
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
Justify the reasons for the proof.
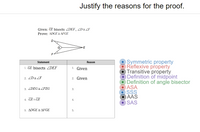
Transcribed Image Text:**Title:** Justify the Reasons for the Proof
**Given:**
- \( \overline{GE} \) bisects \( \angle DEF \)
- \( \angle D \cong \angle F \)
**Prove:**
- \( \triangle DGE \cong \triangle FGE \)
**Diagram Overview:**
- The diagram features triangle \(DEF\) with point \(G\) on line \(EF\), creating two separate triangles, \(DGE\) and \(FGE\). Line \(GE\) is shown as an angle bisector of \( \angle DEF \).
**Proof Structure:**
| **Statement** | **Reason** |
|--------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
| 1. \( \overline{GE} \) bisects \( \angle DEF \) | 1. Given |
| 2. \( \angle D \cong \angle F \) | 2. Given |
| 3. \( \angle DEG \cong \angle FEG \) | 3. |
| 4. \( \overline{GE} \cong \overline{GE} \) | 4. |
| 5. \( \triangle DGE \cong \triangle FGE \) | 5. |
**Reasons Key:**
- Symmetric property
- Reflexive property
- Transitive property
- Definition of midpoint
- Definition of angle bisector
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle)
- SSS (Side-Side-Side)
- AAS (Angle-Angle-Side)
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side)
Each reason must be justified using the properties or definitions listed in the key.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, geometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve the following two column proofs.arrow_forwardProve the attachment please. Thanks. #4arrow_forwardCreate and complete a two-column proof (A two-column geometric proof consists of a list of statements, and the reasons that we know those statements are true. The statements are listed in a column on the left, and the reasons for which the statements can be made are listed in the right column.) to show:arrow_forward
- Give a proof for the statement. (k) If n is composite, then n has a factor that is greater than 1 and less than or equal to √n. Please complete correctly. Thanks.arrow_forwardI am struggling and everyone is giving me incorrect answer.arrow_forwardSuppose that BC financial aid alots a textbook stipend by claiming that the average textbook at BC bookstore costs $ 68.72. You want to test this claim.The null and alternative hypothesis in symbols would be:arrow_forward
- John Wallis and other 17th century mathematicians were struggling with how to fit negative numbers into arithmetic without introducing inconsistencies. Explain the reasoning leading to Wallis's paradoxical claim that, if negative numbers are less than zero, they must be greater than infinity. Wallis's argument depends, in part, on the assertion that (3/-1) = -3. Must this be true? Why or why not? If a student proposed Wallis's argument, how would you respond?arrow_forwardThis is Discreet math please answer questions with proper formatting for proofsarrow_forwardPlease use justification for each step.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning