
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
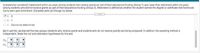
Transcribed Image Text:A researcher wondered if attainment within six years among students who receive grants as sart of their educational funding (Group 1) was lower than attainment within six years
among students who did not receive grants as part of their educational funding (Group 2). Atainment is defined as whether the student earned the degree or certificate that heishe set
out to eam upon enrolment. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
A. 2
1
Cannot be determined
(c) In part (b), we learned that two groups (students who receive grants and students who do not receive grants) are being compared. In addition, the sampling method is
independent. State the null and altemative hypotheses for this test
Hg.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Using the dotplot and the proportion of winners in the store owner's sample, is there convincing evidence that the manufacturer's claim is wrong? A manufacturer of bottled tea runs a promotion in which consumers can win a free bottle of tea if the cap of the bottle says "Winner." The manufacturer claims that 1 in 5 bottles is a winner. A store owner Yes, because a proportion of 0.4 or more occurred 25 out of 100 times, the sample proportion of notices that several of the first bottles of tea sold were winners. Suspecting the manufacturer's claim is false, the store owner decides to randomly select 10 bottles of tea from the next shipment from the manufacturer. She is again surprised when 4 of the bottles are winners is statistically significant and there is convincing evidence that the manufacturer's claim is false. Yes, because a proportion of 0.4 or less occurred 75 out of 100 times, the sample proportion of winners. Assuming the manufacturer's claim is true, she simulates 100 values…arrow_forwarda) Which of the following correctly specifies the null hypothesis? [select all that apply] b) Which of the following correctly specifies the alternative hypothesis? [select all that apply] c) Calculate and report the standard error for the sampling distribution for the difference in means.arrow_forwardYou work for a marketing firm that has a large client in the automobile industry. You have been asked to estimate the proportion of households in Chicago that have two or more vehicles. You have been assigned to gather a random sample that could be used to estimate this proportion to within a 0.035 margin of error at a 99% level of confidence. a) With no prior research, what sample size should you gather in order to obtain a 0.035 margin of error? b) Your firm has decided that your plan is too expensive, and they wish to reduce the sample size required. You conduct a small preliminary sample, and you obtain a sample proportion of ˆp=0.185. Using this new information. what sample size should you gather in order to obtain a 0.035 margin of errorarrow_forward
- 2. Several years ago, a census of all students enrolled at a large undergraduate university revealed that 19% of the students were seniors, 23% were juniors, 27% were sophomores, and 31% were freshmen. This year, the student senate did a survey to see whether these percentages have remained the same. A random sample of 200 students included 50 senior, 46 juniors, 55 sophomores, and 49 freshmen. Using a 2.5% significance level, test the null hypothesis that the percentages are still 19% seniors, 23% juniors, 27% sophomores, and 31% freshmen. Use the Critical Value Approach.arrow_forwardA student organization reports that, of a random sample of 300 college undergraduates, 95% attend all their classes during the first week of the semester and 15% did not attend all their classes during the first week. We know there is a mistake in this report because O A stratified sample would have been less prone to error O It's very unlikely that 15% of students didn't attend all their classes during the first week O There is always a possibility of response bias O 95% plus 15% adds up to more than 100%arrow_forwardJoe Biden (Democrat) will be running for President of the United States in 2020. His campaign is continually, among other things, wanting to estimate the percentage of Americans who will vote for him. a) How many Americans should be sampled to estimate the percentage of those who will vote for Joe Biden if his campaign wants to be 95% confident that the margin of error is no more than 2%? The last poll found that 49% of Americans said they will vote for Biden.arrow_forward
- I am to do a project for an inferential statistics class and I would like some basic guidance. I am to propose a research question. My proposed research question is "Does drinking stimulants such as coffee improve a student's grades?" It was suggested to me that my population could be the students at my school. I will impliment simple random sampling by devising two groups of students, one being a group who often consume stimulants like coffee and another who seldomly or never consume a stimulant such as coffee. Upon gathering the data of each group I will need to compare the average grades for each group using independent samples t-test for both respective groups. My Hypothesis test will be a two independent samples test for mean. My question is what are the limitations? (How could bias and/or confounding variables could limit this study?) Also what graph do you think would be best served to visually display the data?arrow_forwardTo apply the two-sample t procedures, use Option 1 if you have technology that implements that method. Otherwise, use Option 2. Researchers gave 40 index cards to a waitress at an Italian restaurant in New Jersey. Before delivering the bill to each customer, the waitress randomly selected a card and wrote on the bill the same message that was printed on the index card. Twenty of the cards had the message "The weather is supposed to be really good tomorrow. I hope you enjoy the day!" Another 20 cards contained the message "The weather is supposed to be not so good tomorrow. I hope you enjoy the day anyway!" After the customers left, the waitress recorded the amount of the tip (percent of bill) before taxes. Here are the tips for those receiving the good-weather message. 21.0 18.8 20.3 20.9 21.9 23.7 22.8 25.2 22.7 20.8 25.1 22.3 27.3 21.0 22.5 24.2 21.3 22.3 22.0 23.2 The tips for the 20 customers who received the bad-weather message are below. 19.3 18.8 16.1 17.1 14.4 18.0 19.1 19.4…arrow_forwardA university has decided to introduce the use of plus and minus grading as long as there is evidence that 60% of the faculty is in support of this change. Write an appropriate null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis to test if the proportion is greater than 60%.arrow_forward
- 3. Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, p-value(s), conclusion about the null hypothesis, and final conclusion that addresses the original claim. The Genetics and IVF Institute conducted a clinical trial of the XSORT method designed to increase the probability of conceiving a girl. As this book was being written, 325 babies were born to parents using the XSORT method, and 295 of them were girls. Use the sample data with a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that with this method, the probability of a baby being a girl is greater than 0.5. Does the method appear to work?arrow_forwardA community college wants to find out how students enrolled in remote courses feel about remote learning,so a random sample of students is needed to form a focus group. You are a data scientist in charge ofidentifying a sample of students for the focus group. Why is it important to select a random sample in this case? Would it be ok for the college to ask for volunteers for the focus group? Why or why not? Are there pros and cons for each samplingapproach? Which is best and why? Could Stratified Random Sampling have also been used? What benefits might this approach have inselecting the sample of students for the focus group? Explain or give an example of how this could bedone. 874786667172747718114301699108421009846176806728505883964138722994692957574451054463441011799713150445482678936083128648618194219333913373855511070208365643664235172417102465259067655654964950492581611669287944720629621174445585225321068039268392266267994arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman