
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
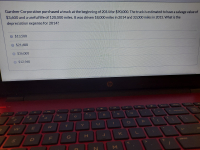
Transcribed Image Text:Gardner Corporation purchased a truck at the beginning of 2014 for $90,000. The truck is estimated to have a salvage value of
$3,600 and a useful life of 120,000 miles. It was driven 18,000 miles in 2014 and 32,000 miles in 2015. What is the
depreciation expense for 2014?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A company purchased a new machine on January 1, 2014. The supplier, "Forever supply" was paid $2,000 in cash. In addition, transportation and installation were $180 (paid in cash), legal costs associated with the asset were $20 (paid in cash). The machine has an estimated life of 5 years and an estimated salvage value of $300. It is company policy to use straight line depreciation for all of its machines. question: Assume the machine was sold on July 1, 2015 to "company A" for $1200 cash. Prepare the journal entry/entries to record this transaction. What was the gain/loss? Include the classification of the accounts and clearly label your debits and credits.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2013, Zane Manufacturing Company purchased a machine for $40,000. The company expects to use the machine a total of 24,000 hours over the next 6 years. The estimated sales price of the machine at the end of 6 years is $4,000. The company used the machine 8,000 hours in 2013 and 12,000 in 2014. What is depreciation expense for 2013 if the company uses straight-line depreciation?arrow_forwardLinton Company purchased a delivery truck for $S34,000 on January 1, 2014. The truck has an expected salvage value of $2,000, and is expected to be driven 100,000 miles over its estimated useful life of 10 years. Actual miles driven were 19,000 in 2014 and 16,000 in 2015. Instructions a) Compute depreciation expense for 2014 and 2015 using (1) the straight-line method and (2) the units-of-activity method (b) Assume that Linton uses the straight-line method, Prepare the journal entry to record 2014 depreciation.arrow_forward
- Marsh Corporation purchased a machine on July 1, 2012, for $1,250,000. The machine was estimated to have a useful life of 10 years with an estimated salvage value of $70,000. During 2015, it became apparent that the machine would become uneconomical after December 31, 2019, and that the machine's salvage value is now $0. Accumulated depreciation on this machine as of December 31, 2014, was $295,000. What should be the charge for depreciation in 2015 under generally accepted accounting principles? O $177,000 O $191,000 O $205,000 O $238,750arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2007, Flax Co. purchased a machine for 528,000 and depreciated it by the straight-line method using an estimateduseful life of eight years with no salvage value. On January 1, 2010, Flax determined that the machine had a useful life of six years from the date of acquisition and will have a salvage value of 48,000. An accounting change was made in 2010 to reflect these additional data. The accumulated depreciation for this machine should have a balance at December 31, 2010 ofa.292,000b.308,000c.320,000d.352,000arrow_forwardThe Giovanni Company purchased a tooling machine in 2007 for $120,000. The machine was being depreciated by the straight-line method over an estimated useful life of 20 years, with no salvage value. At the beginning of 2017, after 10 years of use, Giovanni paid $20,000 to overhaul the machine. Because of this improvement, the machine's estimated useful life would be extended an additional 5 years. What would be the depreciation expense recorded for the above machine in 2017? a.$7,333 b.$4,000 c.$6,000 d.$5,333arrow_forward
- Jersey Corporation, which has a calendar year accounting period, purchased a machine for $400,000 on April 1, 2016. At that time Jersey expected to use the machine for nine years and then sell it for $4,000. The machine was sold for $22,000 on Sept. 30, 2021. Assuming straight-line depreciation, calculate the gain(/(loss) at the sale of the machine.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2016, Rexford Company purchased a drilling machine for $11,500. The machines has an estimated useful life of 4 years and a salvage value of $200. Given this information, if Rexford uses double-declining-balance method of depreciation, and sells the machine on December 31, 2017, for $3,000 cash. Then how much will be gain or loss on disposal of this asset? $ 2,750 loss $ 1,800 loss $1,562 gain $ 125 gainarrow_forwardLone Star Sales & Service acquired a new machine that cost $84,000 in early 2016. The machine is expected to have a five-year useful life and is estimated to have a salvage value of $14,000 at the end of its life. Using the double-declining-balance depreciation method, calculate the depreciation expense for the third year of the machine's life and the net book value of the machine at this point in time.arrow_forward
- ABC Company acquired a machine on January 1, year 2016 for $100,000. The machine is depreciated using the double-declining- balance method, and was estimated to have a 10 year useful life and a salvage value of $10,000. On January 1, year 2018, the company revised its estimations as: a useful life of 5 years beginning from that date, and with a salvage value of $15,000 at the end of 5 years. How much depreciation expense should ABC Company recognize in year 2018? Multiple Choice 13,400 O 21,040 25,600 16,000arrow_forwardRogers Co. had a sheet metal cutter that cost $240,000 on January 1, 2013. This old cutter had an estimated life of ten years and a salvage value of $40,000. On April 1, 2018, the old cutter is exchanged for a new cutter with a fair value of $120,000. Rogers also received $30,000 cash. Assume that the last fiscal period ended on December 31, 2017, and that straight-line depreciation is used. Instruction: Record any entries required on April 1, 2018.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education