
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Given:
diameter of pipe in point 1 = 3.9in
diameter of pipe in point 2 = 2.5in
specific gravity of the liquid = 0.79
h(ft) = 0.60ft
pressure at point 1 = 14.6 psia
pressure at point 2 = 49 psia
pump and motor efficiency = 66%
diameter of pipe in point 4 = 4.5in
diameter of pipe in point 5 = 2.3 in
Z3 = 35ft
With the schematic diagram of a pump, tanks, and piping determine the following:
1) The velocity of the liquid at point 2 (ft/s)
2) Pump work used by the liquid (Wpump U) (hp)
3) Electric motor power in out (kW)
4) In figure 3, the shaded (pink) in the U tube is mercury; determine y. specific gravity of mercury 13.7
5) Mass flow rate
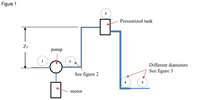
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1
3
Pressurized tank
Z3
pump
2
Different diameters
See figure 3
See figure 2
5
motor
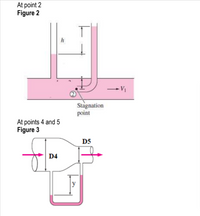
Transcribed Image Text:At point 2
Figure 2
h
Stagnation
point
At points 4 and 5
Figure 3
D5
D4
y
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Pump 50mm Þ 17m Data: f = 0.0067 Pressure at 3 = 194 kN/m² gauge Velocity at 3 = 2.7 m/s p = 830 kg/m³ Pump efficiency = 88% Motor efficiency = 84% Pressure at 1 is atmospheric Velocity at 1 is negligible Determine required input power to motor [1.64 kW] 8. 200mm turbine water gen Data: At 1, p = 230 kN/m² gauge, v = At 2, p = 0 = 0 gauge, v = 0 Turbine efficiency = 80% Generator efficiency = 90% 3.6 m/s %3D Determine output power from generator [19.3 kW]arrow_forwardfluid mechanicsarrow_forwardThe water is flowing through a pipe having diameters 30 cm and 21 cm at sections land 2 respectively. The rate of flow through pipe is 40 litres/s. The section 1 is 7 m above datum and section 2 is 3 m above datum. If the pressure at section 1 is 37 N/cm? , find the following by neglecting losses: (ENTER ONLY THE VALUES BY REFERRING THE UNIT GIVEN IN BRACKETS) ) Area of cross section of section1 (unit in m?) = Area of cross section of section2 (unit in m?) = velocity at section 1 (unit in m/s) = velocity at section 2 (unit in m/s) = (ii) difference in datum head (Unit in m) = Pressure head at section 1 (Unit in m) = pressure head at section 2 (unit in m) =arrow_forward
- Write the expanded form of Darcy’s Law. Draw a tube full of sand, with piezometers, and label the components of the system.arrow_forwardq; = K(P; − P;) - qj q; = K(P; - P;) where qi and q; are fluid flow at nodes i and j, respectively; P; and P; are fluid pressure at nodes i and j, respectively; and K is K = πD4 128μL where D is the diameter of the piper, μ is the viscosity, and L is the length of the pipe. The fluid flow is considered positive away from the node. The viscosity of the fluid is 9×10+ Pa's. a. Write the element matrix equation for the flow in the pipe element. b. The net flow rates into nodes 1 and 2 are 10 and 15 m³/s, respectively. The pressures at the nodes 6, 7, and 8 are all zero. The net flow rate into the nodes 3, 4, and 5 are all zero. What is the outflow rate for elements 4, 6, and 7? Q1 2 1 3 (4) 4 10 5 6 7 Elem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 D(mm) 40 40 50 25 40 25 25 L(m) 1 1 4 2 3 3 8arrow_forwardNeed detailed solution. 4 decimal places. Oil with a specific gravity of 0.82 is flowing in a pipe under the condition below. If the total head loss from point 1 to point 2 is 3 ft, find the pressure at point 2 in psi. *cfs = cubic ft per secarrow_forward
- A pumping station wet well operates between 540- and 550-ft elevation. The pump curve is deϐined by the following points: 80 ft at zero ϐlow, 78 ft at 200 gpm, 65 ft at 800 gpm, and 50 ft at 1200 gpm. The pump discharge contains an equivalent of 50 ft of 6-in. pipe. The discharge pipe is 120-ft long and terminates at a splitter box, elevation 570. Using C=100, plot the pump curve and the corrected pump curve. Plot the pump discharge curves at each wet well elevation and for C=100 and C=140. What is the pump ϐlow at the low and high wet well elevations for newand old pipe?arrow_forwardI want you to draw the HGL and EGL using the second picture.arrow_forwardUse g=32.2 */sec2 (9.81 m/s2) and 60°F (16°C) water unless told to do otherwise.• Google schedule-40 pipe’s thickness at different nominal size to obtain the innerdiameter of the pipe for accurate determinaLon of flow velocity.• Must show your work to support your selecLon. Otherwise, no points will be given.Water flows through a schedule-40 pipe that changes gradually in diameter from 6 in (154mm) at point A to 18 in (429 mm) at point B. The volumetric flow rate is 5.0 *3/sec (130 L/s). The respecLve pressures at points A and B are 10 psia (70 kPa) and 7 psia (48.3 kPa). All lossesare insignificant. What are the direcLon of flow and velocity at point A? (A) 3.2 */sec (1 m/s); from A to B(B) 25 */sec (7.0 m/s); from A to B(C) 3.2 */sec (1 m/s); from B to A(D) 25 */sec (7.5 m/s); from A to Barrow_forward
- 3. In the figure below, ax = 12.88 ft/s? and ay = 0. Find the imaginary free liquid surface and the pressure at B, C, D and E. Ans. B = 0.347psi, C = 0.069psi, D= 1.109 psi, E = 0.693 psi ay B 1ft A+ 3ft ax OIL - Sp. Gr. 0.8 E 3ft 4. With the same figure as Problem 3, if ax = 8.05 ft/s? and ay = 16.1 ft/s?, find the imaginary free liquid surface and the pressure at B, C, D and E. %3D Ans. B = 0.347psi, C = 0.069psi,arrow_forwardSOLVES TEP BY STEP DONT USE CHATGPT DONT USE AI 3. An oil of viscosity 1.8 cp and relative density 0.8 is contained in an open tank located above the application site. A 1.5-inch diameter pipe extends vertically from the bottom of the tank and is 5 m long. The oil level in the tank remains constant at 3 m above the bottom of the tank. In a case with friction the discharge speed can be obtained in the form of the following Equation. Calculate the flow rate of oil discharged per hour. Assume that the pipe is commercial steel (ε=0.05 mm). V= 2gh +f-arrow_forwardWater is stored in a tank sketched in the figure below to support the demand of a nearby community area.The system is designed so that pressure at the location B always lies in the range of 330 to 440 kPa (gauge).Water demand fluctuates between 0.3 and 1 m3/s regardless of pressure at B. The supply pipe of 600 mmdiameter and 1 km length between A and B is made of steel and has the equivalent sand roughness of 1 mm.Although not shown in the figure, the supply pipe has five 90◦ bends, each having the head loss coefficientof 0.8. The figure shows that the bottom end of the tank is located 42 m above the ground, and the pipe isburied 1.5 m below the ground. A pump system regulates so that the tank keeps the same water level all thetime. Assume water at 20◦C, and air in the storage tank has the atmospheric pressure. To meet the designcriterion for pressure at B, what should be the depth of water h in the storage tank?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY