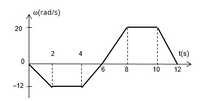
Consider the case of a rotating wheel at rest and starting a clockwise rotation, meaning the negative direction of the
- Find the
angular acceleration in the range from 0 to 2 seconds by applying the corresponding rotationalkinematics equation and write the equation as a function of angular velocity with regard to the time. Write the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Get the slope of the straight line in the range from 0 to 2 seconds and use analytical geometry to build the equation of that line, in the type of equation slope-intercept form. Write the results below:
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Determine how is the acceleration in the range from 2 to 4 seconds where the velocity is constant. Also determine the slope of the straight line and the slope-intercept equation, writing the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Find the angular acceleration in the range from 4 to 6 seconds by applying the corresponding rotational kinematics equation and write the equation as a function of angular velocity with regard to the time. Write the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Get the slope of the straight line in the range from 4 to 6 seconds and use analytical geometry to build the equation of that line, in the slope-intercept equation form. Write the results below:
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Find the angular acceleration in the range from 6 to 8 seconds by applying the corresponding rotational kinematics equation and write the equation as a function of angular velocity with regard to the time. Write the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Get the slope of the straight line in the range from 6 to 8 seconds and use analytical geometry to build the equation of that line, in the type of equation slope-intercept form. Write the results below:
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Determine how is the acceleration in the range from 8 to 10 seconds where the velocity is constant. Also, determine the slope of the straight line and the slope-intercept equation; write the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Find the angular acceleration in the range from 10 to 12 seconds by applying the corresponding rotational kinematics equation and write the equation as a function of angular velocity with respect to time. Write the results below:
|
Acceleration: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
- Get the slope of the straight line in the range from 10 to 12 seconds and use analytical geometry to build the equation of that line, in the slope-intercept form. Write the results below:
|
Slope: |
|
|
Origin intercept: |
|
|
Equation: |
|
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps with 8 images

- Find the
angular acceleration in the range from 4 to 6 seconds by applying the corresponding rotationalkinematics equation and write the equation as a function ofangular velocity with regard to the time
- Find the
angular acceleration in the range from 4 to 6 seconds by applying the corresponding rotationalkinematics equation and write the equation as a function ofangular velocity with regard to the time
- (a) Convert 50.0° to radians. rad (b) Convert 14.0 rad to revolutions. rev (c) Convert 72.5 rpm to rad/s. rad/sarrow_forwardA wheel undergoes angular acceleration of 0.44rad / s ^ 2 for 5 seconds (starting from rest ). Through how much angle (in radians ) has the disk turned after the 5 second interval of time ?arrow_forwardA solid cylinder with a mass of (5 kg) and a radius of (0.2 m) (I =12MR2) is initially rolling along a flat plane with a linear velocity of (10ms). The cylinder then comes to the edge of a ramp that is inclined by (34degrees) to the horizontal and begins to roll up the ramp. How high above the flat plane does the cylinder reach before it starts to roll back down?arrow_forward
- In the figure, wheel A of radiusrA = 13.9 cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C of radius rc = 24.4 cm. The angular speed of wheel A is increased from rest at a constant rate of 1.45 rad/s². Find the time needed for wheel C to reach an angular speed of 50.5 rev/min, assuming the belt does not slip. (Hint: If the belt does not slip, the linear speeds at the two rims must be equal.) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardPeg P is driven by the fork link OA along the curved path described by r 2.8.8 ft. At the instant = 1.3 rad, the angular velocity of the link is = 1.4 rad/s and the angular acceleration is 0=0.66 rad/s². For peg P at this instant, please find: radial acceleration a, a -10.55 transverse acceleration ag= magnitude of total acceleration a= m m m 5²arrow_forwardThe flywheel of a steam engine runs with a constant angular velocity of 132 rev/min. When steam is shut off, the friction of the bearings and of the air stops the wheel in 1.40 h. (a) What is the constant angular acceleration, in revolutions per minute-squared, of the wheel during the slowdown? (b) How many revolutions does the wheel make before stopping? (c) At the instant the flywheel is turning at 66.0 rev/min, what is the tangential component of the linear acceleration of a flywheel particle that is 42.7 cm from the axis of rotation? (d) What is the magnitude of the net linear acceleration of the particle in (c)?arrow_forward
- In the figure, wheel A of radius ra = 13.3 cm is coupled by belt B to wheel Cof radius rc=20.4 cm. The angular speed of wheel A is increased from rest at a constant rate of 1.43 rad/s2. Find the time needed for wheel C to reach an angular speed of 58.1 rev/min, assuming the belt does not slip. (Hint: If the belt does not slip, the linear speeds at the two rims must be equal.) TA Number i Unitsarrow_forwardIn the figure, wheel A of radius -9.40 cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C of radius rc-26.1 cm. The angular speed of wheel A is increased from rest at a constant rate of 2.53 rad/s². Find the time needed for wheel C to reach an angular speed of 63.0 rev/min, assuming the belt does not slip. (Hint: If the belt does not slip, the linear speeds at the two rims must be equal.) Number Ma Units Barrow_forwardA compact disk on a CD player rotates clockwise. The disk completes one revolution in 0.249 s. (a) Find the angular velocity of the disk. magnitude direction clockwise (b) Find the speed of a point on the disk 5.15 cm from the axis of rotation.arrow_forward