
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
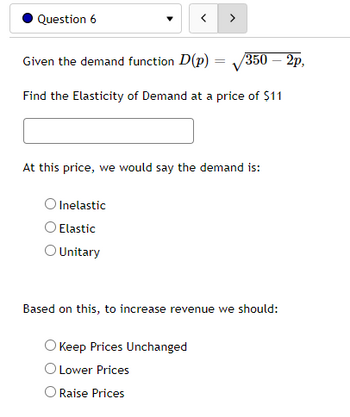
Transcribed Image Text:Question 6
=
Given the demand function D(p) =
/350 - 2p,
Find the Elasticity of Demand at a price of $11
At this price, we would say the demand is:
Inelastic
< >
O Elastic
O Unitary
Based on this, to increase revenue we should:
O Keep Prices Unchanged
O Lower Prices
Raise Prices
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- only typed solutionarrow_forward- Given the demand function D(p) = √√/375 – 4p, Find the Elasticity of Demand at a price of $22 At this price, we would say the demand is: ○ Elastic ○ Unitary O Inelastic Based on this, to increase revenue we should: Raise Prices O Keep Prices Unchanged O Lower Pricesarrow_forward1. Optimal choice of capital Eleanor makes sweaters in her home. Starting with just some knitting needles and yarn, she was able to knit 60 sweaters per year. Now some local stores have expressed interest in her designs and offered to buy her sweaters for $10 each. This makes it worthwhile for her to invest in some capital; in particular, she could produce many more sweaters if she invested in one or more looms, as shown in the following table. Assume that Eleanor's sweater business is a perfectly competitive firm. Complete the following table by calculating the marginal physical product (MPP) of each loom and the marginal revenue product (MRP) of each loom. Quantity of Input (Looms) Output (Sweaters per year) MPP of Each Loom (Sweaters) MRP of Each Loom (Dollars) 0 1 2 3 4 5 60 110 150 184 213 238 50 40 34 29 25 If the rental price of a loom is $270 per year, Eleanor should use 500 400 340 290 250 Suppose the demand for sweaters is very elastic, while the demand for cigarettes is very…arrow_forward
- For an elastic demand function, the derivative of the revenue function with respect to price is: Select one: a. positive. O b. negative. O c. infinite. O d. zero. Clear my choicearrow_forwardFor a certain good, when price rises from $100 to $150, quantity demanded falls from 2,000 to 1,200. The price elasticity of demand here is making the demand for this good in the price range between $100 and $150. 0.8; inelastic O 0.67; inelastic 0.15; inelastic 1.50; elastic O 1.25; elasticarrow_forwardU Un tue policy? 3. Constant Elasticity Consider the following demand curve Id = p" With o E (-1,0). (a) Find the elasticity of the demand. (Hint: Use the formula eq.p d bearrow_forward
- 2arrow_forwardSuppose that the elasticity of supply is 1.60 and the price increases by 5%. We will predict a percent increase in the quantity supplied of: 8% 6% O 3.1% 12%arrow_forward20 Given the demand equation x = 4 + where p represents the price in dollars and x the number of units, determine the elasticity of demand when the price p is equal to $5. Р Elasticity of Demand = Therefore, demand is O elastic O unitary O inelastic when price is equal to $5 and a small increase in price will result in O a decrease in total revenue. O little to no change in total revenue. O an increase in total revenue.arrow_forward
- Using the demand equation below, what can you conclude about the price elasticity of demand for the good or service represented by the equation? Demand: P = 100 - 4Q O a. Demand is price elastic. O b. The price elasticity of demand varies along the demand curve. O c. Demand is price inelastic. O d. Demand is unitary elastic with respect to price. 4arrow_forwardSuppose a firm faces an elasticity of demand of -1 at its current price/quantity levels. This firm would maximize its revenue by: O Maintaining current prices. O Decreasing Prices O Increasing Pricesarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education