
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
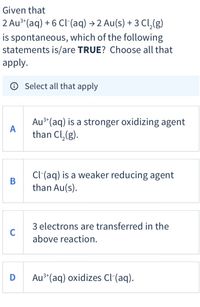
Transcribed Image Text:Given that
2 Au**(aq) + 6 Cl-(aq) → 2 Au(s) + 3 Cl,(g)
is spontaneous, which of the following
statements is/are TRUE? Choose all that
apply.
O Select all that apply
Au³*(aq) is a stronger oxidizing agent
A
than Cl,(g).
3+
Cl(aq) is a weaker reducing agent
than Au(s).
3 electrons are transferred in the
C
above reaction.
Au3*(aq) oxidizes Cl-(aq).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A certain metal M forms a soluble sulfate salt M₂SO4. Suppose the left half cell of a galvanic cell apparatus is filled with a 2.00 M solution of M₂SO4 and the right half cell with a 10.0 mM solution of the same substance. Electrodes made M are dipped into both solutions and a voltmeter is connected between them. The temperature of the apparatus is held constant at 35.0 °C. Which electrode will be positive? What voltage will the voltmeter show? Assume its positive lead is connected to the positive electrode. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits. V left right x10 X Tarrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) F2(g) + 2e → 2F*(aq) 2.870V Co2+*(aq) + 2e → Co(s) |-0.28OV 2+ Mg"(aq) + 2e → Mg(s) -2.37OV (1) The weakest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The strongest reducing agent is: (3) The strongest oxidizing agent is: (4) The weakest reducing agent is: (5) Will Mg(s) reduce F2(g) to F"(aq)? (6) Which species can be reduced by Co(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forward2 A certain metal M forms a soluble nitrate salt M(NO3)₂. Suppose the left half cell of a galvanic cell apparatus is filled with a 1.00 M solution of M(NO3), and the right half cell with a 100. mM solution of the same substance. Electrodes made of M are dipped into both solutions and a voltmeter is connected between them. The temperature of the apparatus is held constant at 35.0 °C. left x10 Which electrode will be positive? right X ? What voltage will the voltmeter show? Assume its positive lead is connected to the positive electrode. 0 Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Consider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction ° (V) Br2(1) + 2e → 2Br°(aq) |1.080V Sn²+ (aq) + 2e . Sn(s) |-0.140V Zn2*(aq) + 2e → Zn(s)|-0.763V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Br2(0) oxidize Zn(s) to Zn2*(aq)? (6) Which species can be oxidized by Sn2*(aq)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardA certain metal M forms a soluble nitrate salt M(NO3). Suppose the left half cell of a galvanic cell apparatus is filled with a 4.00 M solution of M(NO3), and the right half cell with a 200. mM solution of the same substance. Electrodes made of M are dipped into both solutions and a voltmeter is connected between them. The temperature of the apparatus is held constant at 30.0 °C. Which electrode will be positive? What voltage will the voltmeter show? Assume its positive lead is connected to the positive electrode. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits. left ☐ x10 rightarrow_forwardA certain metal M forms a soluble sulfate salt M, SO4. Suppose the left half cell of a galvanic cell apparatus is filled with a 250. mM solution of M,SO, and the right half cell with a 2.50 M solution of the same substance. Electrodes made of M are dipped into both solutions and a voltmeter is connected between them. The temperature of the apparatus is held constant at 35.0 °C. left Which electrode will be positive? Ox10 right ? What voltage will the voltmeter show? Assume its positive lead is connected to the positive electrode. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- 5. A more complex example where other atoms are involved. Balance the following reaction in basic solution. r (aq) + MnO4 (aq) MnO, (s)+ BrO;" (aq) TABLE 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C Reduction Half-Reaction E'(V) F + 20 H,0,(aq) + 2 H(aq)+2 e 2F(aq) 2.87 Stronger oxidizing agent Weaker 2 H,0 - PBSO (s) +2 H,0) -Mn0(s)+ 2 H,0) Mn (aq) 4 H,O) - Auts) 1.78 reducing agent PO,(s) + 4 H"(ag) + S0,2-(aq) + 2 e 1.69 Mno, (aq)+ 4 H'(aq) 3 e Mno, (aa) + 8 H (aq)+5 e Au (aq)+3e PbO,(s)+ 4 H(aa) + 2 e Cl,(g) + 2 e" 1.68 1.51 1.50 1.46 - P (ag) + 2 HO - 2a(aq) 1.36 1.33 Cr0, (aq) + 14 H'(ag) + 6 e 0+ 4 H (aq) + 4 e MnO(s)+4 H'(aq) +2 e 10, (aq) 6 H'(aq) + 5e Br+2e vo, (aq) + 2 H'(aq) + e NO, (aq) + 4 H°(aq) + 3e CIO+e 2 C"(aq) + 7 H,On - 2 H,O1) 1.23 Mn (aq) + 2 HyOV) 121 ulae) + 3 H,0() 2 Br (ag) - vo"(aq) +H,00 - NO + 2 H,O0 - CIO, (aa) - Agis) 1.20 1.09 1.00 0.96 0.95 Ag"(aa) + e 0.80 Fe (aq) + O+2 H'(aq)+2e - Fe*(aq) 0.77 - H,O,(ag) 0.70 Mn0, Taa) + e Mn0 (aa) 0.56 8) + 2 e…arrow_forwardI need the solution (with work) for Darrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: (1) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (2) The strongest reducing agent is: (3) The strongest oxidizing agent is: (4) The weakest reducing agent is: (5) Will Mg(s) reduce F₂(g) to F'(aq)? | + Half-reaction F₂(g) + 2e 2H+(aq) + 2e™ Mg2+ (aq) + 2e™ (6) Which species can be reduced by H₂(g)?| If none, leave box blank. E° (V) 2.870V H₂(g) 0.000V Mg(s) -2.370V 2F (aq) enter formulaarrow_forward
- (a) A silver wire is placed in a solution of CuCl₂. Does this reaction occur under standard conditions? O The reaction occurs. No reaction occurs. (b) Cl2 gas is bubbled into a solution of Nal. Write a balanced net-ionic equation. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) 21 (aq) +C1₂(g) Calculate E, AG, and K. E = 0.82 AG = -158.235 K =7.345x10^13 →2Cl(aq) + 1,(s) The reaction occurs. O No reaction occurs. V kj Does this reaction occur, under standard conditions?arrow_forwardB) Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: I03 - (aq) + NO2(g) → NO3 (aq) + I»(s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY