
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the figure, the wheel rolls with no slippage at the angular velocity shown. Based on the IC of the system as shown, determine:
a. The angular velocity of bar AB with respect to time
b. The speed of the slider at B
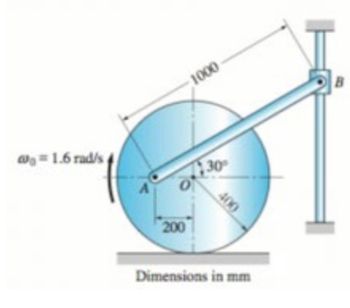
Transcribed Image Text:The image is a mechanical diagram illustrating a rotating system with key measurements and parameters, likely part of an educational resource on rotational dynamics.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- **Components:**
- There is a circular object (representing a wheel) with center "O."
- Point "A" is marked on the circumference of the wheel.
- A rod connects point "A" to point "B," which is fixed at the opposite end.
- **Measurements:**
- The distance from point "A" to point "O" (radius of the wheel) is 200 mm.
- The rod "AB" has a length of 1000 mm.
- The wheel radius ("AO") makes an angle of 30° from a vertical line passing through "O."
- **Angular Velocity:**
- The initial angular velocity (ω₀) of the wheel is 1.6 radians per second, indicated by the curved arrow.
- **Dimensions:**
- All measurements are specified in millimeters (mm).
This diagram likely serves to illustrate concepts such as rotational motion, angular velocity, and the relationship between linear and angular displacement in mechanical systems.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The system shown in the figure is composed of bar AB which is pin-supported at A and attached to bar BC. The end of bar BC is connected to the slider block C. At the instant shown, the acceleration of point B is 1.125 m/s2 downward and the angular velocity of bar BC is 0.5625 rad/s counterclockwise. What is the angular acceleration of bar AB?arrow_forwardAt the instant mechanisms is shown below, for the gear its angular velocity is 6rad/s counterclockwise and its angular acceleration is 5rad/s2 clockwise. For the position depicited in the figure, using the vector method only, determine a) The angular veleocity of link BD and AB B) the angular acceleration of link AB and BDarrow_forwardGiven the figure below, what is the velocity at B?arrow_forward
- For the mechanism composed of the discs A and B, and the BCD bar; Find the angular velocity of disk A and the velocity of point D. From the table, use the values in the last row for the velocity of point C and the distances and angle marked in the image. Notes Discs A and B have a non-slip contact. Point C is bolted to the yellow collar and bar B. The movement of the collar is defined by the gray bar, which is fixed. The bolt allows the BDC bar to rotate at that point. The BCD bar is a single rigid bodyarrow_forwardThe elements of a power hacksaw are shown in Figure 2. The saw blade ismounted in a frame that slides along the horizontal guide. If the motor turns the flywheel at a constant counter-clockwise speed of 60 r.p.m. Make use of vector diagram to calculate: the acceleration of the blade for the position where angle ? = 90o The corresponding angular acceleration of the link AB.arrow_forwardIn the figure, Pulley A, rotating at 20 rad/s, controls the motion of Pulley B. The motor of pulley A is cut off, and friction eventually brings the pulleys to a stop with an angular acceleration of α = -2.5t rad/s2. If there is no slippage, determine: a. The angular velocity of B with respect to time b. The angular displacement of B during the deceleration c. The acceleration of point C with respect to timearrow_forward
- Bar OC rotates with a clockwise angular velocity woc = 5.3 rad/s and a counterclockwise angular acceleration doc = 4.6 rad/s². The bar OC is a slotted member which accommodates the pin A attached to the sector. Determine the angular velocity w and the angular acceleration a of the sector. The angular velocity and the angular acceleration are positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. Assume OA = 500 mm, d = 385 mm, 0 = 21°. Answers: W = B a = i i d aoc rad/s rad/s² @ocarrow_forwardIn the mechanism shown below, the wheel is pinned at the center. The radius from O to C is 0.2 m and link CB is 0.55 m long. CB makes an initial angle of 25° with the horizontal as shown. The hydraulic ram at B is moving left at 7 m/s. At the moment shown, what is the angular velocity of link BC and the wheel pivoted at 0? 0000 Ninbet tatis rad/sarrow_forwardI need all answers pleasearrow_forward
- The mechanism below has a crank that revolves clockwise at point O at a speed of 2000 rpm. Using vector diagrams, determine: a) The linear velocity of the piston and the angular velocity of the link AB about A. b) The angular acceleration of the link AB about A and the inertial resistance produced by the piston. c)Using trigonometry, confirm your results for the velocity in parts (i), explain your reasons behind which method is preferable, and identify the error margin for your velocity answers.arrow_forwardanswer the question in the picturearrow_forwardPlease acceptarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY