
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
homework
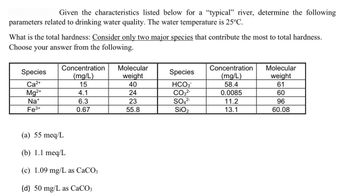
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website:**
---
**Water Quality Analysis of a "Typical" River**
Given the characteristics listed below for a “typical” river, determine the following parameters related to drinking water quality. The water temperature is 25°C.
**What is the total hardness?** Consider only two major species that contribute the most to total hardness. Choose your answer from the following:
| **Species** | **Concentration (mg/L)** | **Molecular weight** |
|-------------|--------------------------|----------------------|
| Ca²⁺ | 15 | 40 |
| Mg²⁺ | 4.1 | 24 |
| Na⁺ | 6.3 | 23 |
| Fe³⁺ | 0.67 | 55.8 |
| **Species** | **Concentration (mg/L)** | **Molecular weight** |
|-------------|--------------------------|----------------------|
| HCO₃⁻ | 58.4 | 61 |
| CO₃²⁻ | 0.0085 | 60 |
| SO₄²⁻ | 11.2 | 96 |
| SiO₂ | 13.1 | 60.08 |
**Possible Answers:**
(a) 55 meq/L
(b) 1.1 meq/L
(c) 1.09 mg/L as CaCO₃
(d) 50 mg/L as CaCO₃
---
**Explanation:**
The table above provides the concentration and molecular weight of various species found in river water that contribute to its hardness. The task is to calculate total hardness using only the two major species, which typically are calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺), as they are the primary contributors to water hardness.
Hardness is typically expressed in terms of the equivalent amount of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
The tables list both cationic species (such as Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺) and anionic species (such as HCO₃⁻ and SO₄²⁻). However, only cationic species are used in determining total hardness in water.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning