
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
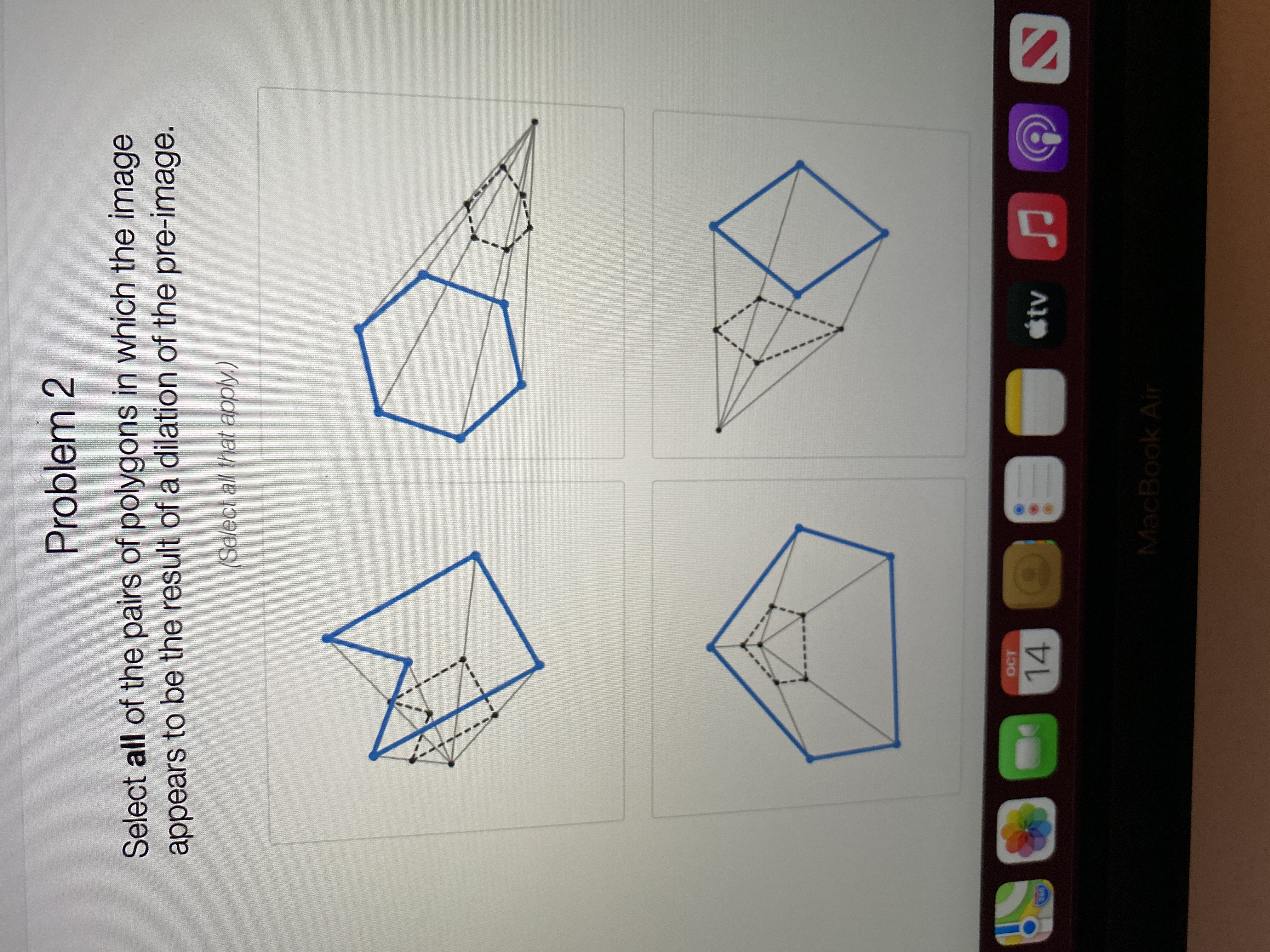
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 2**
Select **all** of the pairs of polygons in which the image appears to be the result of a dilation of the pre-image.
(*Select all that apply.*)
**Description of Each Diagram:**
1. **Top Left Diagram:**
- Shows two polygons with a series of dotted lines connecting corresponding vertices. The inner polygon appears smaller and is located inside the larger polygon. However, the shapes appear different, suggesting a transformation other than dilation.
2. **Top Right Diagram:**
- Displays two polygons connected by dashed lines extending from a common external point (center of dilation). The smaller polygon is inside the larger one and maintains a similar shape, indicative of dilation.
3. **Bottom Left Diagram:**
- Features two polygons in which a smaller polygon is nested within a larger one. Both polygons share a similar shape and are connected by lines drawn from each vertex of the inner polygon extending towards corresponding points on the outer polygon, suggesting dilation.
4. **Bottom Right Diagram:**
- Two polygons are connected by dashed lines emanating from a point outside both polygons. The polygons have a different orientation and do not appear to maintain similarity in shape, indicating a transformation other than dilation.
**Instructions for Solution:**
Carefully analyze each pair of polygons to identify those that maintain proportionality and similarity indicating a dilation transformation. Select those that fulfill these criteria.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side for the right-angled triangle given in the figure below. It has base 112 m and height 15 m. If you would like to enlarge the graph or make numbers and letters easier to read, you may click on it to open it in a new window. You may then enlarge that window with your mouse. To further enlarge the image, use your browser's zoom capabilities. On a PC this is usually ctrl shift + (and zooming out is ctrl -). On an Apple computer this is usually apple shift + (and zooming out is apple -). 15 n 112 n • If you need to use the square root symbol, as in x = V17, type it using: sqrt(17) • Units need to be entered using their standard abbreviations, without a period. For example, type m for meters, m^2 for square meters, etc.arrow_forwardElementary school students were given a geometry assignment they were to measure the area of several rectangles to measure the diagonal of the rectangle as shown on the table.arrow_forwardCould you explain in detail or steps how to do these type of special triangles?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning