
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
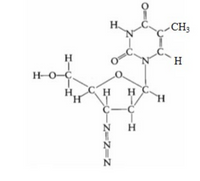
One of the first drugs to be approved for use in treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) was azidothymidine (AZT). It is pictured in the image attached.
g) What is the H−O−C bond angle in the side group attached to the five-membered ring (on the far left of the molecule)?
h) What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in the CH2OH group on the far left of the molecule?
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the chemical structure of caffeine, a central nervous system stimulant commonly found in coffee, tea, and other beverages.
### Explanation of the Diagram:
- **Carbon (C):** Represented by the letter "C", most carbon atoms in the structure form the backbone of the molecule.
- **Hydrogen (H):** Represented by the letter "H", hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms.
- **Oxygen (O):** Represented by the letter "O", oxygen atoms are double-bonded to carbon, shown at the top of the structure.
- **Nitrogen (N):** Represented by the letter "N", nitrogen atoms are part of the rings, contributing to the unique properties of caffeine.
### Structural Features:
- **Methyl Groups (CH₃):** A methyl group is attached to the nitrogen atom in the top ring, contributing to caffeine's hydrophobic properties.
- **Rings:** The two interconnected rings are part of a purine structure, which is a characteristic feature of xanthine derivatives like caffeine.
This molecular structure explains the stimulant effects of caffeine due to its ability to interact with various neuroreceptors in the human brain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2arrow_forwardWhat is the hybridization of the carbon atom (in red) in the molecule shown? H -CEN : sp sp2 sp3 sp4 sp3d O sp3d2 O none of thesearrow_forwardConsider the two structures shown below: + C6 Which of the following statements is incorrect? O c is bonded to only one hydrogen. o cD is sp²-hybridized. C has a nonbonded lone pair of electrons. C is bonded to only one hydrogen. The octet rule is satisfied for CD.arrow_forward
- A 3D representation of a cyclohexane (C6H₁2) molecule, a 12 cyclic compound used in the manufacture of nylon and found in the distillation of petroleum, is shown. Name the geometry around each carbon atom. geometry: What is the hybridization of each carbon atom? 3 sp d 32 sp d 2 sp 3 sp sp 9 Rotate X Rotate Y C Rotate Z OH Zoom In Q Zoom Out A Label Atomsarrow_forward5) Oxazepam is a benzodiazepine used for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia. Fill in the boxes with the hybridization of the indicated atoms. N -OH CI Narrow_forwardWhat is the hybridization of the atom indicated by the arrow? H3C CH =CH 우 CH3arrow_forward
- Picric acid, a benzene derivative shown below, was once used in landmines because it is sensitive to shock. What is the electron domain geometry, hybridization and bond angles of the carbon atoms? NO2 C NO2 NO2arrow_forwardWhat is the hybridization of the carbon atom indicated with a star in the given structure?arrow_forward5) Identify the hybridization of the carbon atom in formaldehyde, H2C=Oarrow_forward
- 2) a) Consider the following molecule . Given what you have learned about hybridization theory, draw an image or images explaining the bonding situation in this molecule. I want you to draw out all of the orbitals, hybrid orbitals and how they overlap to form the bonds in the molecule. Indicate the % s or p character in the given atomic and hybrid orbitals. Which C-C bond or bonds are the longest? In a paragraph or so explain the image or images you just drew. b) Lastly, consider the molecule below. Indicate the Molecular formula, the molar mass, label the hybridization of each atom except for hydrogen, indicate any chiral centers with a *, which bond or bonds are the shortest, identify by name of each functional group with an arrow pointing to the group.arrow_forwardNO2-?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY