
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![**Title: Analyzing Economic Equilibrium and Real GDP**
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph depicts an economic model with three curves:
1. **Aggregate Demand (AD)**: Represented by the orange upward-sloping line, which indicates the relationship between price level and output (GDP).
2. **Aggregate Supply**: The blue downward-sloping line, showing another potential economic relationship between price level and output.
3. **Potential GDP Line**: The green vertical line represents the level of output where the economy is at full employment, also known as potential GDP.
The intersection point of the AD curve and the Aggregate Supply curve shows the current equilibrium output and price level.
**Questions:**
1. **True or False**: The economy is currently in short-run equilibrium.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
2. **Fill in the Blank**: The current level of real GDP is __________ the potential GDP.
- [ ] less than
- [ ] equal to
- [ ] greater than
Consider the economic implications of the graph to determine the answers.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/53f1060f-458a-4cbe-8e1e-f5859b384d35/512bf83b-9ef9-4de3-a417-3d5f445049f7/1yvace_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Analyzing Economic Equilibrium and Real GDP**
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph depicts an economic model with three curves:
1. **Aggregate Demand (AD)**: Represented by the orange upward-sloping line, which indicates the relationship between price level and output (GDP).
2. **Aggregate Supply**: The blue downward-sloping line, showing another potential economic relationship between price level and output.
3. **Potential GDP Line**: The green vertical line represents the level of output where the economy is at full employment, also known as potential GDP.
The intersection point of the AD curve and the Aggregate Supply curve shows the current equilibrium output and price level.
**Questions:**
1. **True or False**: The economy is currently in short-run equilibrium.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
2. **Fill in the Blank**: The current level of real GDP is __________ the potential GDP.
- [ ] less than
- [ ] equal to
- [ ] greater than
Consider the economic implications of the graph to determine the answers.
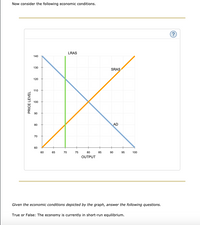
Transcribed Image Text:Now consider the following economic conditions.
### Graph Explanation:
The graph represents economic conditions with three key curves:
1. **LRAS (Long-Run Aggregate Supply):** This is a vertical green line at 70 on the output axis. It indicates the economy’s potential output when all resources are used efficiently, unaffected by the price level.
2. **SRAS (Short-Run Aggregate Supply):** This is an upward-sloping orange line. It shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing to produce in the short run.
3. **AD (Aggregate Demand):** This is a downward-sloping blue line. It reflects the total quantity of goods and services demanded at different price levels.
### Key Details:
- The vertical axis is labeled "PRICE LEVEL," ranging from 60 to 140.
- The horizontal axis is labeled "OUTPUT," ranging from 60 to 100.
Given the economic conditions depicted by the graph, answer the following questions.
**True or False:** The economy is currently in short-run equilibrium.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate total GDP for this economy given the following components of demand. Round your answer to the nearest tenth and enter the value in trillions of dollars. Components of GDP on the Demand Side (in trillions of dollars) Consumption Investment Government spending Exports Imports Provide your answer below: trillion Total GDP 12.9 3.8 4.2 3.0 4.2 ?arrow_forwardbased on the following diagram CID CIC, CIC S I 18. In autarky, the economy would be in general equilibrium at point (a) I. (b) D. (c) E. (d) F.arrow_forwardThe following graph illustrates the market for cashews. It plots the monthly supply of cashews and the monthly demand for cashews. Suppose an increase in pests destroys a major portion of cashew trees. Show the effect this shock has on the market for cashews by shifting the demand curve, supply curve, or both. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 4 8 12 Supply Demand QUANTITY (Thousands of tons) 16 Total Revenue (Thousands of Dollars) 20 Demand Supply ? One of the growers is pleased with the price increase caused by the pests because she believes it will lead to increased revenue. Using elasticities, you will be able to determine whether this price change will lead to a rise or fall in total revenue in this market. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand…arrow_forward
- Which of the following indicators is used to measure the overall level of prices for goods and services in an economy over a period of time? Options: A) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) B) Consumer Price Index ( CPI) C) Unemployment rate D) Balance of tradearrow_forwardChanges in macroeconomic indicators can often be of relevance to business and influence decision-making concerning a range of issues related to things like profit forecasts, expected sales growth, expansion plans, etc. Assume you are employed as a business analyst with a large Singaporean based multinational corporation that manufactures electronic products. Identify and discuss how each of the following macroeconomic issues may be relevant to the firm. Rising unemployment in Singapore and other developed nations.arrow_forward1. What is a market-clearing model? When is it appropriate to assume that market clear? 2. Use the model of supply and demand to explain how fall in the price of frozen yogurt would affect the price of ice cream and the quantity of ice cream sold. In your explanation, identify the exogenous and endogenous variables. 3. Consider an economy that produces and consumes hot dogs and hamburgers. In the following table are data for two different years. Goods Hot dogs Hamburgers Quantity (2010) 200 200 Price (2010) $2 $3 Quantity (2020) 250 250 Price (2020) $4 $4 Using 2010 data as the base year Compute the following statistics for each year. Nominal GDP, Real GDP, GDP Deflator, Inflation rate using GDP deflator, CPI, Inflation rate using CPI. (Hint: i) to calculate CPI use base year fixed quantity Hot dogs 200 and Hamburgers 200, ii) To calculate inflation rate, use percentage change in price level between two years.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education