
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
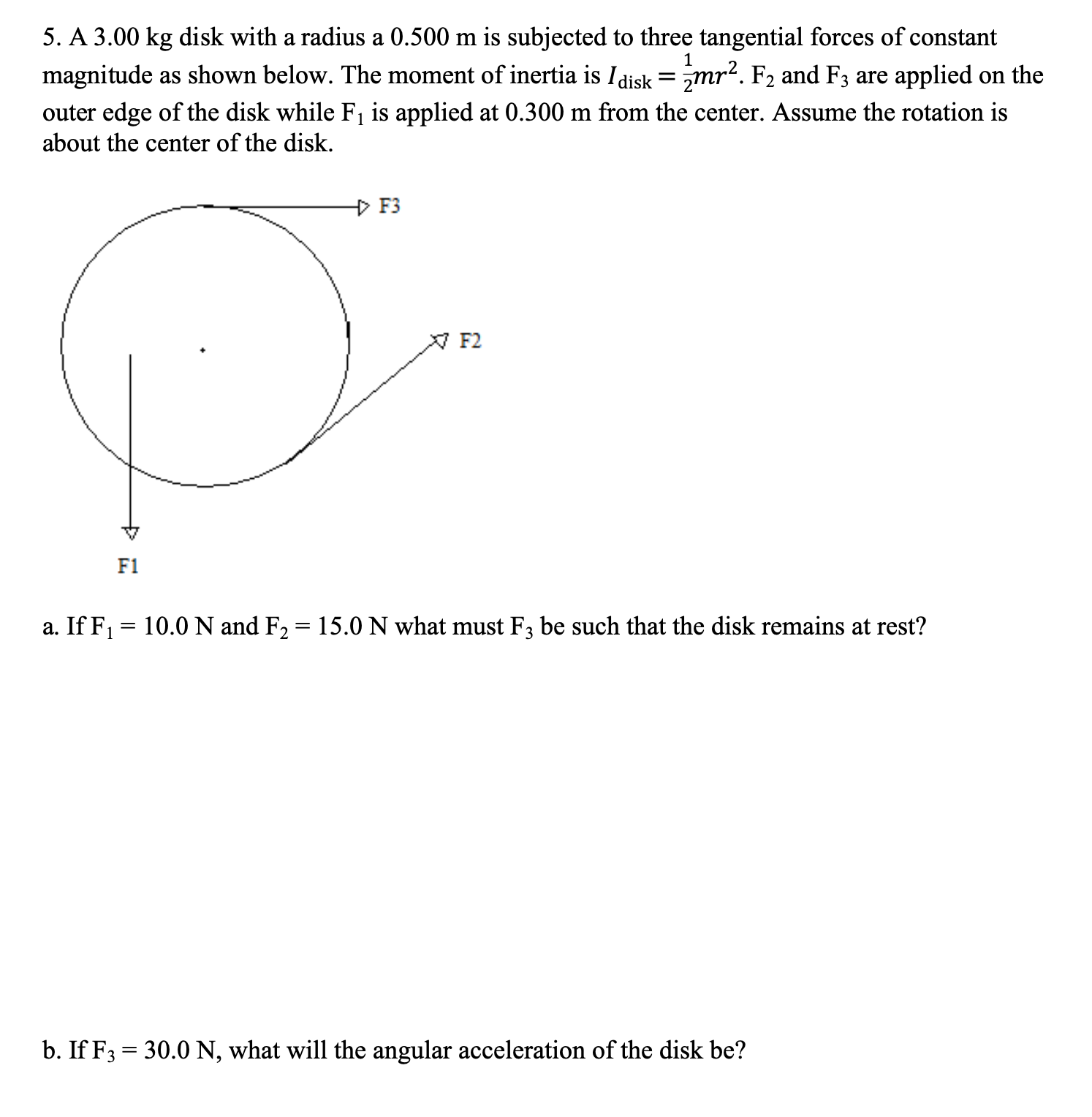
Transcribed Image Text:g disk with a radius a 0.500 m is subjected to three tangential forces of constant
as shown below. The moment of inertia is Idisk =mr?. F2 and F3 are applied on the
of the disk while F, is applied at 0.300 m from the center. Assume the rotation is
enter of the disk.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a top with radius 10cm, mass 2 kg has a string around the edge and is initially at rest. assume the top can be reasonably approximated as a solid cylinder. the top is held in place as the string is pulled. the string applies a force of 10N tangential to the edge for 2s. what is the angular velocity (in radians per second) of the top after 3 seconds? what is the angular momentum of the top after the string is pulled? after the string is pulled, the top is released. it travels away from its initial position at a linear velocity of 10m/s. what is the rotational velocity (in radians per s) at this top? assume no frictionarrow_forwardThe radius of a park merry-go-round is 2.5 m. To start it rotating, you wrap a rope around it and pull with a force of 260 N for 20 s. During this time, the merry-go-round makes one complete rotation. (a) Find the angular acceleration of the merry-go-round. rad/s2 (b) What is the magnitude of the torque exerted by the rope on the merry-go-round? N-m (c) What is the moment of inertia of the merry-go-round? kg-m2 eBookarrow_forwardSolve for d, e, f onlyarrow_forward
- A uniform sphere is placed inside hemispherical bowl of radius R = 75.0 cm. It is released from rest at an angle 0 = 40.0°. What is the speed of the sphere at the bottom of the bowl if it rolls without slipping? Ishpere = 2/5 mr². Assume r<arrow_forwardA bowler throws a bowling ball of radius R = 11 cm along a lane. The ball (the figure) slides on the lane with initial speed vcom.O friction between the ball and the lane is 0.29. The kinetic frictional force 7k acting on the ball causes a linear acceleration of the ball while producing a torque that causes an angular acceleration of = 8.4 m/s and initial angular speed wo 0. The coefficient of kinetic the ball. When speed vcom has decreased enough and angular speed p has increased enough, the ball stops sliding and then rolls smoothly. During the sliding, what are the ball's (a) linear acceleration and (b) angular acceleration? (c) How long does the ball slide? (d) How far does the ball slide? (e) What is the linear speed of the ball when smooth rolling begins? Note that the clockwise direction is taken as negative. Vcotm (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units (e) Number Unitsarrow_forwardThe axis of rotation of a thin plate is located at the left side, as shown in the figure. Calculate the moment of inertia I if the plate has a length L of 9.00 cm, a width w of 7.00 cm, and a uniform mass density of 2.50 g/cm². I = kg.m² W Larrow_forwardA toy Ferris wheel that is at rest has a radius of 20.0 cm. A perpendicular force of 1.5 N is applied to the outer most part of the Ferris wheel. The toy Ferris when has a rotational inertia of 0.050 kg m2 . a) What is net Torque applied to the Ferris wheel? b) What is the angular acceleration of the Ferris wheel? k) If the Ferris wheel maintains this angular acceleration for 3.0 seconds, what will its final angular velocity be? d) What will be its rotational Kinetic Energy after 3.0 seconds?arrow_forwardA thin hoop of radius 2.00 cm and mass 0.0300 kg rolls down a frictionless ramp of length 4.00 m that makes an angle of 10.0° with the horizontal. The hoop starts from rest from the top of the ramp.a. Find the angular speed of the hoop at the bottom of the ramp.b. After the hoop rolls off the ramp, it is traveling along a horizontal surface with friction that causes a frictional torque of magnitude 0.400 N·m on the hoop. How much time will it take for the hoop to come to rest?arrow_forwardA clock hangs on a wall. a) What is the direction of the average angular velocity of the seconds hand? b) What is the magnitude of the average angular velocity of the seconds hand?arrow_forwardA counterweight of mass m = 3.60 kg is attached to a light cord that is wound around a pulley as shown in the figure below. The pulley is a thin hoop of radius R = 7.00 cm and mass M = 1.50 kg. The spokes have negligible mass. M m (a) What is the net torque on the system about the axle of the pulley? magnitude 2.058 x N.m direction to the right along the axis of rotation (b) When the counterweight has a speed v, the pulley has an angular speed = v/R. Determine the magnitude of the total angular momentum of the system about the axle of the pulley. (0.357 kg. m)v (c) Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the counterweight. 5.76 x m/s²arrow_forwardT m A 25.0 kg mass is hung from a rope that is passed over a pulley and held by a man standing on a ramp. The pulley can be treated as a solid disk with a mass of 10.0 kg that has a radius of 0.400 m. The man pulls the rope so that the pulley rotates from rest through an angular displacement of 15.0 rad in 2.00s. A. What is the angular acceleration of the disk? B. What is the tension of the rope as it pulls up on the box? C. What is the force applied by the man on the rope as he pulls the box upward?arrow_forwardA diver performs a flip in the air. The radius of gyration is 0.43 when the diver initially leave the board and the diver is rotating at an angular velocity of 6.3 rad/sec. What is the linear velocity of the head when they decrease their radius of gyration to 0.24. The distance from the head to the center of gravity of the individual is 0.3 meters?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON