
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
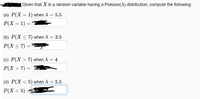
Transcribed Image Text:Given that X is a random variable having a Poisson(A) distribution, compute the following:
(a) Р(X — 1) when A %3 5.5
Р(X — 1) —
(b) P(X < 7) when A = 3.5
Р(X < 7) 3
(c) P(X > 7) when A = 4
P(X > 7) = |
(d) P(X < 5) when A = 5.5
%3|
Р(X < 5) -
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose X is a discrete random variable which only takes on positive integer values. For the cumulative distribution function associated to X the following values are known: F(18)=0.4F(25)=0.44F(33)=0.5F(41)=0.53F(46)=0.56F(52)=kF(57)=0.64F(65)=0.67 Assuming that Pr[25<X≤52]=0.17, determine the value of k.arrow_forwardSuppose X is a random variable of uniform distribution between 1 and 7. Find E(X)arrow_forwardFor a random variable, its hazard function also referred to as the instantaneous failure rate is defined as the instantaneous risk (conditional probabilty) that an event of interest will happen in a narrow span of time duration. For a discrete random variable X, its hazard function is defined by the formula hX(k) =P(X=k+ 1|X > k) =pX(k)1−FX(k). For a Poisson distribution with λ= 4.2, find hX(k) and use R to plot the hazard function.arrow_forward
- 2. The random variable X is the amount of fructose in apples (in ounces) grown at a local orchard and is represented by the following cdf: 2(x +), 1arrow_forwardA random variable X is distributed as Poisson distribution with λ = 3.5. Usethis Poisson distribution (Table A.3) to determine the following probabilities: (a)P(X < 5), (b) P(2 ≤ X ≤ 6), (c) P(X > 7), (d) P(X ≥ 5).arrow_forwardGiven that X is a random variable having a Poisson(A) distribution, compute the following: (a) P(X = 1) when A = 5.5 Р(X — 1) — (b) P(X 7) when A = 4 Р(X > 7) %3D (d) P(X < 5) when A = 5.5 P(X < 5) =arrow_forward
- A child gets a weekly allowance (a certain non-negative number of dollars). The amount (in dollars) is random with expectation equal to 6 and variance equal to 6. Let’s denote this random variable by X. I want to estimate (from above) the chances that the child gets 10 dollars or more on a given week. In other words, I want to find c such that P(X ≥ 10) ≤ c, with c that is as small as possible.(a) Use the Markov inequality to find c such that P(X ≥ 10) ≤ c.(b) Use the Chebyshev inequality for the variance to find c such that P(X ≥ 10) ≤ c.(c) Read about the one-sided Chebyshev inequality, and use it to find c such that P(X ≥ 10) ≤ c.arrow_forwardThe maintenance department in a factory claims that the number of breakdowns of a particular machine follows a Poisson distribution with a mean of 2 breakdowns every 428 hours. Let x denote the time (in hours) between successive breakdowns. (a) Find λ and Ux. (Write the fraction in reduced form.) ux = f(x) = 214 (b) Write the formula for the exponential probability curve of x. P(x <4) ✔ Answer is complete and correct. 1 P(115arrow_forwardSuppose X is a discrete random variable which only takes on positive integer values. For the cumulative distribution function associated to X the following values are known: F(23) 0.34 F(29) = =0.38 F(34) 0.42 F(39) 0.47 F(44) = 0.52 F(49) 0.55 F(56) = 0.61 = Determine Pr[29arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman