevator cable snaps during the acceleration, describe the subsequent motion of the block relative to the freely falling elevator. What is the amplitude of its motion? Additional Materials OeBookarrow_forwardA block of mass 2.9 kg is sitting on a frictionless ramp with a spring at the bottom that has a spring constant of 470 N/m (refer to the figure). The angle of the ramp with respect to the horizontal is 13°. a) The block, starting from rest, slides down the ramp a distance 54 cm before hitting the spring. How far, in centimeters, is the spring compressed as the block comes to momentary rest? b) After the block comes to rest, the spring pushes the block back up the ramp. How fast, in meters per second, is the block moving right after it comes off the spring? c) What is the change of the gravitational potential energy, in joules, between the original position of the block at the top of the ramp and the position of the block when the spring is fully compressed?arrow_forward
- The system is released from rest with no slack in the cable and with the spring unstretched. Determine the distances traveled by the 4.5-kg cart before it comes to rest (a) if m approaches zero and (b) if m= 2.8 kg. Assume no mechanical interference and no friction. The distances is positive if up the incline, negative if down. k = 160 N/m 4.5 kg m Answers: (a) m = 0, S= i (b) m = 2.8 kg, S= i 28° m marrow_forwardYou pull on a string with a horizontal force of magnitude Fyb = 69 N that is attached to a block of mass m 6 kg, then to the axle of a solid cylinder of mass me = 4.4 kg and radius r = 0.5 m, then to a spring of spring constant k = 115 N/m. This is all done on an inclined plane where there is friction (μs = 0.65 and μk = 0.36), and the incline angle is 0 = 30 degrees. Everything starts at rest, and the spring is unstretched. The block slides down the plane, the cylinder rolls down the plane (without slipping), and the spring stretches. k lllllllll Fyb b 0 Speed First, what is the speed of the block and cylinder after you have pulled the block and cylinder 172 cm down the plane? V=arrow_forwardRecitation A 2.35-kg uniform bar of length 1.30 m is held in a horizontal position by three vertical springs. The two lower springs are compressed and exert upward forces on the bar of magnitude Fl 6.80 N and F2 = 9.50 N, respectively. Find (a) the force F exerted by the top spring on the bar, and (b) the location x of the upper spring that will keep the bar in equilibrium.arrow_forward
- A small ball is attached to one end of a spring that has an unstrained length of 0.222 m. The spring is held by the other end, and the ball is whirled around in a horizontal circle at a speed of 4.52 m/s. The spring remains nearly parallel to the ground during the motion and is observed to stretch by 0.0102 m. By how much would the spring stretch if it were attached to the ceiling and the ball allowed to hang straight down, motionless? Number i eTextbook and Media Units +arrow_forwardThe left end of a 1.200 m-long board is raised 0.300 m above the level table and a 0.800 kg cart (frictionless wheels) is placed on the ramp near the top (left) end. The cart is held in place by a compression spring that pushes into the cart horizontally. [ a) compute the ramp's distance along the horizontal. ] b) compute the spring Force magnitude. [c) compute the ramp Force magnitude. ] [ d) calculate the cart's acceleration if released from the spring. ] 2.450 N 7.840 N 2.024 N my answer is very different than any of these others 30.364 N 8.097 N 1.960 Narrow_forwardTwo identical, side-by-side springs with spring constant 240 N/m support a 2.00 kg hanging box. Each spring supports the same weight. By how much is each spring stretched?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON